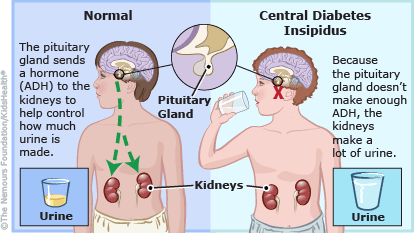
The nurse is creating the care plan for a patient with symptoms of DI who was admited to the hospital for evaluation and treatment of the condition. An appropriate nursing diagnosis for the patient is:
Excess fluid volume related to intake greater than output.
Risk for impaired skin integrity related to generalized edema.
Activity intolerance related to muscle cramps and weakness.
Insomnia related to waking at night to void.
The Correct Answer is A
Excess fluid volume related to intake greater than output would be the most appropriate nursing diagnosis for a patient with symptoms of DI (diabetes insipidus). This condition results in excessive urine output and, as a consequence, can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. Therefore, monitoring and managing fluid volume is a priority for patients with DI.
Risk for impaired skin integrity related to generalized edema is more commonly associated with conditions that cause fluid retention such as heart failure, liver failure, or kidney disease, rather than DI.
Activity intolerance related to muscle cramps and weakness is a possible nursing diagnosis for patients with conditions that affect muscle function, such as muscular dystrophy or multiple sclerosis, but not specifically for DI.
Insomnia related to waking at night to void is more commonly associated with urinary frequency or nocturia due to conditions such as urinary tract infections or benign prostatic hyperplasia, but not specifically for DI.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Although increasing fluid intake and fiber intake are important interventions for preventing constipation, it is important to first assess the patient's current situation and risk factors for constipation. Additionally, while a daily bowel movement is not necessary for everyone, it is important to understand the patient's usual bowel habits and whether or not their current regimen is effective for them. Therefore, the nurse should perform a focused nursing assessment to identify the patient's risk factors for constipation and evaluate their current bowel regimen before providing specific interventions or recommendations.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
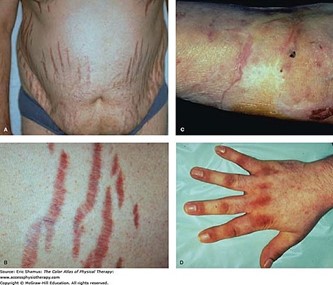
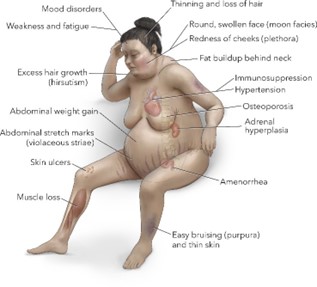
Cushing syndrome is a hormonal disorder caused by prolonged exposure to high levels of cortisol hormone in the body. It can cause a variety of physical manifestations, including truncal obesity, thin arms, and legs, decreased axillary and pubic hair, hypertension, glucose intolerance, osteoporosis, and purple striae (stretch marks) on the abdomen.
Out of the options given, the nurse would expect to find purplish-red streaks on the abdomen as an additional manifestation of Cushing syndrome.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
