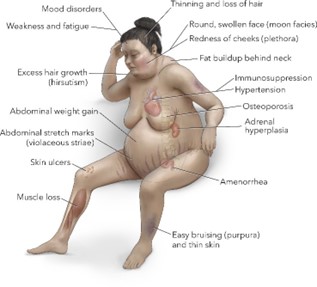
A nursing assessment of a patient with Cushing syndrome reveals that the patient has truncal obesity and thin and legs. An additional manifestation of Cushing syndrome that the nurse would expect to find is:
decreased axillary and pubic hair.
chronically low blood pressure,
bronzed appearance of the skin.
purplish red streaks on the abdomen.
The Correct Answer is D
Cushing syndrome is a hormonal disorder caused by prolonged exposure to high levels of cortisol hormone in the body. It can cause a variety of physical manifestations, including truncal obesity, thin arms, and legs, decreased axillary and pubic hair, hypertension, glucose intolerance, osteoporosis, and purple striae (stretch marks) on the abdomen.
Out of the options given, the nurse would expect to find purplish-red streaks on the abdomen as an additional manifestation of Cushing syndrome.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
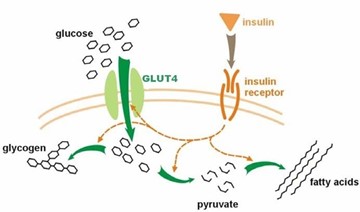
Exercise can help to lower blood glucose levels by improving insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake by muscles. It also helps with weight loss, which is important for managing type 2 diabetes since excess weight can make it harder for insulin to work properly. The nurse can also discuss with the patient other ways to make exercise more enjoyable, such as finding a physical activity that they enjoy, like dancing, swimming, or walking with a friend or family member.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
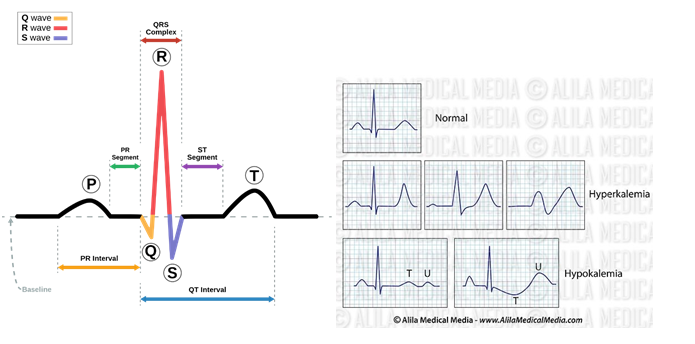
Electrocardiographic (ECG) changes and dysrhythmias related to hypokalemia are the main reasons for initiating cardiac monitoring in patients with diabetic ketoacidosis. In diabetic ketoacidosis, insulin deficiency causes the body to break down fat for energy, leading to the production of ketones and resulting in metabolic acidosis. In addition, glucose and potassium are lost in the urine due to osmotic diuresis. Hypokalemia can cause ECG changes and dysrhythmias, which can be life-threatening.
Hypokalemia is a common complication of DKA and can lead to ECG changes such as ST-segment depression, T-wave inversion, and U waves².
Hypovolemic shock related to osmotic diuresis is an important consideration in the management of diabetic ketoacidosis, but it is not the primary reason for initiating cardiac monitoring.
Cardiovascular collapse resulting from the effects of hyperglycemia is not a common complication of diabetic ketoacidosis, and it is not the primary reason for initiating cardiac monitoring.
Fluid overload resulting from aggressive fluid replacement is a potential complication of diabetic ketoacidosis, but it is not the primary reason for initiating cardiac monitoring.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.