The nurse is providing teaching to parents of a child diagnosed with rheumatic fever (RF). Which would be included within the teaching plan?
there should be a management regimen for electrolyte imbalance
The child will recover fully requiring no further treatment in the future
the child will need prophylactic antibiotics for invasive procedures
a diagnosis of RF may have genetic implications for future offspring
The Correct Answer is C
Rheumatic fever (RF) is a complication that can occur after an untreated or inadequately treated streptococcal throat infection (strep throat). It can affect the heart, joints, skin, and brain. One important aspect of managing RF is to prevent further episodes of strep throat, as it can trigger recurrent RF. Therefore, the child with a history of RF will require prophylactic antibiotics (usually penicillin or a related antibiotic) before certain invasive procedures, dental work, or surgeries to prevent strep throat and subsequent recurrence of RF.
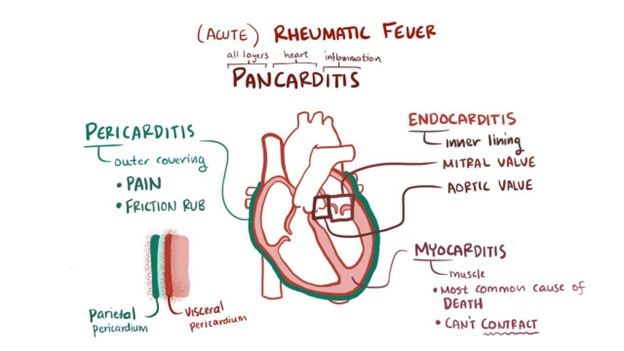
Option A is not specific to rheumatic fever, and while electrolyte imbalances may be monitored and managed in certain cases of severe illness, it is not a core aspect of managing RF.
Option B is not accurate. While many children with RF do recover fully with appropriate treatment, they may be at risk of developing rheumatic heart disease, which can lead to long-term complications if not managed properly.
Option D is not a direct implication of RF. Rheumatic fever is not a genetically inherited condition, but a complication of strep throat caused by a bacterial infection. There is no evidence to suggest that having RF would directly affect the genetic implications for future offspring.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Correct answer: B
A. Increased pain: Increased pain is a common and expected finding after a tonsillectomy. The surgical removal of tonsils creates wounds in the throat, which can cause discomfort and pain during the healing process. However, increased pain alone is not a specific manifestation of hemorrhage. Hemorrhage would be indicated by other signs, such as drooling, frequent swallowing, or vomiting blood.
B. Frequent swallowing: This can indicate that the child is swallowing blood, which is a common sign of bleeding at the surgical site. Children might not always show obvious signs of bleeding in the mouth, so frequent swallowing can be a subtle but critical indicator of hemorrhage.
C. Poor fluid intake: Poor fluid intake is a common concern after a tonsillectomy due to postoperative pain and discomfort in the throat. The child may be reluctant to drink or eat initially because of their sore throat. However, poor fluid intake alone is not an indicative sign of hemorrhage. Hemorrhage would present with other symptoms, such as drooling, frequent swallowing, or vomiting blood.
D. Drooling:While drooling can occur due to discomfort, pain, or difficulty swallowing, it is not as specific or immediate a sign of hemorrhage as frequent swallowing.
Correct Answer is ["260"]
Explanation
To calculate the total fluid intake, we need to convert all the measurements to milliliters (mL) and then add them up:
1 cup = 240 mL
1 oz = 30 mL
Given fluid intake:
Juice: ½ cup = 0.5 * 240 mL = 120 mL
Gelatin: 3 oz = 3 * 30 mL = 90 mL
Ice pop: 1 oz = 1 * 30 mL = 30 mL
Ginger ale: 20 mL
Total fluid intake = 120 mL + 90 mL + 30 mL + 20 mL = 260 mL
So, the nurse should record 260 mL as the child's fluid intake.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
