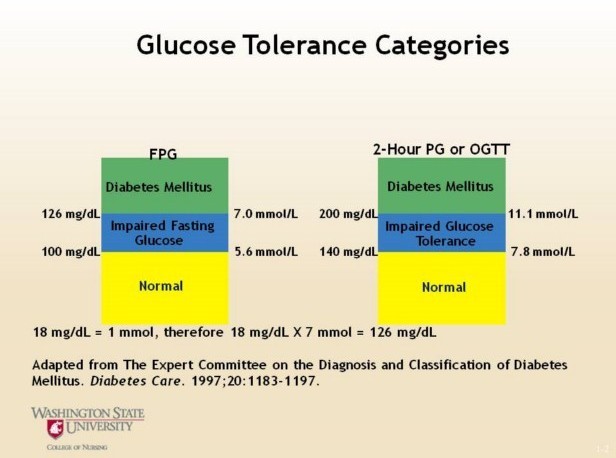
A program of weight loss and exercise is recommended for a patient with impaired fasting glucose (IFG). When teaching the patient about the reason for these lifestyle changes, the nurse will tell the patient that:
The onset of diabetes and the associated cardiovascular risks can be delayed or prevented by weight loss and exercise.
Although the fasting plasma glucose levels do not currently indicate diabetes, the glycosylated hemoglobin will be elevated.
The high insulin levels associated with this syndrome damage the lining of blood vessels leading to vascular disease.
The liver is producing excessive glucose, which will eventually exhaust the ability of the pancreas to produce insulin, and exercise will normalize glucose production.
The Correct Answer is A
This statement is correct. Impaired fasting glucose (IFG) is a condition in which the fasting blood glucose level is higher than normal but not high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes. However, people with IFG are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Weight loss and exercise can help to prevent or delay the onset of diabetes and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
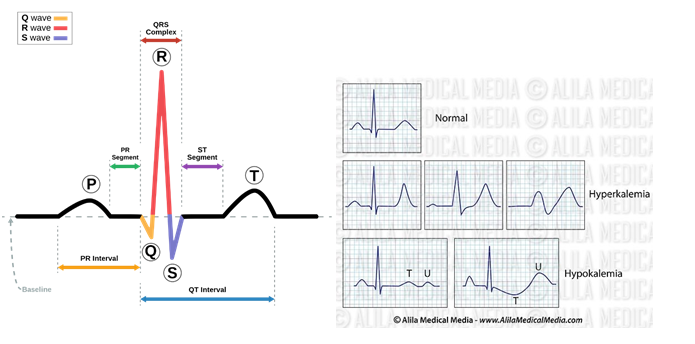
Electrocardiographic (ECG) changes and dysrhythmias related to hypokalemia are the main reasons for initiating cardiac monitoring in patients with diabetic ketoacidosis. In diabetic ketoacidosis, insulin deficiency causes the body to break down fat for energy, leading to the production of ketones and resulting in metabolic acidosis. In addition, glucose and potassium are lost in the urine due to osmotic diuresis. Hypokalemia can cause ECG changes and dysrhythmias, which can be life-threatening.
Hypokalemia is a common complication of DKA and can lead to ECG changes such as ST-segment depression, T-wave inversion, and U waves².
Hypovolemic shock related to osmotic diuresis is an important consideration in the management of diabetic ketoacidosis, but it is not the primary reason for initiating cardiac monitoring.
Cardiovascular collapse resulting from the effects of hyperglycemia is not a common complication of diabetic ketoacidosis, and it is not the primary reason for initiating cardiac monitoring.
Fluid overload resulting from aggressive fluid replacement is a potential complication of diabetic ketoacidosis, but it is not the primary reason for initiating cardiac monitoring.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
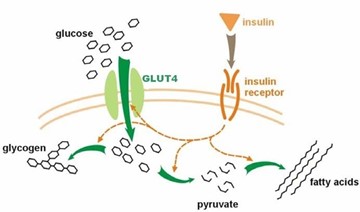
Exercise can help to lower blood glucose levels by improving insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake by muscles. It also helps with weight loss, which is important for managing type 2 diabetes since excess weight can make it harder for insulin to work properly. The nurse can also discuss with the patient other ways to make exercise more enjoyable, such as finding a physical activity that they enjoy, like dancing, swimming, or walking with a friend or family member.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.