A nurse is caring for a 6-month-old infant who is postoperative following a myringotomy. Which of the following pain scales should the nurse use to determine the infant's pain level?
Oucher
FLACC
FACES
Visual Analog Scale
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A: The Oucher pain scale is not suitable for a 6-month-old infant, as it is designed for children aged 3 to 13 years who can point to pictures of faces that match their pain level. A 6-month-old infant cannot communicate verbally or point to pictures.
Choice B: The FLACC pain scale is suitable for a 6-month-old infant, as it is designed for infants and children aged 2 months to 7 years who cannot verbalize their pain. The FLACC pain scale assesses five behavioral indicators of pain: face, legs, activity, cry, and consolability. Each indicator is scored from 0 to 2 based on the observation of the nurse. The total score ranges from 0 to 10, with higher scores indicating more pain.
Choice C: The FACES pain scale is not suitable for a 6-month-old infant, as it is designed for children aged 3 years and older who can select a face that matches their pain level. A 6-month-old infant cannot communicate verbally or select a face.
Choice D: The Visual Analog Scale (VAS) is not suitable for a 6-month-old infant, as it is designed for adults and older children who can mark a point on a line that represents their pain level. A 6-month-old infant cannot communicate verbally or mark a point on a line.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason: This choice is incorrect because the radial artery is not an ideal site to assess the heart rate in an infant. The radial artery is located on the thumb side of the wrist, and it can be palpated by placing two fingers over it. It may be used for adults or older children who have a strong pulse, but it may be difficult to locate or feel in an infant who has a small or weak pulse.
Choice B reason: This choice is incorrect because the carotid artery is not an ideal site to assess the heart rate in an infant. The carotid artery is located on either side of the neck, and it can be palpated by placing two fingers over it. It may be used for adults or older children who have a cardiac arrest or shock, but it may be risky to use in an infant who has a fragile neck or airway.
Choice C reason: This choice is incorrect because the brachial artery is not an ideal site to assess the heart rate in an infant. The brachial artery is located on the inner side of the upper arm, and it can be palpated by placing two fingers over it. It may be used for infants or young children who have a blood pressure measurement, but it may be uncomfortable or inaccurate to use for a heart rate assessment.
Choice D reason: This choice is correct because the apex of the heart is an ideal site to assess the heart rate in an infant. The apex of the heart is located at the fifth intercostal space on the left midclavicular line, and it can be auscultated by placing a stethoscope over it. It may be used for infants or young children who have a regular and strong heartbeat, and it may provide the most accurate measurement of the heart rate.
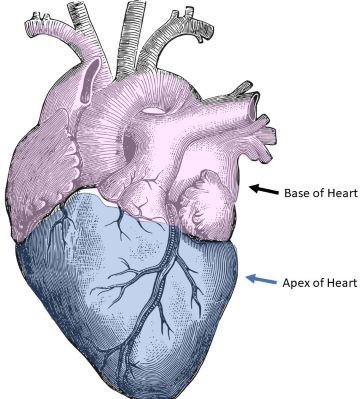
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A: Placing the child on a no-salt-added diet is an important intervention for acute glomerulonephritis, as salt can increase fluid retention and blood pressure. However, this is not the priority action, as it does not address the immediate problem of fluid overload.
Choice B: Maintaining a saline lock is a useful measure for acute glomerulonephritis, as it allows for easy access to administer fluids or medications if needed. However, this is not the priority action, as it does not monitor the fluid status of the child.
Choice C: Educating the parents about potential complications is an essential part of nursing care for acute glomerulonephritis, as it can help them recognize signs of worsening conditions and seek timely medical attention. However, this is not the priority action, as it does not assess the current condition of the child.
Choice D: Checking the child's daily weight is the priority action for acute glomerulonephritis, as it is the most accurate indicator of fluid balance and kidney function. A sudden increase in weight can indicate fluid retention and edema, which can lead to heart failure or pulmonary edema. A decrease in weight can indicate dehydration or diuresis, which can lead to hypovolemia or electrolyte imbalance.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
