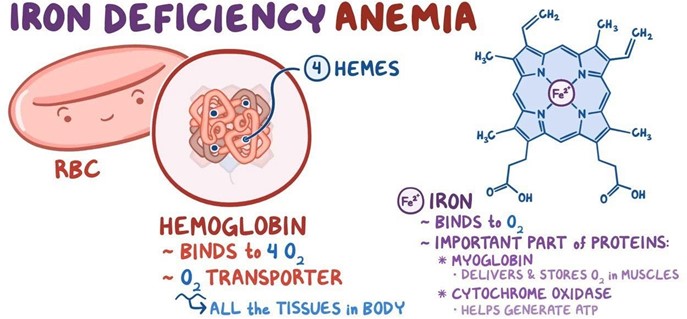
A nurse in a pediatric clinic is caring for a child who has iron deficiency anemia and a new prescription for ferrous sulfate tablets. Which of the following instructions should the nurse provide the parents regarding the administration of this medication?
Iron (Ferrous Sulfate) may turn stools tarry green.
Administer at bedtime.
Give with a 240 mL (8 oz) glass of milk.
Administer at mealtimes.
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A: This instruction is correct, as iron supplements can cause a change in the color and consistency of stools, making them dark, green, or black. This is not a sign of bleeding or infection, but a normal side effect of iron therapy. The parents should be informed of this possibility and reassured that it is harmless.
Choice B: This instruction is incorrect, as iron supplements should not be administered at bedtime, but rather one hour before or two hours after meals. This is because iron absorption is reduced by food, especially dairy products, antacids, or calcium supplements. The parents should be instructed to give the medication on an empty stomach or with a small amount of food if it causes nausea.
Choice C: This instruction is incorrect, as iron supplements should not be given with milk, as milk contains calcium, which can interfere with iron absorption and reduce its effectiveness. The parents should be instructed to avoid giving milk or other dairy products within two hours of the medication.
Choice D: This instruction is incorrect, as iron supplements should not be administered at mealtimes, but rather one hour before or two hours after meals. This is because iron absorption is reduced by food, especially dairy products, antacids, or calcium supplements. The parents should be instructed to give the medication on an empty stomach or with a small amount of food if it causes nausea.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A reason: This choice is incorrect because taking glyburide with breakfast is not recommended for an adolescent who has type 1 diabetes mellitus. Glyburide is an oral hypoglycemic medication that lowers blood glucose levels by stimulating insulin secretion from the pancreas. It may be used for clients who have type 2 diabetes mellitus, but it does not work for clients who have type 1 diabetes mellitus or DKA.
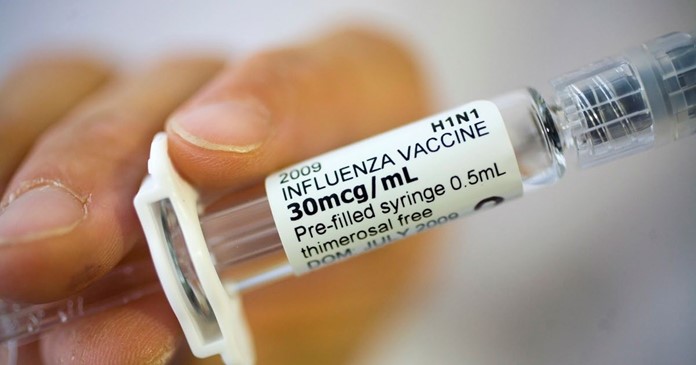
Choice B reason: This choice is correct because obtaining an influenza vaccine annually is recommended for an adolescent who has type 1 diabetes mellitus. The influenza vaccine is a vaccine that protects against influenza, a viral infection that affects the respiratory system. It may prevent or reduce the severity of influenza and its complications, such as pneumonia or sepsis. It is recommended for everyone who is 6 months or older, especially those who have chronic conditions such as diabetes mellitus that increase their risk of influenza-related complications.
Choice C reason: This choice is incorrect because administering glucagon for hyperglycemia is not indicated for an adolescent who has type 1 diabetes mellitus. Glucagon is a hormone that raises blood glucose levels by stimulating glycogen breakdown in the liver. It may be used for clients who have hypoglycemia, which is a condition in which blood glucose levels are lower than normal (less than 70 mg/dL). It may cause symptoms such as sweating, trembling, confusion, or loss of consciousness. However, in type 1 diabetes mellitus, hyperglycemia (high blood glucose levels) rather than hypoglycemia is more likely to occur due to insulin deficiency or resistance.
Choice D reason: This choice is incorrect because injecting insulin in the deltoid muscle is not an optimal method for an adolescent who has type 1 diabetes mellitus. Insulin is a hormone that lowers blood glucose levels by facilitating glucose uptake into the cells. It may be administered by injection or infusion, and it may vary in onset, peak, and duration of action. The preferred sites for insulin injection are the abdomen, the thighs, the buttocks, or the upper arms, as they have more subcutaneous fat and less muscle tissue. Injecting insulin into the deltoid muscle may cause faster absorption and shorter duration of action, which can affect blood glucose control and increase the risk of hypoglycemia.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A reason: This choice is incorrect because bradycardia is not a common finding in a child who is in a sickle cell crisis. Bradycardia is a condition in which the heart rate is slower than normal (less than 60 beats per minute). It may be caused by various factors such as hypothermia, hypothyroidism, or medication side effects, but it does not indicate a sickle cell crisis.
Choice B reason: This choice is incorrect because constipation is not a common finding in a child who is in a sickle cell crisis. Constipation is a condition in which the bowel movements are infrequent, hard, or difficult to pass. It may be caused by various factors such as dehydration, a low-fiber diet, or lack of physical activity, but it does not indicate a sickle cell crisis.
Choice C reason: This choice is correct because pain is a common finding in a child who is in a sickle cell crisis. Sickle cell crisis is a condition in which the red blood cells become sickle-shaped and clump together, blocking the blood flow and oxygen delivery to the organs and tissues. It may cause severe pain in the chest, abdomen, joints, or bones, as well as symptoms such as pallor, jaundice, fatigue, or shortness of breath.
Choice D reason: This choice is incorrect because high fever is not a specific finding in a child who is in a sickle cell crisis. High fever may indicate infection, inflammation, or dehydration, but it does not indicate sickle cell crisis. However, the infection can trigger or worsen the sickle cell crisis, so it should be treated promptly with antibiotics and fluids.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
