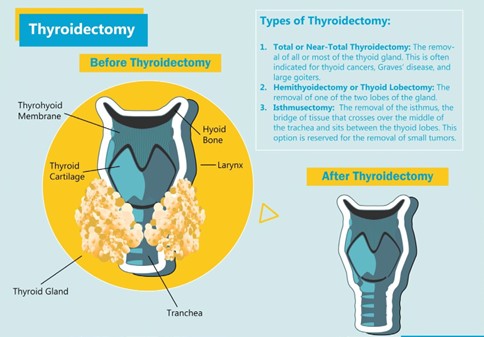
While assessing a patient who has just arrived in the post-anesthesia recovery unit (PACU) after a thyroidectomy, the nurse obtains this data. Which is the most important to communicate to the surgeon?
The patient’s voice is weak and hoarse sounding.
The patient is complaining of a 7/10 incisional pain.
The patient’s cardiac monitor shows a heart rate of 112.
The patient is increasingly swelling at the neck.
The Correct Answer is D
This is a critical finding that could indicate bleeding or compromised airway, both of which are potentially life-threatening complications following a thyroidectomy. Immediate intervention may be necessary to prevent further harm to the patient. The other options are important to note and should be addressed, but they do not require immediate intervention as the swelling in the neck does.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
This response acknowledges the patient's concerns and provides reassurance that the changes are temporary and will improve after surgery. Response is dismissive of the patient's concerns and may make the patient feel unheard. Response c may be helpful, but it does not address the patient's emotional concerns. Response d is not accurate because the patient has expressed feeling awful about their appearance.
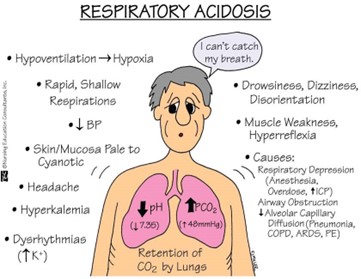
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
The pH value is less than the normal range of 7.35-7.45, indicating acidosis. The PaCO2 value is elevated above the normal range of 35-45 mmHg, indicating respiratory acidosis. The PaO2 value is lower than normal, but not significantly low enough to indicate hypoxemia. The HCO3- level is within the normal range, but not significantly high enough to indicate metabolic compensation for respiratory acidosis.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
