What symptom is more common to a duodenal ulcer than a gastric ulcer?
Nighttime pain
Anorexia
Postprandial pain (occurring after a meal)
Nausea and vomiting
The Correct Answer is C
A) Nighttime pain:
Nighttime pain, also known as nocturnal pain, is a symptom associated with both duodenal and gastric ulcers. It occurs when the stomach or duodenal lining is empty and no food is present to buffer the effect of gastric acid. While nighttime pain can occur in both types of ulcers, it is not more specific to duodenal ulcers compared to gastric ulcers.
B) Anorexia:
Anorexia, or loss of appetite, can occur in both duodenal and gastric ulcers due to factors such as pain, discomfort, and inflammation. It is not a symptom that is more commonly associated with one type of ulcer over the other.
C) Postprandial pain (occurring after a meal).
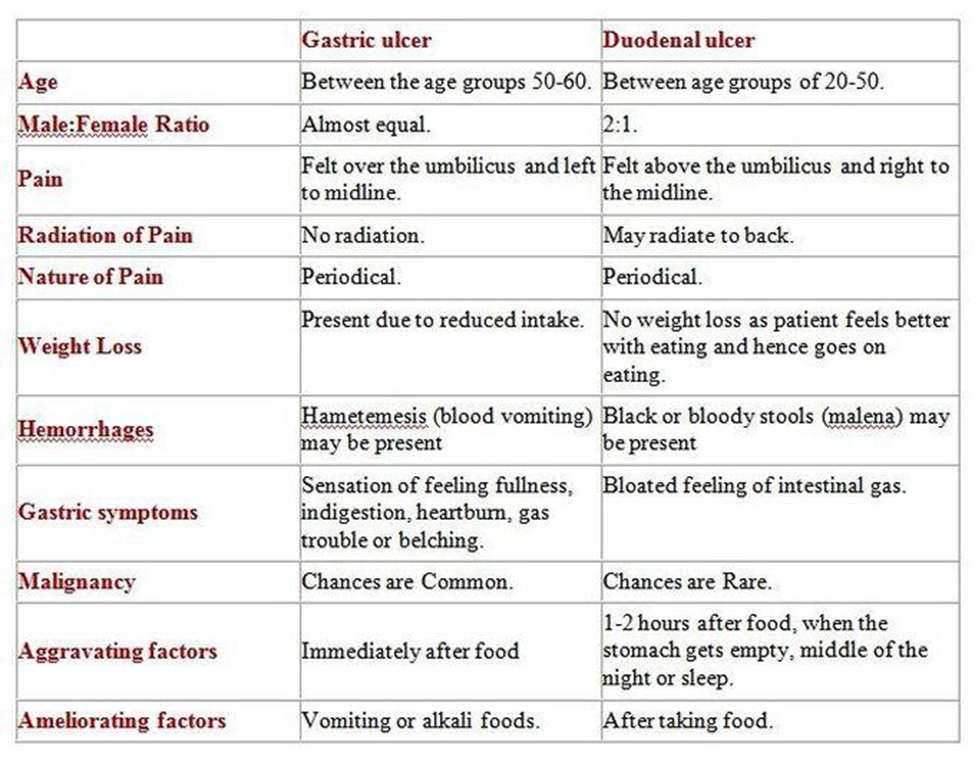
Postprandial pain, which occurs after a meal, is more commonly associated with duodenal ulcers than gastric ulcers. This pain typically occurs 2 to 3 hours after eating, as it is often triggered by the release of gastric acid and duodenal contractions stimulated by food intake. Duodenal ulcers tend to cause this type of pain because they are located in the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine, which is exposed to gastric acid and bile after a meal.
D) Nausea and vomiting:
Nausea and vomiting can occur in both duodenal and gastric ulcers, particularly if the ulcer is accompanied by complications such as obstruction or perforation. These symptoms are not more specific to duodenal ulcers compared to gastric ulcers.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["10"]
Explanation
To administer the correct dose of amoxicillin, the nurse needs to calculate the volume of suspension that contains the prescribed dose of 500 mg.
Since the available suspension has a concentration of 250 mg per 5 ml, the nurse can calculate the required volume using the formula: (prescribed dose/concentration) x volume of concentration = required volume.
Plugging in the numbers: (500 mg / 250 mg) x 5 ml = 2 x 5 ml = 10 ml.
Therefore, the nurse should administer 10 ml of the amoxicillin suspension to deliver a dose of 500 mg.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A) H2-receptor blockers:
H2-receptor blockers, such as ranitidine and famotidine, are commonly used to reduce stomach acid production and treat peptic ulcer disease. They help promote ulcer healing and alleviate symptoms. These medications are generally safe and appropriate for use in clients with peptic ulcer disease.
B) Antacids:
Antacids are medications that neutralize stomach acid and provide symptomatic relief from peptic ulcer disease. While they do not directly treat the underlying cause of the ulcer, they can help alleviate symptoms such as pain and discomfort. Antacids are generally safe for use in clients with peptic ulcer disease.
C) PPIs (Proton Pump Inhibitors):
PPIs, such as omeprazole and pantoprazole, are potent acid-suppressing medications commonly used to treat peptic ulcer disease and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). They are effective at reducing stomach acid production and promoting ulcer healing. PPIs are generally safe and appropriate for use in clients with peptic ulcer disease.
D) NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs).
NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen, can exacerbate peptic ulcer disease by increasing the risk of gastric irritation, erosion, and ulceration. These medications inhibit the production of prostaglandins, which help protect the stomach lining. Chronic or excessive use of NSAIDs can lead to the development of new ulcers or worsening of existing ulcers. Therefore, clients with peptic ulcer disease are typically advised to avoid NSAIDs or to use them with caution under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
