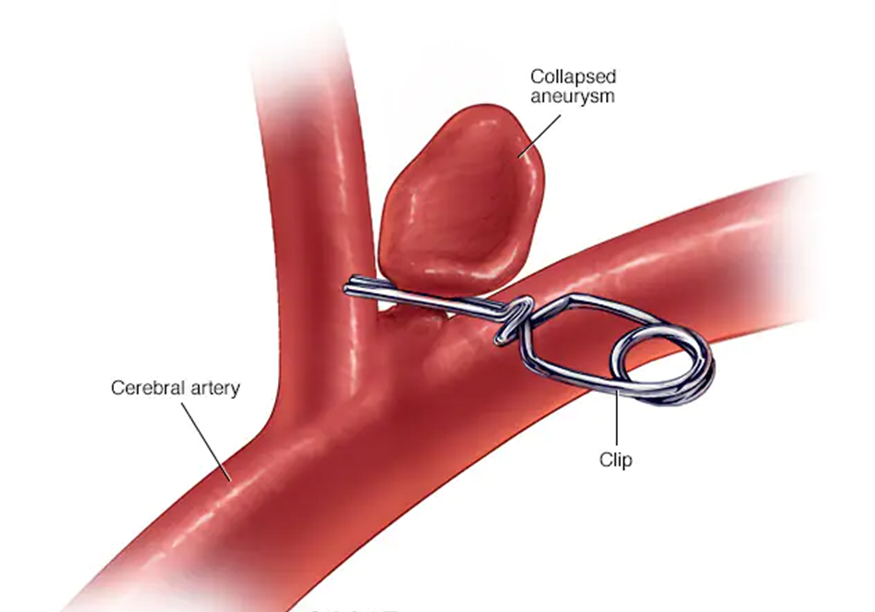
Which of the following is a potential complication of a treated aneurysm?
Improved blood flow to surrounding tissues
Rupture leading to severe internal bleeding
Decreased risk of blood clot formation
Reduced risk of infection
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A Reason:
Improved blood flow to surrounding tissues is generally a desired outcome of treating an aneurysm, not a complication. When an aneurysm is successfully treated, the goal is to restore normal blood flow and prevent the aneurysm from rupturing. Improved blood flow indicates that the treatment was effective and that the risk of complications has been minimized.
Choice B Reason:
Rupture leading to severe internal bleeding is a significant potential complication of a treated aneurysm. Even after treatment, there is a risk that the aneurysm could rupture, especially if the treatment was not entirely successful or if the aneurysm was particularly large or complex. A rupture can lead to life-threatening internal bleeding and requires immediate medical attention. This is why ongoing monitoring and follow-up care are crucial for patients who have had an aneurysm treated.
Choice C Reason:
Decreased risk of blood clot formation is another desired outcome rather than a complication. Treating an aneurysm often involves measures to prevent blood clots, such as using anticoagulant medications. A successful treatment should reduce the risk of clot formation, which can otherwise lead to complications like stroke or embolism.
Choice D Reason:
Reduced risk of infection is also a desired outcome of aneurysm treatment. Infection can be a complication of any surgical procedure, including those used to treat aneurysms. However, with proper surgical techniques and post-operative care, the risk of infection can be minimized. Therefore, a reduced risk of infection is not a complication but rather an indication of successful treatment and good medical practice.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
0.9% sodium chloride is an isotonic crystalloid solution often used for fluid resuscitation. However, it is not the preferred choice for burn patients because it lacks the necessary electrolytes to replace those lost through burn injuries. While it can be used if Lactated Ringer's is unavailable, it does not provide the same balanced electrolyte composition.
Choice B Reason:
Lactated Ringer's is the preferred fluid for initial resuscitation in burn patients. It is an isotonic crystalloid solution that closely mimics the body's plasma, providing essential electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, calcium, and lactate. The lactate in the solution acts as a buffer, helping to correct metabolic acidosis, which is common in burn patients. The Parkland formula, widely used for calculating fluid needs in burn patients, specifically recommends Lactated Ringer's for the first 24 hours.
Choice C Reason:
Dextrose 5% in water is a hypotonic solution that provides free water and calories but lacks electrolytes. It is not suitable for initial fluid resuscitation in burn patients because it does not address the electrolyte imbalances and large fluid shifts that occur after a burn injury. Using this solution could lead to further complications such as hyponatremia.
Choice D Reason:
Dextrose 5% in 0.9% sodium chloride is a hypertonic solution that provides both glucose and electrolytes. However, it is not typically used for initial burn resuscitation because the high glucose content can lead to hyperglycemia, which is detrimental to burn patients. Additionally, the solution's osmolarity can exacerbate fluid shifts and worsen edema.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Allowing the client to control the timing and frequency of the therapy might seem beneficial, but it can lead to inconsistent participation and lack of progress. Structured therapy sessions are essential for rehabilitation, and while some flexibility is important, a completely client-controlled schedule may not provide the necessary consistency.
Choice B Reason:
Limiting visiting hours until the client begins to participate in therapy is not an effective approach. Social support from family and friends is crucial for the emotional well-being of the client and can actually motivate them to engage more in their rehabilitation efforts. Restricting visits could lead to increased feelings of isolation and resistance.
Choice C Reason:
Establishing a plan of care with the client that sets attainable goals is the most effective approach. Involving the client in their care plan fosters a sense of ownership and motivation. Setting realistic and achievable goals helps the client see progress, which can boost their confidence and willingness to participate in therapy.
Choice D Reason:
Informing the client that privileges are related to participation in therapy can be perceived as punitive and may not be effective in motivating the client. It is important to use positive reinforcement and encouragement rather than threats or restrictions to foster cooperation and engagement in the rehabilitation process.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
