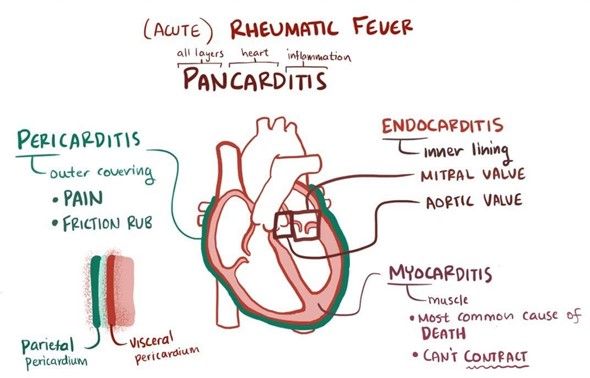
A nurse is caring for an 8-year-old child who has acute rheumatic fever. Which of the following assessments is the nurse's priority immediately after admission?
Using a pain-rating tool to determine the severity of the joint pain
Assessing the client's erythematous rash
Identifying the degree of parental anxiety related to the diagnosis
Auscultating the rate and regularity of the child's heart sounds and notifying the provider immediately of abnormalities
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A: Using a pain-rating tool to determine the severity of the joint pain is not the priority assessment for an 8-year-old child who has acute rheumatic fever, which is an inflammatory condition that can affect various organs, especially the heart, joints, skin, and brain. Joint pain is one of the major criteria for diagnosing acute rheumatic fever and can affect one or more large joints, such as knees, ankles, elbows, or wrists. Joint pain can be managed with analgesics or anti-inflammatory drugs.
Choice B: Assessing the client's erythematous rash is not the priority assessment for an 8-year-old child who has acute rheumatic fever, which is an inflammatory condition that can affect various organs, especially the heart, joints, skin, and brain. The erythematous rash is one of the minor criteria for diagnosing acute rheumatic fever and can appear as pink or red patches on the trunk or limbs. The erythematous rash can fade or change location over time and does not require any specific treatment.
Choice C: Identifying the degree of parental anxiety related to the diagnosis is not the priority assessment for an 8-year-old child who has acute rheumatic fever, which is an inflammatory condition that can affect various organs, especially the heart, joints, skin, and brain. Parental anxiety related to the diagnosis can affect their coping skills and ability to care for their child. Parental anxiety can be addressed by providing education, support, and referral to appropriate resources.
Choice D: Auscultating the rate and regularity of the child's heart sounds and notifying the provider immediately of abnormalities is the priority assessment for an 8-year-old child who has acute rheumatic fever, as it can indicate cardiac involvement, which is the most serious complication of acute rheumatic fever. Cardiac involvement can cause damage to the heart valves, myocardium, or pericardium and lead to heart failure or death. Abnormalities in heart sounds may include murmurs, rubs, gallops, or arrhythmias.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason: This choice is incorrect because a regular diet, no added salt may not be sufficient to prevent fluid retention and hypertension in a child who has acute glomerulonephritis. Acute glomerulonephritis is an inflammation of the glomeruli, which are the tiny blood vessels that filter blood in the kidneys. It may cause symptoms such as hematuria, proteinuria, oliguria, edema, or hypertension. Therefore, avoiding salt alone may not reduce sodium and water intake and excretion.
Choice B reason: This choice is incorrect because a low-protein, low-potassium diet may not be necessary for a child who has acute glomerulonephritis. A low-protein, low-potassium diet may be indicated for a child who has chronic kidney disease or end-stage renal disease, which can cause uremia, hyperkalemia, or metabolic acidosis. However, in acute glomerulonephritis, the kidney function usually recovers within weeks or months, and the protein and potassium levels are not significantly affected.
Choice C reason: This choice is incorrect because a low-carbohydrate, low-protein diet may not be appropriate for a child who has acute glomerulonephritis. A low-carbohydrate, low-protein diet may be used for a child who has diabetes mellitus or ketosis-prone epilepsy, which can cause hyperglycemia or ketone production. However, in acute glomerulonephritis, carbohydrate metabolism is not impaired, and the protein intake should be adequate to prevent malnutrition and promote healing.
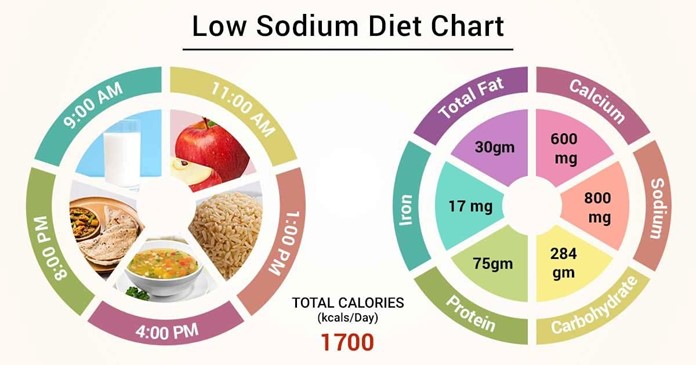
Choice D reason: This choice is correct because a low-sodium, fluid-restricted diet is an appropriate diet for a child who has acute glomerulonephritis. A low-sodium, fluid-restricted diet helps to reduce the fluid retention and hypertension by limiting the sodium and water intake and excretion. The sodium intake should be less than 2 g per day, and the fluid intake should be equal to the urine output plus 500 mL per day.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A reason: This choice is incorrect because mumps is not the common name for pertussis. Mumps is a viral infection that causes inflammation of the salivary glands, especially the parotid glands. It may cause symptoms such as fever, headache, and swelling of the cheeks or jaw. It can be prevented by vaccination with the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine.
Choice B reason: This choice is correct because whooping cough is the common name for pertussis. Pertussis is a bacterial infection that causes severe coughing spells, which may be followed by a high-pitched whoop sound or vomiting. It may cause complications such as pneumonia, seizures, or brain damage, especially in infants and young children. It can be prevented by vaccination with the diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis (DTaP) vaccine.
Choice C reason: This choice is incorrect because the fifth disease is not the common name for pertussis. The fifth disease is a viral infection that causes a rash on the face, trunk, and limbs, which may resemble a slapped cheek appearance. It may cause mild symptoms such as fever, runny nose, or joint pain. It usually affects children and is self-limiting.
Choice D reason: This choice is incorrect because chickenpox is not the common name for pertussis. Chickenpox is a viral infection that causes an itchy rash with fluid-filled blisters all over the body. It may cause symptoms such as fever, headache, or loss of appetite. It can be prevented by vaccination with the varicella-zoster (VZV) vaccine.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
