A nurse in an emergency department is caring for an infant who has a 2-day history of vomiting and an elevated temperature. Which of the following should the nurse recognize as the most reliable indicator of fluid loss?
Skin integrity
Respiratory rate
Body weight
Blood pressure
The Correct Answer is C
In an infant with a history of vomiting and fever, body weight is the most reliable indicator of fluid loss. Monitoring the infant's weight over time can help assess the degree of dehydration and guide the appropriate fluid replacement therapy. A significant decrease in body weight suggests significant fluid loss.
Option A: Skin integrity is important to assess for signs of dehydration, but it is not as reliable as body weight in determining the extent of fluid loss.
Option B: Respiratory rate can be affected by various factors and is not a direct indicator of fluid loss.
Option D: Blood pressure is not the most reliable indicator of fluid loss in an infant with dehydration. In severe cases of dehydration, blood pressure can drop, but it is not as sensitive as body weight in assessing the extent of fluid loss.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Severe anemia is a condition characterized by a significant decrease in the number of red blood cells or hemoglobin in the blood, leading to reduced oxygen-carrying capacity. This can result in fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath in the affected individual.
A red blood cell transfusion is given to a child with severe anemia to increase the number of red blood cells and, consequently, the hemoglobin level in the blood. This helps improve oxygen delivery to tissues and organs, which can lead to increased energy levels and reduced fatigue.
Option A is incorrect because red blood cell transfusion is not given to help the body stop bleeding by forming a clot. Platelets are responsible for clot formation, not red blood cells.
Option B is incorrect because a red blood cell transfusion is not used to fight infections. White blood cells and the immune system are responsible for fighting infections.
Option D is incorrect because a red blood cell transfusion is not given to allow her parents to come to visit her. Transfusions are medical treatments to address specific medical conditions and are not related to visitation rights.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
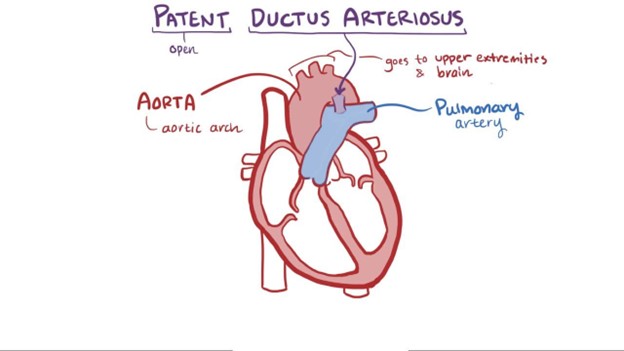
A patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a congenital heart defect associated with increased pulmonary blood flow. In normal fetal circulation, the ductus arteriosus allows blood to bypass the lungs since the baby receives oxygen from the mother's placenta. After birth, the ductus arteriosus should close, redirecting blood flow to the lungs for oxygenation. However, in some infants with PDA, the ductus arteriosus remains open, causing an abnormal connection between the aorta and the pulmonary artery. As a result, oxygenated blood from the aorta flows back into the pulmonary artery, increasing the workload on the lungs.
The other options are as follows:
A. Coarctation of the aorta - Coarctation of the aorta is a narrowing of the aorta, which obstructs blood flow and leads to increased blood pressure in the upper body and reduced blood flow to the lower body.
C. Tetralogy of Fallot - Tetralogy of Fallot is a combination of four heart defects that results in decreased pulmonary blood flow due to a ventricular septal defect (VSD), overriding aorta, pulmonary stenosis, and right ventricular hypertrophy.
D. Tricuspid atresia - Tricuspid atresia is a congenital heart defect where the tricuspid valve does not develop correctly, resulting in an absent or abnormal tricuspid valve. This defect prevents blood flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle and, therefore, reduces pulmonary blood flow.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
