A nurse is providing teaching to the parent of an infant who has gastroesophageal reflux. Which of the following statements by the parent indicates an understanding of the teaching?
"I will keep my baby in an upright position after feedings
"My baby's formula can be thickened with oatmeal.
"I should position my baby side-lying during sleep.
"I will have to feed my baby formula rather than breast milk."
The Correct Answer is A
A. "I will keep my baby in an upright position after feedings."
Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) is a condition where the stomach contents flow back into the esophagus, which can cause spitting up or regurgitation in infants. Keeping the baby in an upright position after feedings can help reduce the likelihood of reflux episodes. By holding the baby in an upright position for about 30 minutes after feeding, gravity can aid in keeping the stomach contents from flowing back into the esophagus.
The other statements are incorrect or do not address the management of gastroesophageal reflux:
B. "My baby's formula can be thickened with oatmeal." - Thickening formula with oatmeal is not a standard recommendation for managing GER in infants. In some cases, thickening formulas may be recommended, but it should be done under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
C. "I should position my baby side-lying during sleep." A side-lying position is not recommended for sleep in infants, as it increases the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). The safe sleep position for infants is on their back.
D. "I will have to feed my baby formula rather than breast milk." - The type of feeding (formula or breast milk) does not directly impact the occurrence of gastroesophageal reflux. Both breast milk and formula can cause reflux in some infants. It is essential to discuss feeding options with a healthcare provider to determine the best approach for the individual infant's needs.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
During a sickle cell crisis, the child experiences severe pain due to the sickled red blood cells blocking blood flow in the vessels, leading to tissue ischemia and infarction. Pain is the hallmark symptom of sickle cell crisis and can occur in various parts of the body, such as the abdomen, chest, back, joints, and extremities.
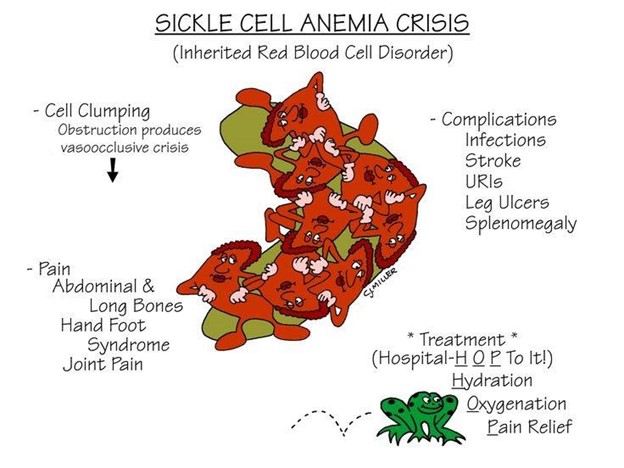
A. Constipation is not a common symptom of sickle cell crisis. It may be associated with other conditions but is not directly related to sickle cell crisis.
C. High fever is not a typical finding in sickle cell crisis. Fever may occur due to infections, which individuals with sickle cell disease are at increased risk of developing, but it is not a direct symptom of the crisis itself.
D. Bradycardia (slow heart rate) is not commonly associated with sickle cell crisis. Tachycardia (rapid heart rate) may occur in response to pain, but bradycardia is not a typical finding.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Correct answer: A
A. Encourage the parents to rock the infant:Rocking provides comfort and soothing for the infant. It helps reduce anxiety and promotes relaxation during the immediate postoperative period
B. Administer ibuprofen as needed for pain:Administering ibuprofen as needed for pain is not typically recommended for infants under 6 months of age without specific instructions from the healthcare provider. Ibuprofen is generally avoided in young infants due to potential risks of adverse effects, especially in the immediate postoperative period
C. Position the infant on her abdomen: After cleft lip repair surgery, it is generally recommended to position the infant on her back to prevent any pressure on the surgical site and to minimize the risk of infection. Placing the infant on her abdomen may interfere with the healing process and increase the risk of complications.
D. Offer the infant a pacifier.
Avoid the use of oral suction or placing objects in the mouth such as a tongue depressor, thermometer, straws, spoons, forks, or pacifiers.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
