A nurse is preparing to administer vaccines to a 1-year-old child. Which of the following vaccines should the nurse give? (Select two)
Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR)
Rotavirus (RV)
Human papillomavirus (HPV4)
Varicella (VAR)
Diphtheria, tetanus and acellular pertussis (DTaP)
Correct Answer : A,D
The correct answer is a. Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR) and d. Varicella (VAR).
Choice A reason:
Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR): The MMR vaccine is recommended for children at 12-15 months of age. It protects against three serious diseases: measles, mumps, and rubella. The first dose is typically given at 12-15 months, with a second dose at 4-6 years. Measles can cause severe complications such as pneumonia and encephalitis. Mumps can lead to meningitis and hearing loss, while rubella can cause congenital rubella syndrome in pregnant women. Administering the MMR vaccine at the recommended age ensures that the child is protected from these potentially severe diseases.
Choice B reason:
Rotavirus (RV): This vaccine is given to infants at 2, 4, and possibly 6 months of age. It is not typically administered to a 1-year-old child as the series should be completed by 8 months. Rotavirus is a leading cause of severe diarrhea and dehydration in infants and young children. The vaccine is given orally and is highly effective in preventing rotavirus gastroenteritis. However, since the vaccine series is completed by 8 months, it is not appropriate for a 1-year-old child.
Choice C reason:
Human papillomavirus (HPV4): The HPV vaccine is recommended starting at 11-12 years of age. It is not suitable for a 1-year-old child. HPV is a common virus that can lead to certain types of cancers, including cervical cancer. The vaccine is most effective when given before exposure to HPV, which is why it is recommended for preteens. Administering the HPV vaccine to a 1-year-old would not be appropriate as it is not within the recommended age range.
Choice D reason:
Varicella (VAR): The VAR vaccine is recommended for children at 12-15 months of age to protect against chickenpox. A second dose is given at 4-6 years. Chickenpox can cause an itchy rash, fever, and tiredness. In some cases, it can lead to severe skin infections, pneumonia, and encephalitis. Vaccinating at the recommended age ensures that the child is protected from these complications. The first dose at 12-15 months is crucial for building immunity against the varicella virus.
Choice E reason:
Diphtheria, tetanus and acellular pertussis (DTaP): The DTaP vaccine is given in a series of five doses at 2, 4, 6, 15-18 months, and 4-6 years. The 4th dose is given at 15-18 months, not at 1 year. DTaP protects against three serious diseases: diphtheria, which can cause breathing problems and heart failure; tetanus, which causes painful muscle stiffness; and pertussis (whooping cough), which can lead to severe coughing spells and pneumonia. The timing of the doses is crucial for ensuring effective immunity, and the 1-year mark is not one of the recommended times for the DTaP vaccine.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A: Lice cannot survive for more than 48 hours away from the host. This statement is false and should not be included in the teaching, as it can cause unnecessary anxiety or confusion.
Choice B: Washing your child's hair daily will not prevent lice, as lice do not depend on hair cleanliness or hygiene. This statement is false and should not be included in the teaching, as it can create a false sense of security or stigma.
Choice C: Lice cannot jump or fly from one child to another, as they only crawl. This statement is false and should not be included in the teaching, as it can cause unnecessary fear or panic.
Choice D: Encouraging your child to avoid sharing hats with other children can prevent lice, as lice can be transmitted by direct contact or by sharing personal items. This statement is true and should be included in the teaching, as it can help prevent lice infestation or spread.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason: This choice is incorrect because the radial artery is not an ideal site to assess the heart rate in an infant. The radial artery is located on the thumb side of the wrist, and it can be palpated by placing two fingers over it. It may be used for adults or older children who have a strong pulse, but it may be difficult to locate or feel in an infant who has a small or weak pulse.
Choice B reason: This choice is incorrect because the carotid artery is not an ideal site to assess the heart rate in an infant. The carotid artery is located on either side of the neck, and it can be palpated by placing two fingers over it. It may be used for adults or older children who have a cardiac arrest or shock, but it may be risky to use in an infant who has a fragile neck or airway.
Choice C reason: This choice is incorrect because the brachial artery is not an ideal site to assess the heart rate in an infant. The brachial artery is located on the inner side of the upper arm, and it can be palpated by placing two fingers over it. It may be used for infants or young children who have a blood pressure measurement, but it may be uncomfortable or inaccurate to use for a heart rate assessment.
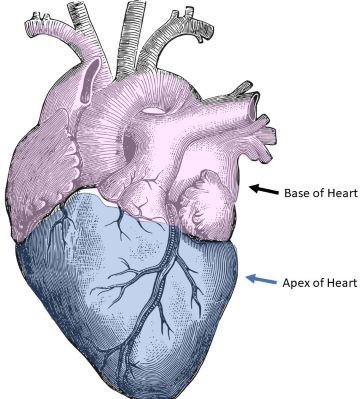
Choice D reason: This choice is correct because the apex of the heart is an ideal site to assess the heart rate in an infant. The apex of the heart is located at the fifth intercostal space on the left midclavicular line, and it can be auscultated by placing a stethoscope over it. It may be used for infants or young children who have a regular and strong heartbeat, and it may provide the most accurate measurement of the heart rate.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
