A registered nurse (RN) and an experienced licensed practical nurse (LPN) are caring for a group of clients. Which of the following tasks should the RN delegate to the LPN? SELECT ALL THAT APPLY
Initiate a plan of care for a client who is postoperative from an appendectomy.
Administer a tap-water enema to a client who is preoperative.
Provide discharge instructions to a confused client's spouse.
Catheterize a client who has not voided in 8 hours.
Obtain vital signs from a client who is 6 hours postoperative.
Correct Answer : B,D,E
Choice A reason: Initiating a plan of care for a client who is postoperative from an appendectomy is not a task that the RN should delegate to the LPN, as it requires nursing judgment, critical thinking, and assessment skills that are beyond the scope of practice of the LPN. The RN is responsible for developing, implementing, and evaluating the plan of care for each client based on their individual needs, preferences, and goals. The RN can delegate some aspects of the plan of care to the LPN, such as performing routine tasks or monitoring the client's status, but the RN must supervise and evaluate the LPN's performance.
Choice B reason: Administering a tap-water enema to a client who is preoperative is a task that the RN can delegate to the LPN, as it is a standardized procedure that does not require nursing judgment or assessment. The LPN has the knowledge and skills to perform this task safely and effectively, following the established policies and protocols of the facility. The RN should provide clear instructions and expectations to the LPN, such as the type, amount, and temperature of the solution, the position and comfort of the client, and the signs and symptoms to report. The RN should also verify that the LPN has completed the task and documented the outcome.
Choice C reason: Providing discharge instructions to a confused client's spouse is not a task that the RN should delegate to the LPN, as it involves teaching, counseling, and evaluating the client's and family's understanding and readiness for discharge. These are complex activities that require nursing judgment, communication skills, and evaluation skills that are beyond the scope of practice of the LPN. The RN is responsible for ensuring that the client and family receive adequate information and education about the client's condition, treatment, medications, follow-up care, and community resources. The RN can delegate some aspects of discharge planning to the LPN, such as collecting data or providing reinforcement of teaching, but the RN must supervise and evaluate the LPN's performance.
Choice D reason: Catheterizing a client who has not voided in 8 hours is a task that the RN can delegate to the LPN, as it is a standardized procedure that does not require nursing judgment or assessment. The LPN has the knowledge and skills to perform this task safely and effectively, following the established policies and protocols of the facility. The RN should provide clear instructions and expectations to the LPN, such as the type and size of the catheter, the sterile technique, and the urine output measurement. The RN should also verify that the LPN has completed the task and documented the outcome.
Choice E reason: Obtaining vital signs from a client who is 6 hours postoperative is a task that the RN can delegate to the LPN, as it is a routine task that does not require nursing judgment or assessment. The LPN has the knowledge and skills to perform this task safely and effectively, using appropriate equipment and techniques. The RN should provide clear instructions and expectations to the LPN, such as the frequency and parameters of vital signs monitoring. The RN should also verify that the LPN has completed the task and documented the outcome.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason: Analgesics are medications that relieve pain by blocking pain signals or reducing inflammation. They include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), opioids, and acetaminophen. However, analgesics are not very effective in treating trigeminal neuralgia, as they do not address the underlying cause of the pain, which is the compression or irritation of the trigeminal nerve.
Choice B reason: Antihistamines are medications that block the effects of histamine, a chemical that causes allergic reactions such as itching, sneezing, and swelling. They include diphenhydramine, cetirizine, and loratadine. Antihistamines are not effective in treating trigeminal neuralgia, as they do not affect the trigeminal nerve or its function.
Choice C reason: Antibiotics are medications that kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria that cause infections. They include penicillin, amoxicillin, and ciprofloxacin. Antibiotics are not effective in treating trigeminal neuralgia, as they do not target the trigeminal nerve or its pathology.
Choice D reason: Anticonvulsants are medications that prevent or reduce the frequency and severity of seizures by stabilizing the electrical activity of the brain. They include carbamazepine, gabapentin, and phenytoin. Anticonvulsants are the most effective medications in treating trigeminal neuralgia, as they reduce the abnormal firing of the trigeminal nerve that causes the pain. Anticonvulsants are considered the first-line therapy for trigeminal neuralgia and can provide significant relief for most clients.
