A nurse in an emergency department is assessing an infant who is dehydrated. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
Irritability
Tetany
slow, bounding pulse
Decreased temperature
The Correct Answer is A
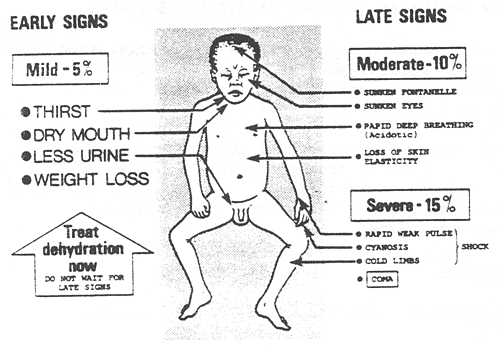
The nurse should expect to find irritability in an infant who is dehydrated. Dehydration in infants can lead to changes in behavior and irritability due to the imbalance in fluid and electrolytes. Other common signs of dehydration in infants may include:
Poor skin turgor (skin tenting)
Sunken fontanelles (soft spots on the baby's head)
Dry mucous membranes (dry mouth and tongue)
Decreased urine output or concentrated urine
Rapid heart rate (tachycardia)
Increased respiratory rate
Sunken eyes
Decreased tears when crying
B. Tetany is a condition characterized by involuntary muscle contractions and is more commonly associated with hypocalcemia (low calcium levels) rather than dehydration.
C. A slow, bounding pulse is not typically associated with dehydration. Dehydration often leads to a rapid heart rate (tachycardia) as the body attempts to compensate for the loss of fluid.
D. Decreased temperature is not a typical finding in dehydration. Dehydration can lead to fever in some cases due to an underlying infection, but it does not cause a decrease in body temperature on its own.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Correct answer: B
A. Increased pain: Increased pain is a common and expected finding after a tonsillectomy. The surgical removal of tonsils creates wounds in the throat, which can cause discomfort and pain during the healing process. However, increased pain alone is not a specific manifestation of hemorrhage. Hemorrhage would be indicated by other signs, such as drooling, frequent swallowing, or vomiting blood.
B. Frequent swallowing: This can indicate that the child is swallowing blood, which is a common sign of bleeding at the surgical site. Children might not always show obvious signs of bleeding in the mouth, so frequent swallowing can be a subtle but critical indicator of hemorrhage.
C. Poor fluid intake: Poor fluid intake is a common concern after a tonsillectomy due to postoperative pain and discomfort in the throat. The child may be reluctant to drink or eat initially because of their sore throat. However, poor fluid intake alone is not an indicative sign of hemorrhage. Hemorrhage would present with other symptoms, such as drooling, frequent swallowing, or vomiting blood.
D. Drooling:While drooling can occur due to discomfort, pain, or difficulty swallowing, it is not as specific or immediate a sign of hemorrhage as frequent swallowing.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
When caring for a child with acute appendicitis, the nurse should anticipate an elevated white blood cell count (WBC) in the laboratory values. A high WBC count is a common finding in acute appendicitis, as it indicates an inflammatory response and infection in the body. The body's immune system responds to the inflammation caused by the infected appendix, leading to an increase in WBCs to fight off the infection.
The other options are not necessarily specific to acute appendicitis:
A. RBC 4.2 million/mm³: The red blood cell count (RBC) measures the number of red blood cells in the bloodstream. This value may be within the normal range, but it is not the primary marker for diagnosing or monitoring acute appendicitis.
B. Lymphocytes 3,000/mm3: Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell involved in the body's immune response. While changes in lymphocyte levels can occur during inflammation, it is not the primary marker for diagnosing or monitoring acute appendicitis.
C. Neutrophils 3.000/mm³: Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell that increases in response to infection and inflammation. However, the absolute neutrophil count is not as relevant as the overall WBC count in determining the presence and severity of acute appendicitis.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
