An emergency room nurse is performing secondary triage on clients transported from the scene of a chemical spill. After caring for the clients, the EMS workers complained of nausea and dizziness. Which immediate interventions need to be taken by the triage nurse? SELECT ALL THAT APPLY
Continue with the triage process.
Evacuate the emergency department.
Place the client in a private room.
Treat the client after contaminated items are removed.
Send the client and EMS crew to decontamination.
Correct Answer : B,E
Choice A reason: Continuing with the triage process is not an immediate intervention that needs to be taken by the triage nurse, as it may expose more people to the chemical hazard and worsen the situation. The triage nurse should stop the triage process and alert the emergency department staff and management about the potential contamination. The triage nurse should also follow the facility's emergency preparedness plan and protocols for dealing with chemical spills.
Choice B reason: Evacuating the emergency department is an immediate intervention that needs to be taken by the triage nurse, as it helps to protect the safety and health of the staff, clients, and visitors. The triage nurse should assist with evacuating everyone from the emergency department to a safe and designated area, away from the source of contamination. The triage nurse should also ensure that everyone is accounted for and that no one re-enters the emergency department until it is cleared by the authorities.
Choice C reason: Placing the client in a private room is not an immediate intervention that needs to be taken by the triage nurse, as it may not prevent the spread of contamination or provide adequate care to the client. The client who have been exposed to a chemical spill should not be moved to another area of the facility, as they may contaminate other people or surfaces along the way. The client should be kept in a separate and isolated area until they are decontaminated and assessed.
Choice D reason: Treating the client after contaminated items are removed is not an immediate intervention that needs to be taken by the triage nurse, as it may delay or compromise the care of the client. The client who has been exposed to a chemical spill should be treated as soon as possible, as some chemicals can cause serious or irreversible damage to the skin, eyes, lungs, or other organs. The triage nurse should provide basic life support measures, such as airway management, oxygen therapy, or bleeding control while wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). The triage nurse should also remove any contaminated clothing or jewelry from the client and place them in a sealed bag.
Choice E reason: Sending the client and EMS crew to decontamination is an immediate intervention that needs to be taken by the triage nurse, as it helps to remove or neutralize any harmful chemicals from their skin, hair, or clothing. The triage nurse should direct or escort the client and EMS crew to a designated decontamination area or unit, where they will undergo a thorough washing process with water and soap or other solutions. The triage nurse should also monitor their vital signs and symptoms during and after decontamination.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["A","C","E"]
Explanation
Choice A reason: The integumentary system is a portal of entry for anthrax because the bacteria can enter through cuts or abrasions on the skin. This is called cutaneous anthrax, and it is the most common and least deadly form of anthrax infection.
Choice B reason: The endocrine system is not a portal of entry for anthrax because the bacteria do not affect the glands or hormones of the body. The endocrine system is mainly involved in regulating metabolism, growth, development, and reproduction.
Choice C reason: The central nervous system is a portal of entry for anthrax because the bacteria can spread to the brain and spinal cord from other parts of the body. This is called meningeal anthrax, and it is a rare and fatal complication of anthrax infection.
Choice D reason: The renal system is not a portal of entry for anthrax because the bacteria do not infect the kidneys or urinary tract. The renal system is mainly involved in filtering waste products and excess fluids from the blood.
Choice E reason: The respiratory system is a portal of entry for anthrax because the bacteria can be inhaled into the lungs. This is called inhalation anthrax, and it is the most deadly form of anthrax infection.
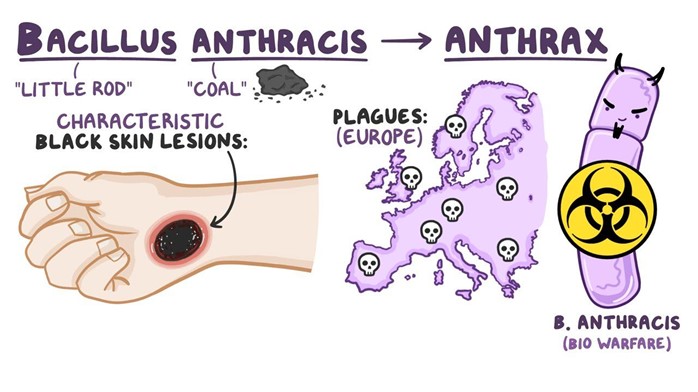
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A reason: It is a tool that is used to determine your maximum level of self-sufficiency as the appropriate nursing response, as it accurately describes the purpose and function of the FIM. The FIM measures how much assistance you need to perform 18 activities of daily living, such as eating, dressing, toileting, walking, and communicating. The FIM helps to evaluate your functional status, monitor your progress, and plan your rehabilitation goals and interventions. ¹²³
Choice B reason: It is a test that determines which activities you feel most comfortable performing is not an appropriate nursing response, as it does not reflect the objective and standardized nature of the FIM. The FIM is not a subjective or self-reported measure of your preferences or comfort level, but rather an observational and rating scale that assesses your actual performance and independence in various tasks. The FIM uses a 7-point ordinal scale that ranges from 1 (total assistance) to 7 (complete independence) and requires trained and certified raters to administer and score it. ¹²³
Choice C reason: It is a tool used by insurance companies to determine qualifications for medical reimbursement is not an appropriate nursing response, as it does not capture the primary purpose and benefit of the FIM. The FIM is not a financial or administrative tool that determines your eligibility or coverage for medical services, but rather a clinical and research tool that measures your functional outcomes and quality of care. The FIM provides a uniform system of measurement for disability based on the International Classification of Impairment, Disabilities, and Handicaps and allows for comparison and evaluation of different rehabilitation programs and settings. ¹²³
Choice D reason: It is a tool that is used to assess what services you will need a home health aide to perform for you is not an appropriate nursing response, as it does not reflect the comprehensive and multidimensional scope of the FIM. The FIM is not a specific or limited tool that assesses only your home care needs or dependence on others, but rather a general and broad tool that assesses your functional abilities and disabilities in various domains and environments. The FIM covers both motor and cognitive aspects of functioning, such as comprehension, expression, social interaction, problem-solving, and memory. The FIM can be used with all diagnoses within rehabilitation and can be applied across different levels and settings of care.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
