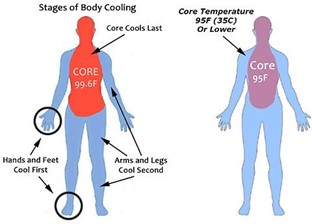
The nurse is caring for a patient with hypothermia and fluid volume excess. Which of the following would be included in the plan of care?
Fluid restriction
Administration of hypotonic IV fluids
Placement of an indwelling urinary catheter
Administration Of action-exchange resin
The Correct Answer is A
The plan of care for a patient with hypothermia and fluid volume excess would typically include measures to increase the patient's body temperature and decrease their fluid volume. Therefore, option a (fluid restriction) would be appropriate for this patient.
Options b (administration of hypotonic IV fluids) and d (administration of ion-exchange resin) would not be appropriate because they would increase the patient's fluid volume rather than decrease it.
Option c (placement of an indwelling urinary catheter) may be appropriate to closely monitor the patient's urine output, which is an important indicator of their fluid status. However, this alone would not be sufficient to manage the patient's hypothermia and fluid volume excess.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
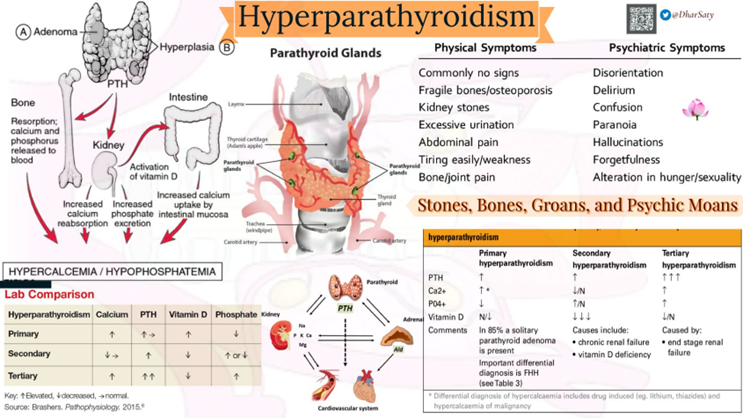
The patient with primary hyperparathyroidism has high levels of calcium in the blood (hypercalcemia) which can lead to symptoms such as kidney stones, bone pain, and weakness. High urine calcium levels may also be present due to the increased calcium in the blood.
One important intervention for managing hypercalcemia is to encourage fluid intake to promote increased urine output and prevent the formation of kidney stones. Therefore, the nurse should encourage the patient to drink at least 4000 ml of fluids per day.
Seizure precautions (a), range-of-motion exercises (b), and monitoring for positive Chvostek’s or Trousseaus sign (d) are not directly related to managing hypercalcemia and are not necessary in this case.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
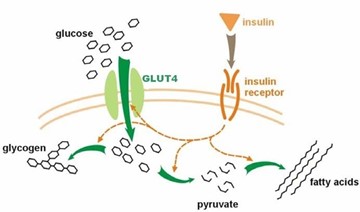
Exercise can help to lower blood glucose levels by improving insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake by muscles. It also helps with weight loss, which is important for managing type 2 diabetes since excess weight can make it harder for insulin to work properly. The nurse can also discuss with the patient other ways to make exercise more enjoyable, such as finding a physical activity that they enjoy, like dancing, swimming, or walking with a friend or family member.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
