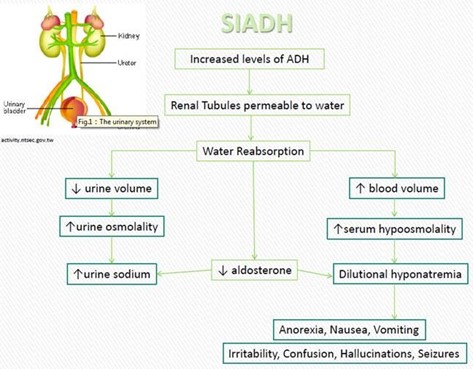
When teaching a patient with chronic SIADH about long-term management of the disorder, the nurse determines that additional instruction is needed when the patient says:
I should weigh myself daily and report any sudden weight loss or gain."
I need to limit my fluid intake to no more than 1 quart of liquids a day,"
I will eat foods high in potassium because the diuretics cause potassium loss.”
I need to shop for foods that are low in sodium and avoid adding salt to foods.
The Correct Answer is C
The correct answer is c. I will eat foods high in potassium because the diuretics cause potassium loss.
Rationale for Choice A:
- Statement: "I should weigh myself daily and report any sudden weight loss or gain."
- Rationale: This statement is correct. It's crucial for patients with SIADH to monitor their weight daily as even slight fluctuations can signal fluid imbalances. Sudden weight gain can indicate fluid retention, while sudden weight loss might suggest dehydration. Both scenarios warrant medical attention.
Rationale for Choice B:
- Statement: "I need to limit my fluid intake to no more than 1 quart of liquids a day."
- Rationale: This statement is also correct. Fluid restriction is a cornerstone of SIADH management. By limiting fluid intake, patients can help prevent the buildup of excess fluid in the body, which can lead to complications such as hyponatremia (low sodium levels in the blood) and edema.
Rationale for Choice C:
- Statement: "I will eat foods high in potassium because the diuretics cause potassium loss."
- Rationale: This statement is incorrect. While some diuretics used in the treatment of SIADH can indeed cause potassium loss, this is not a universal side effect. Furthermore, increasing potassium intake without medical supervision can be dangerous, potentially leading to hyperkalemia (high potassium levels in the blood). It's essential for patients to consult with their healthcare providers for individualized guidance on potassium intake.
Rationale for Choice D:
- Statement: "I need to shop for foods that are low in sodium and avoid adding salt to foods."
- Rationale: This statement is correct. A low-sodium diet is often recommended for patients with SIADH to help manage fluid balance and prevent hyponatremia. Restricting sodium intake can reduce fluid retention and help maintain appropriate sodium levels in the blood.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Electrocardiographic (ECG) changes and dysrhythmias related to hypokalemia are the main reasons for initiating cardiac monitoring in patients with diabetic ketoacidosis. In diabetic ketoacidosis, insulin deficiency causes the body to break down fat for energy, leading to the production of ketones and resulting in metabolic acidosis. In addition, glucose and potassium are lost in the urine due to osmotic diuresis. Hypokalemia can cause ECG changes and dysrhythmias, which can be life-threatening.
Hypokalemia is a common complication of DKA and can lead to ECG changes such as ST-segment depression, T-wave inversion, and U waves².
Hypovolemic shock related to osmotic diuresis is an important consideration in the management of diabetic ketoacidosis, but it is not the primary reason for initiating cardiac monitoring.
Cardiovascular collapse resulting from the effects of hyperglycemia is not a common complication of diabetic ketoacidosis, and it is not the primary reason for initiating cardiac monitoring.
Fluid overload resulting from aggressive fluid replacement is a potential complication of diabetic ketoacidosis, but it is not the primary reason for initiating cardiac monitoring.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
This meal choice is low in sodium as it contains fresh ingredients and does not include processed or pre-packaged foods that are typically high in sodium. Chicken, bread, and carrots are naturally low in sodium, and the client can control the amount of added salt or seasoning. In contrast, the other food choices are likely to be high in sodium due to added salt, cheese, or processed ingredients.
Therefore, the nurse should encourage the client to choose fresh, low-sodium foods and avoid processed or pre-packaged meals.

Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.