A patient who is unconscious after a head injury has cerebral edema. Which nursing intervention will be included in the plan of care?
Encourage coughing and deep breathing
Position the patient with knees and hips flexed
Perform nursing interventions once an hour to provide rest periods
Keep the head of the bed elevated to 30 degrees
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A Reason: This is incorrect because encouraging coughing and deep breathing can increase intracranial pressure (ICP), which is the pressure inside the skull that can affect brain function. Coughing and deep breathing can increase blood flow and oxygen demand to the brain, which can worsen cerebral edema. The nurse should suction the patient as needed and maintain a patent airway.
Choice B Reason: This is incorrect because positioning the patient with knees and hips flexed can increase ICP by reducing venous drainage from the head. The nurse should position the patient with neck and body in alignment and avoid extreme flexion or extension of any joints.
Choice C Reason: This is incorrect because performing nursing interventions once an hour can disturb the patient's sleep and increase ICP by stimulating brain activity. The nurse should cluster nursing interventions and provide quiet and dark environment to promote rest and reduce stress.
Choice D Reason: This is correct because keeping the head of the bed elevated to 30 degrees can decrease ICP by facilitating venous drainage from the head and reducing cerebral blood volume. The nurse should monitor the patient's blood pressure and pulse to ensure adequate cerebral perfusion.

Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is incorrect because using sign language when communicating with the client is not an appropriate action for the nurse to take. Sign language is a form of communication that uses hand gestures, facial expressions, and body movements. It is not a universal language and requires training and practice. The nurse should not assume that the client knows or prefers sign language unless they have indicated so.
Choice B reason: This is incorrect because speaking loudly and into the client's good ear is not an appropriate action for the nurse to take. Speaking loudly can distort the sound quality and cause discomfort or irritation to the client. Speaking into the client's good ear can also create a sense of imbalance and isolation. The nurse should speak at a normal volume and tone, and face the client directly.
Choice C reason: This is the correct answer because speaking directly to the client in a normal, clear voice is an appropriate action for the nurse to take. Speaking directly to the client can help them see the nurse's mouth movements and facial expressions, which can enhance understanding and communication. Speaking in a normal, clear voice can help convey the message clearly and respectfully.
Choice D reason: This is incorrect because sitting by the client's side and speaking very slowly is not an appropriate action for the nurse to take. Sitting by the client's side can make it difficult for them to see the nurse's face and hear their voice. Speaking very slowly can also make the message unclear and patronizing. The nurse should sit in front of the client and speak at a normal pace.
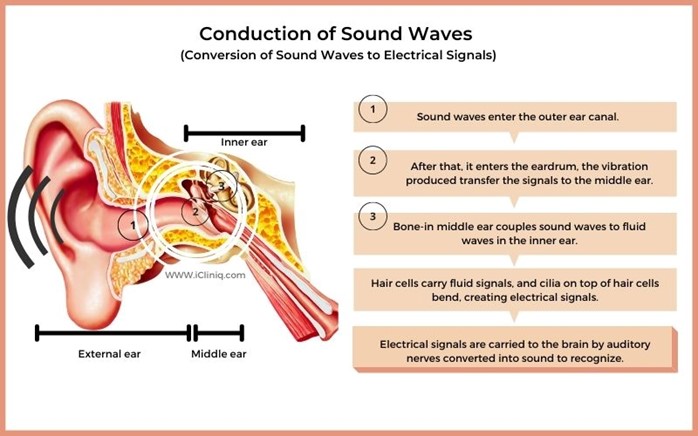
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
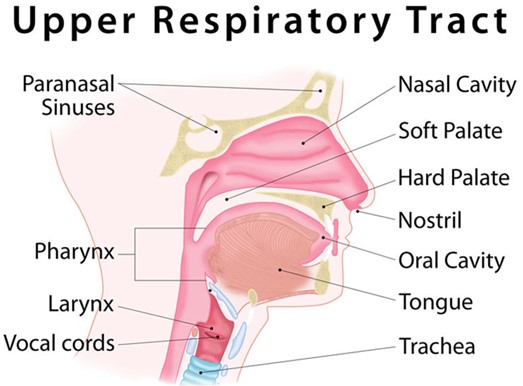
Choice A reason: This is incorrect because education about mastoidectomy is not relevant for a client with an upper respiratory infection. Mastoidectomy is a surgical procedure that removes part or all of the mastoid bone behind the ear, which can become infected or inflamed due to chronic or recurrent middle ear infections. The nurse should assess
the client's ear for signs of mastoiditis, such as swelling, tenderness, or redness behind the ear, but mastoidectomy is not a common or first-line treatment for upper respiratory infection.
Choice B reason: This is incorrect because a referral for a hearing test is not necessary for a client with an upper respiratory infection. Hearing test is a diagnostic tool that measures how well a person can hear different sounds at different frequencies and intensities. The nurse should ask the client about any changes in hearing or tinnitus, which are possible complications of upper respiratory infection, but a hearing test is not a routine or urgent intervention for this condition.
Choice C reason: This is correct because education on the administration of oral antibiotics can help treat an upper respiratory infection. Antibiotics are drugs that kill or inhibit bacteria that cause infections. Upper respiratory infections can be caused by various pathogens, such as viruses, bacteria, or fungi, but bacterial infections are more likely to cause fever, otalgia, or purulent nasal drainage. The nurse should instruct the client on how to take antibiotics as prescribed, such as dosage, frequency, duration, side effects, and interactions.
Choice D reason: This is incorrect because a prescription for an antifungal cream is not appropriate for a client with an upper respiratory infection. Antifungal cream is a topical medication that kills or inhibits fungi that cause skin infections. Upper respiratory infection is not a skin infection, but an infection of the nose, throat, or sinuses. Antifungal cream has no effect on upper respiratory infection and may cause adverse effects or resistance.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
