A nurse is caring for a toddler who has acute laryngotracheobronchitis and has been placed in a cool mist tent. Which of the following findings indicates that the treatment has been effective?
Barking cough
Decreased stridor
Improved hydration
Decreased temperature
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A: A barking cough is not a finding that indicates that the treatment has been effective, but rather a symptom of acute laryngotracheobronchitis, which is also known as croup. Croup is a condition that causes inflammation and narrowing of the upper airway and produces a characteristic barking or seal-like cough. A barking cough may persist for several days after the onset of croup and does not reflect the severity of the airway obstruction.
Choice B: Decreased stridor is a finding that indicates that the treatment has been effective, as stridor is a sign of airway obstruction caused by acute laryngotracheobronchitis. Stridor is a high-pitched, noisy breathing sound that occurs when the air passes through the narrowed airway. Stridor may be inspiratory, expiratory, or biphasic,
depending on the level of obstruction. Decreased stridor means that the airway is less obstructed and the child can breathe more easily.
Choice C: Improved hydration is not a finding that indicates that the treatment has been effective, but rather a goal of treatment for acute laryngotracheobronchitis. Dehydration can worsen the symptoms and complications of croup by thickening the mucus and increasing the risk of infection. Improved hydration can help thin out the mucus and prevent dehydration. Hydration can be improved by encouraging oral fluids, administering intravenous fluids, or providing humidified air.
Choice D: Decreased temperature is not a finding that indicates that the treatment has been effective, but rather a possible outcome of treatment for acute laryngotracheobronchitis. Fever may or may not be present in croup, depending on the cause and severity of the condition. Fever can be caused by viral or bacterial infection, inflammation, or dehydration. Decreased temperature can indicate that the infection or inflammation is resolving or that the dehydration is corrected.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A: Using a pain-rating tool to determine the severity of the joint pain is not the priority assessment for an 8-year-old child who has acute rheumatic fever, which is an inflammatory condition that can affect various organs, especially the heart, joints, skin, and brain. Joint pain is one of the major criteria for diagnosing acute rheumatic fever and can affect one or more large joints, such as knees, ankles, elbows, or wrists. Joint pain can be managed with analgesics or anti-inflammatory drugs.
Choice B: Assessing the client's erythematous rash is not the priority assessment for an 8-year-old child who has acute rheumatic fever, which is an inflammatory condition that can affect various organs, especially the heart, joints, skin, and brain. The erythematous rash is one of the minor criteria for diagnosing acute rheumatic fever and can appear as pink or red patches on the trunk or limbs. The erythematous rash can fade or change location over time and does not require any specific treatment.
Choice C: Identifying the degree of parental anxiety related to the diagnosis is not the priority assessment for an 8-year-old child who has acute rheumatic fever, which is an inflammatory condition that can affect various organs, especially the heart, joints, skin, and brain. Parental anxiety related to the diagnosis can affect their coping skills and ability to care for their child. Parental anxiety can be addressed by providing education, support, and referral to appropriate resources.
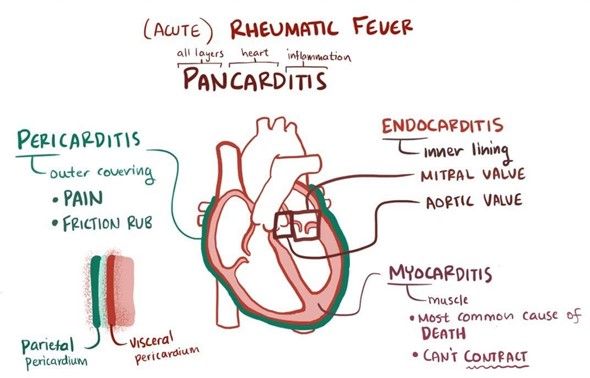
Choice D: Auscultating the rate and regularity of the child's heart sounds and notifying the provider immediately of abnormalities is the priority assessment for an 8-year-old child who has acute rheumatic fever, as it can indicate cardiac involvement, which is the most serious complication of acute rheumatic fever. Cardiac involvement can cause damage to the heart valves, myocardium, or pericardium and lead to heart failure or death. Abnormalities in heart sounds may include murmurs, rubs, gallops, or arrhythmias.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A reason: This choice is correct because a child who has nephrotic syndrome is the most appropriate roommate for a child who has leukemia. Nephrotic syndrome is a kidney disorder that causes proteinuria, edema, hypoalbuminemia, and hyperlipidemia. It does not pose any risk of infection or injury to the child who has leukemia, and it does not require any isolation or special precautions. Therefore, placing these two children in the same room can help to conserve resources and promote socialization.
Choice B reason: This choice is incorrect because a child recovering from a ruptured appendix is not an appropriate roommate for a child who has leukemia. A ruptured appendix is a medical emergency that occurs when the appendix becomes inflamed and bursts, releasing bacteria and pus into the abdominal cavity. It may cause peritonitis, sepsis, or abscess formation, and it requires surgery and antibiotics. It may pose a risk of infection to a child who has leukemia, who has a weakened immune system due to chemotherapy or bone marrow suppression. Therefore, placing these two children in the same room can increase the chance of cross-contamination and complications.
Choice C reason: This choice is incorrect because a child who has rheumatic fever is not an appropriate roommate for a child who has leukemia. Rheumatic fever is an inflammatory disease that occurs as a complication of streptococcal infection, such as strep throat or scarlet fever. It may affect the heart, joints, skin, or nervous system, and it requires anti-inflammatory and antibiotic medications. It may pose a risk of infection to the child who has leukemia, who has a compromised immune system due to cancer or treatment. Therefore, placing these two children in the same room can increase the likelihood of transmission and infection.
Choice D reason: This choice is incorrect because a child who has cystic fibrosis is not an appropriate roommate for a child who has leukemia. Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disorder that affects the mucus glands of the lungs, pancreas, liver, intestines, and reproductive organs. It causes thick and sticky mucus to build up in the organs, leading to chronic lung infections, pancreatic insufficiency, malnutrition, and infertility. It requires respiratory therapy, enzyme supplements, nutritional support, and antibiotics. It may pose a risk of infection to the child who has leukemia, who has a reduced ability to fight germs due to malignancy or therapy. Therefore, placing these two children in the same room can increase the possibility of exposure and infection.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
