A parent calls a clinic and reports to a nurse that his 2-month-old infant is hungry more than usual but is projectile vomiting immediately after eating. Which of the following responses should the nurse make?
"Bring your baby into the clinic today."
"Give your infant an oral rehydration solution."
"Burp your baby more frequently during feedings."
"Try switching to a different formula."
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A: This response is appropriate, as it indicates urgency and concern for the infant's condition. Projectile vomiting immediately after eating can be a sign of pyloric stenosis, which is a condition that causes the narrowing of the pylorus, which is the opening between the stomach and the small intestine. Pyloric stenosis can prevent food from passing through and cause dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, or weight loss. The infant needs to be evaluated by a provider as soon as possible and may need surgery to correct the problem.
Choice B: This response is not appropriate, as it does not address the underlying cause of the infant's condition. Oral rehydration solution can help replace fluids and electrolytes lost through vomiting, but it does not treat pyloric stenosis or prevent further vomiting. Oral rehydration solution may also be vomited out by the infant if given too soon or too much.
Choice C: This response is not appropriate, as it does not address the underlying cause of the infant's condition. Burping the baby more frequently during feedings can help release air bubbles and prevent gas or colic, but it does not treat pyloric stenosis or prevent further vomiting. Burping may also trigger vomiting by increasing pressure on the stomach.
Choice D: This response is not appropriate, as it does not address the underlying cause of the infant's condition. Switching to a different formula can help if the infant has an allergy or intolerance to certain ingredients in their current formula, but it does not treat pyloric stenosis or prevent further vomiting. Switching formulas may also cause diarrhea or constipation by changing the infant's bowel flora.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A: Torticollis is not a disorder that causes lateral curvature of the spine, but rather a condition that causes tilting or twisting of the neck due to contraction or spasm of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Torticollis can cause pain, stiffness, or limited range of motion in the neck. Torticollis can be congenital or acquired due to injury, infection, or posture.
Choice B: Lordosis is not a disorder that causes lateral curvature of the spine, but rather a condition that causes excessive inward curvature of the lower spine. Lordosis can cause back pain, stiffness, or difficulty in movement. Lordosis can be congenital or acquired due to obesity, pregnancy, osteoporosis, or spondylolisthesis.
Choice C: Kyphosis is not a disorder that causes lateral curvature of the spine, but rather a condition that causes excessive outward curvature of the upper spine. Kyphosis can cause a hunchback appearance, back pain, stiffness, or breathing problems. Kyphosis can be congenital or acquired due to aging, osteoporosis, arthritis, or spinal injury.
Choice D: Scoliosis is a disorder that causes lateral curvature of the spine in one or more places. Scoliosis can cause uneven shoulders or hips, back pain, fatigue, or breathing problems. Scoliosis can be congenital or idiopathic (unknown cause). Scoliosis can be diagnosed by physical examination and X-ray and treated by braces or surgery depending on the severity and progression of the curve.
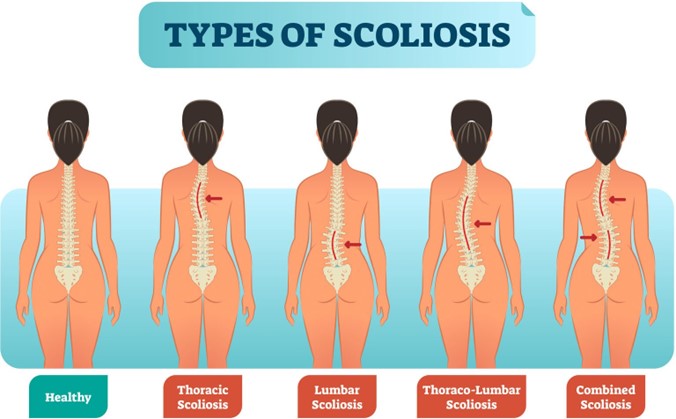
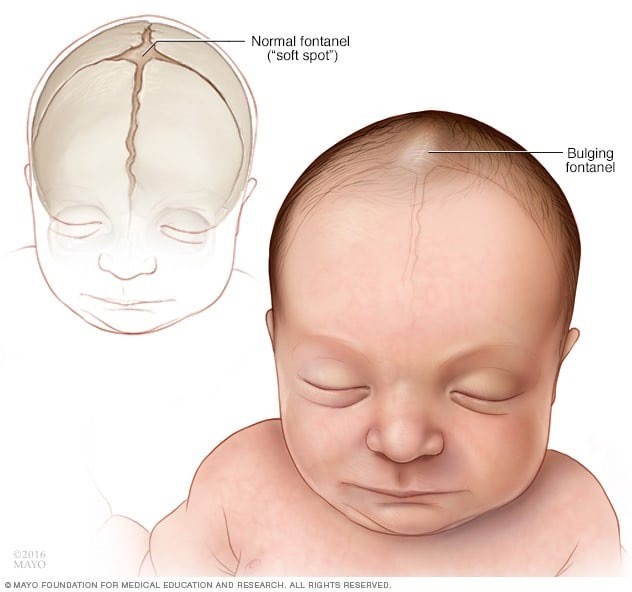
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A: Oliguria is a condition of reduced urine output, which can indicate dehydration, kidney failure, or urinary tract obstruction. It is not associated with a CNS infection, which affects the brain and spinal cord.
Choice B: A negative Brudzinski sign is a normal finding that indicates no meningeal irritation. It is elicited by flexing the neck of a supine patient and observing no involuntary flexion of the hips and knees. A positive Brudzinski sign, on the other hand, is a sign of meningitis, which is a type of CNS infection.
Choice C: A bulging fontanel is an abnormal finding that indicates increased intracranial pressure, which can be caused by a CNS infection, such as meningitis or encephalitis. A fontanel is a soft spot on the skull of an infant that allows for brain growth and development.
Choice D: Jaundice is a condition of yellowing of the skin and eyes, which can indicate liver disease, hemolytic anemia, or neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. It is not associated with a CNS infection, which affects the brain and spinal cord.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
