A nurse is caring for a child who was admitted with suspected rheumatic fever. The provider prescribes an antistreptolysin O (ASO) titer. The parent asks the nurse about the purpose of the test. Which of the following responses should the nurse make?
"This test will indicate if your child has rheumatic fever."
"This test will confirm if your child had a recent streptococcal infection."
"This test will indicate if your child has a therapeutic blood level of an aminoglycoside."
"This test will confirm if your child has immunity to streptococcal bacteria."
The Correct Answer is B
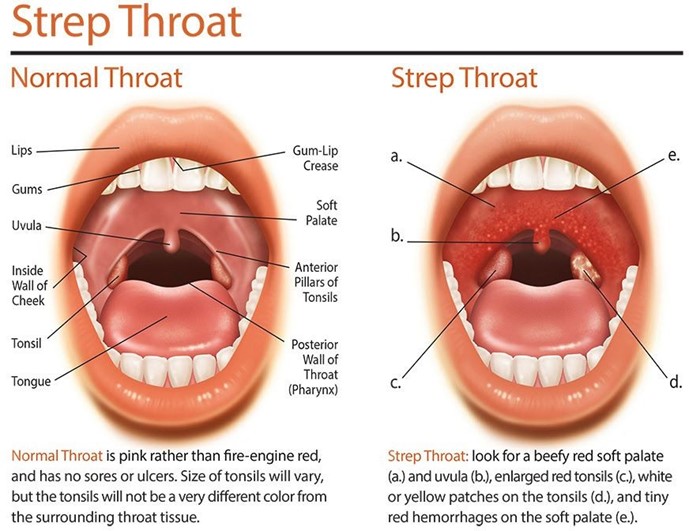
Choice A: This test will not indicate if the child has rheumatic fever, as rheumatic fever is a complication of an untreated or inadequately treated streptococcal infection that affects the heart, joints, skin, and brain. Rheumatic fever is diagnosed based on clinical criteria, such as carditis, polyarthritis, chorea, erythema marginatum, and subcutaneous nodules.
Choice B: This test will confirm if the child had a recent streptococcal infection, as antistreptolysin O (ASO) is an antibody that the body produces in response to streptococcal bacteria. A high ASO titer indicates that the child was exposed to streptococcal bacteria within the past few weeks. A streptococcal infection can cause pharyngitis, tonsillitis, scarlet fever, or impetigo.
Choice C: This test will not indicate if the child has a therapeutic blood level of an aminoglycoside, as an aminoglycoside is a type of antibiotic that is used to treat serious bacterial infections. A therapeutic blood level of an aminoglycoside means that the drug is effective and safe in the body. A therapeutic blood level of an aminoglycoside is measured by a peak and trough level.
Choice D: This test will not confirm if the child has immunity to streptococcal bacteria, as immunity to streptococcal bacteria means that the body can resist or fight the infection. Immunity to streptococcal bacteria can be acquired by natural exposure or vaccination. Immunity to streptococcal bacteria is measured by an antibody titer or a skin test.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A:In actual practice, log rolling is typically done every 2 hoursto align with standard nursing protocols for preventing complications such as pressure injuries, maintaining skin integrity, and ensuring patient comfort. Repositioning every 2 hours also helps promote better circulation and reduces the risk of complications like pneumonia and deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
as a unit without twisting or bending the spine. The nurse should use a draw sheet and at least two other staff
members to assist with log rolling.
Choice B: This intervention is incorrect, as keeping the head of the bed at a 30-degree angle can cause flexion of the spine and compromise spinal alignment. The head of the bed should be kept flat or slightly elevated, depending on the provider's orders and the client's comfort. The nurse should avoid raising or lowering the head of the bed without checking with the provider first.
Choice C: This intervention is unnecessary, as placing the client in protective isolation is not indicated for a client who is postoperative following scoliosis repair with Harrington rod instrumentation. Protective isolation is used for clients who have compromised immune systems and are at high risk of acquiring infections from others, such as transplant recipients, cancer patients, or patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy. The nurse should follow standard precautions and surgical site care to prevent infection in this client.
Choice D: This intervention is optional, as initiating the use of a PCA pump for pain control may or may not be appropriate for a client who is postoperative following scoliosis repair with Harrington rod instrumentation. A PCA pump is a device that allows the client to self-administer a preset dose of analgesic medication by pressing a button. A PCA pump can provide effective and individualized pain relief, but it requires careful monitoring and education. The nurse should assess the client's pain level, preference, and ability to use a PCA pump and consult with the provider before initiating it.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is a therapeutic response that acknowledges the parent's feelings and provides reassurance that the behavior is normal and temporary. The other responses are either dismissive, judgmental, or self-disclosing, which are not helpful for the parent.
Choice B reason: This is a judgmental response that implies that the parent is overreacting or has unrealistic expectations for their child.
Choice C reason: This is a dismissive response that minimizes the parent's concern and does not offer any support
or information.
Choice D reason: This is a self-disclosing response that shifts the focus from the parent to the nurse and does not
address the issue at hand.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
