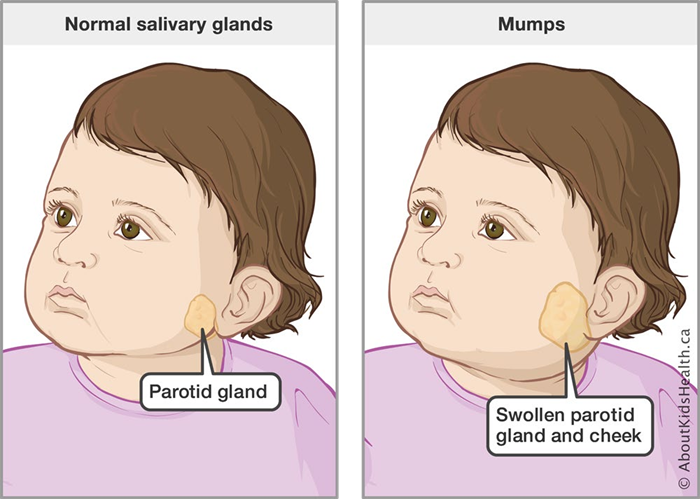
A nurse is planning care for a child who has mumps. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the plan?
Initiate contact precautions.
Initiate standard precautions.
Initiate airborne precautions.
Initiate droplet precautions.
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A: Contact precautions are not necessary for a child who has mumps, as mumps is not transmitted by direct or indirect contact with the infected person or their environment. Contact precautions are used for infections that are spread by contact with skin, wounds, body fluids, or contaminated surfaces.
Choice B: Standard precautions are always used for any patient care, regardless of their diagnosis or infection status. Standard precautions include hand hygiene, use of personal protective equipment (PPE), safe injection practices, and proper disposal of waste and sharps. However, standard precautions alone are not sufficient for a child who has mumps, as mumps are transmitted by respiratory droplets.
Choice C: Airborne precautions are not necessary for a child who has mumps, as mumps are not transmitted by small particles that remain suspended in the air and can be inhaled by others. Airborne precautions are used for infections that are spread by airborne transmission, such as tuberculosis, measles, or chickenpox.
Choice D: Droplet precautions are required for a child who has mumps, as mumps are transmitted by large respiratory droplets that are expelled when the infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. Droplet precautions include wearing a surgical mask when within 3 feet of the patient, placing the patient in a private room or cohorts with other patients with the same infection, and limiting visitors and staff who are susceptible to the infection.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A: Using a pincer grasp indicates a need for further evaluation, as it is a developmental milestone that is usually achieved by 9 to 10 months of age. A pincer grasp is the ability to pick up small objects using the thumb and index finger. A 7-month-old infant should be able to use a raking grasp, which is the ability to scoop up objects using all fingers.
Choice B: Having a fear of strangers does not indicate a need for further evaluation, as it is a normal and expected behavior for a 7-month-old infant. A fear of strangers is a sign of attachment and recognition of familiar and unfamiliar faces. A 7-month-old infant may cry, cling, or turn away from strangers.
Choice C: Showing preferences towards foods does not indicate a need for further evaluation, as it is a normal and expected behavior for a 7-month-old infant. Showing preferences towards foods is a sign of individuality and taste development. A 7-month-old infant may accept or reject certain foods based on their flavor, texture, or appearance.
Choice D: Babbling one-syllable sounds does not indicate a need for further evaluation, as it is a normal and expected behavior for a 7-month-old infant. Babbling one-syllable sounds is a sign of language and communication development. A 7-month-old infant may make sounds such as "ba", "da", "ga", or "ma".
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A: A WBC count of 17,000/mm³ is an abnormal result that the nurse should anticipate when reviewing this client's laboratory values, as it indicates leukocytosis, which is an increase in white blood cells. Leukocytosis can occur in a child who has cystic fibrosis (CF), which is a condition that causes thick mucus to block the airways and lungs and causes respiratory infections and inflammation. A normal WBC count for children is 5,000 to 10,000/mm³.
Choice B: A neutrophil count of 3,000/mm³ is not an abnormal result that the nurse should anticipate when reviewing this client's laboratory values, as it indicates normal neutrophil levels. Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell that fight bacterial infections. A normal neutrophil count for children is 1,500 to 8,000/mm³.
Choice C: A lymphocyte count of 3,000/mm³ is not an abnormal result that the nurse should anticipate when reviewing this client's laboratory values, as it indicates normal lymphocyte levels. Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that fight viral infections. A normal lymphocyte count for children is 1,500 to 4,000/mm³.
Choice D: An RBC count of 4.2 million/mm³ is not an abnormal result that the nurse should anticipate when reviewing this client's laboratory values, as it indicates normal red blood cell levels. Red blood cells carry oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout the body. A normal RBC count for children is 4 to 5.5 million/mm³.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
