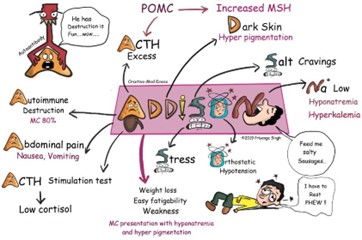
A patient is hospitalized with acute adrenal insufficiency. The nurse determines that the patient is responding favorably to treatment on finding:
Decreasing serum sodium
Decreasing blood glucose
Decreasing serum potassium
Increasing urinary output
The Correct Answer is D
One of the hallmarks of adrenal insufficiency is dehydration and decreased urinary output, which can lead to electrolyte imbalances such as hyperkalemia and hyponatremia. As treatment begins to take effect, the patient's fluid and electrolyte balance should improve, leading to an increase in urinary output. Acute adrenal insufficiency, also known as the Addisonian crisis, is a life-threatening condition caused by a sudden decrease in cortisol and aldosterone hormones. Treatment usually involves the administration of intravenous glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids to replace the deficient hormones.
Decreasing serum sodium (a) and decreasing blood glucose (b) are not signs of improvement but rather indicative of continued adrenal insufficiency. Decreasing serum potassium (c) is also not a sign of improvement as it could indicate that the patient is developing hyperkalemia, which is a potential complication of adrenal crisis.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
The operating room is a sterile environment, and it is critical to maintain a clean and controlled environment to reduce the risk of infection to the patient. The measures taken include maintaining positive air pressure, controlling temperature and humidity, filtering the air, using sterile surgical instruments, and limiting traffic in and out of the operating room. These measures help to prevent the spread of infectious agents that may be present in the operating room. While the other options (a, b, and d) may also be important considerations in the design of the operating room, preventing transmission of infection is the primary goal.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
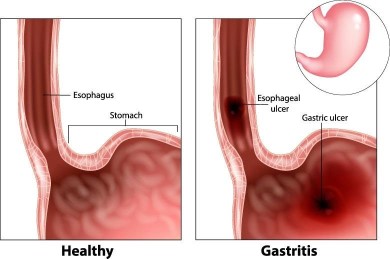
Clients with acute gastritis are recommended to eat smaller, frequent meals instead of three large meals. This helps to reduce the workload on the digestive system and allows the stomach to heal. Therefore, option A is not a suitable nursing intervention for a client with acute gastritis.
Options b, c, and d are all appropriate nursing interventions for a client with acute gastritis. Observing stool characteristics can help to identify any bleeding or inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract, evaluating intake and output can help to identify any fluid imbalances, and monitoring laboratory reports of electrolytes can help to identify any imbalances that may occur because of vomiting or diarrhea.

Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.