A nurse is planning care for a 5-month-old infant who is scheduled for a lumbar puncture to rule out meningitis. Which of the following actions should the nurse include in the plan of care?
Apply a eutectic mixture of lidocaine and prilocaine cream topically 15 min prior to the procedure.
Keep the infant NPO for 6 hr prior to the procedure.
Hold the infant's chin to his chest and knees to his abdomen during the procedure.
Place the infant in an infant seat for 2 hr following the procedure.
The Correct Answer is C
The correct answer is: c. Hold the infant’s chin to his chest and knees to his abdomen during the procedure.
Choice A: Apply a eutectic mixture of lidocaine and prilocaine cream topically 15 min prior to the procedure.
Applying a eutectic mixture of lidocaine and prilocaine (EMLA) cream can help reduce pain during procedures like lumbar punctures. However, it typically needs to be applied 30 to 60 minutes before the procedure to be effective. Applying it only 15 minutes prior would not provide adequate analgesia.
Choice B: Keep the infant NPO for 6 hr prior to the procedure.
Keeping an infant NPO (nothing by mouth) for 6 hours is generally recommended before procedures requiring sedation or anesthesia to reduce the risk of aspiration. However, lumbar punctures do not typically require such prolonged fasting, especially in infants, unless sedation is planned.
Choice C: Hold the infant’s chin to his chest and knees to his abdomen during the procedure.
This is the correct positioning for a lumbar puncture in infants. The infant should be held in a curled-up position, with the chin to the chest and knees to the abdomen, to maximize the space between the vertebrae and allow easier access to the lumbar region. This position helps to stabilize the infant and reduce movement during the procedure.
Choice D: Place the infant in an infant seat for 2 hr following the procedure.
Post-procedure care for a lumbar puncture typically involves monitoring the infant for any signs of complications, such as headache or infection. Placing the infant in an infant seat for 2 hours is not a standard recommendation. Instead, the infant should be observed and allowed to rest comfortably.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The correct answer is: A. Tugging on the affected ear lobe.
Choice A reason:
Tugging on the affected ear lobe is a common sign of discomfort in children with otitis media. This behavior indicates that the child is experiencing pain or pressure in the ear, which is a typical symptom of this condition. Children often cannot verbalize their discomfort, so they may tug or pull at their ears to express their pain.
Choice B reason:
Erythema and edema of the affected ear are more indicative of otitis externa (swimmer's ear) rather than otitis media. Otitis media involves inflammation and infection of the middle ear, which is not typically visible externally. The primary signs of otitis media are observed through otoscopic examination, showing a bulging or erythematous tympanic membrane.
Choice C reason:
Pain when manipulating the affected ear lobe is also more characteristic of otitis externa. In otitis media, the pain is usually deeper within the ear and not exacerbated by touching the outer ear. The pain in otitis media is due to the pressure and inflammation in the middle ear space.
Choice D reason:
Clear drainage from the affected ear is not typical of otitis media. If there is drainage, it is usually purulent (pus-like) and indicates a ruptured eardrum due to the infection. Clear drainage is more commonly associated with conditions like otitis externa or a perforated eardrum without infection.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
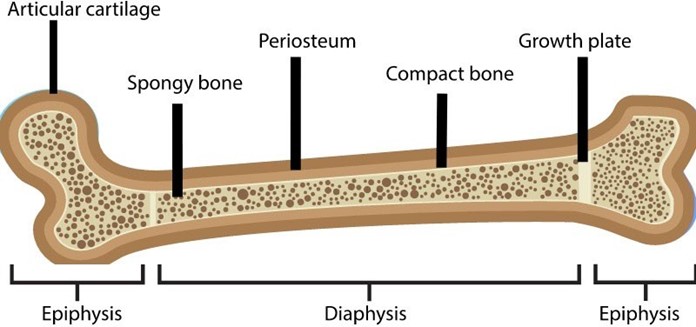
Choice A: This statement is correct, as a fracture of an epiphyseal plate, which is a cartilage layer at the end of a long bone where growth occurs, can impair the normal growth and development of the bone. Depending on the type and severity of the fracture, the epiphyseal plate may close prematurely, stop growing, or grow unevenly, resulting in deformity, shortening, or angular deviation of the affected limb.
Choice B: This statement is incorrect, as a fracture of an epiphyseal plate does not necessarily disrupt the blood supply to the bone unless there is also damage to the periosteum, which is a membrane that covers and nourishes
the bone. A disruption of the blood supply to the bone can cause avascular necrosis, which is a condition that causes bone death due to lack of oxygen and nutrients.
Choice C: This statement is incorrect, as a fracture of an epiphyseal plate does not cause bone marrow loss through the fracture unless there is damage to the medullary cavity, which is a hollow space within the bone that contains bone marrow. Bone marrow loss through the fracture can cause bleeding, infection, or anemia.
Choice D: This statement is incorrect, as a fracture of an epiphyseal plate does not take longer to heal in younger children than in older children. In fact, younger children tend to heal faster than older children due to their higher metabolic rate, greater blood supply, and more active growth factors. The healing time of a fracture depends on various factors, such as the type and location of the fracture, the treatment method, and the presence of complications.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