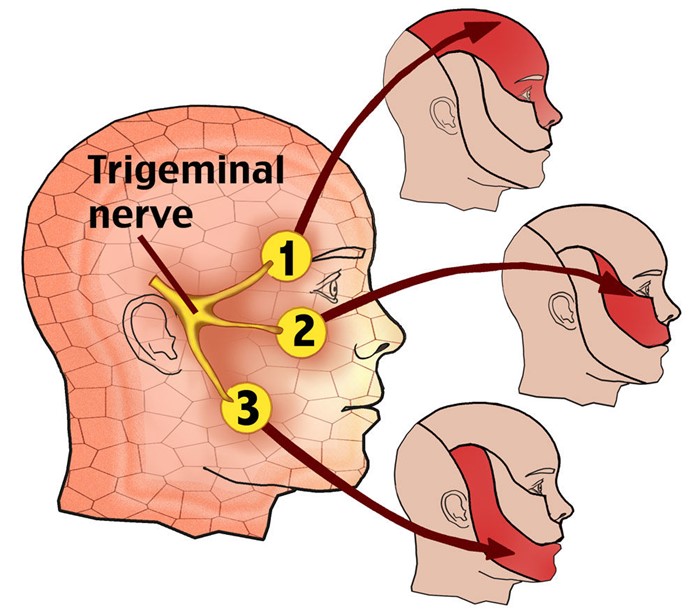
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason: Providing total assistance with all ADLs is not an intervention that should be included in the client's plan. ADLs are activities of daily living, such as bathing, dressing, eating, and toileting. Providing total assistance with all ADLs can reduce the client's independence and self-esteem, and increase their dependence and learned helplessness. The nurse should encourage and assist the client to perform as much as they can by themselves and provide partial or intermittent assistance only when needed.
Choice B reason: Ordering a low-residue diet is not an intervention that should be included in the client's plan. A low-residue diet is a type of diet that limits foods that are high in fiber or indigestible material, such as whole grains, nuts, seeds, fruits, and vegetables. A low-residue diet may be recommended for clients who have inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), diverticulitis, or bowel obstruction, as it can reduce bowel frequency and irritation. However, it is not indicated for clients who have MS, unless they have other comorbidities that require it. A balanced diet that includes adequate fiber, fluids, and nutrients is more beneficial for clients who have MS.
Choice C reason: Encouraging the client to void every hour is not an intervention that should be included in the client's plan. Voiding every hour can be inconvenient and impractical for the client, and may not address their bladder problems effectively. MS can cause bladder dysfunction, such as urinary urgency, frequency, incontinence, or retention, due to nerve damage that affects bladder control. The nurse should assess the type and severity of the bladder dysfunction, and provide appropriate interventions, such as medication, catheterization, pelvic floor exercises, or bladder training.
Choice D reason: Instructing the client on daily muscle stretching is an intervention that should be included in the client's plan. Muscle stretching is a type of exercise that involves extending or elongating a muscle or group of muscles to their full length. Muscle stretching can help prevent or relieve muscle spasticity, stiffness, pain, or contractures that may occur in clients who have MS. The nurse should teach the client how to perform muscle stretching safely and correctly, and encourage them to do it daily or as prescribed.
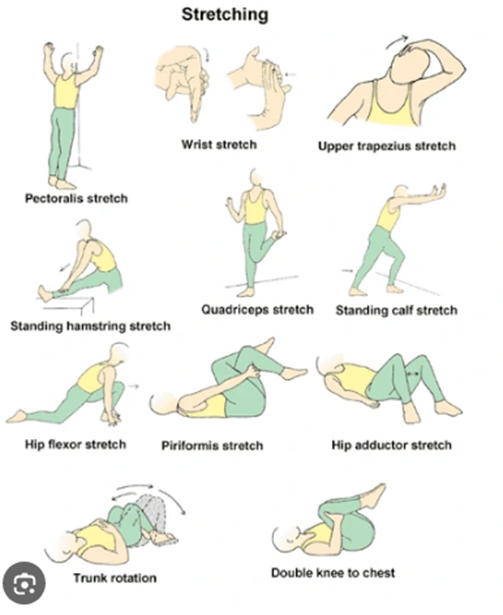
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
