This type of hypersensitivity reaction involves failure of the development of self-tolerance:
delayed hypersensitivity reaction
antibody-mediated reaction
autoimmune reaction
immediate hypersensitivity reaction
The Correct Answer is C
A. Delayed hypersensitivity reaction: This type of hypersensitivity reaction, also known as Type IV hypersensitivity, involves a delayed response by the immune system and is mediated by T cells. It does not necessarily involve a failure of self-tolerance.
B. Antibody-mediated reaction: This type of hypersensitivity reaction, also known as Type II hypersensitivity, involves antibodies targeting specific antigens on cell surfaces, leading to cell destruction. It doesn't directly indicate a failure of self-tolerance but rather an immune response against specific cells or tissues.
C. Autoimmune reaction: In autoimmune reactions, the immune system fails to recognize certain body tissues or substances as "self," leading to an immune response against the body's own cells or tissues. This results from a breakdown in self-tolerance, where the immune system mistakenly targets its own body.
D. Immediate hypersensitivity reaction: This type of hypersensitivity reaction, also known as Type I hypersensitivity, involves an immediate response by the immune system to an allergen. It includes conditions like allergies and anaphylaxis, where the immune system reacts strongly to substances that are normally harmless. This response does not necessarily indicate a failure of self-tolerance but rather an exaggerated response to specific antigens.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
A. Macrophage: This is the correct answer. An activated monocyte is also known as a macrophage. Monocytes are white blood cells that can mature into macrophages when they move into tissues. Macrophages play a crucial role in the immune system by phagocytosing (engulfing and digesting) pathogens and cellular debris.
B. Lymphocyte: Lymphocytes are another type of white blood cell that plays a central role in the immune system. They include B cells, T cells, and natural killer cells. Lymphocytes are primarily involved in adaptive immune responses, such as antibody production (B cells) and cell-mediated immune responses (T cells).
C. Plasma Cell: Plasma cells are a type of B cell that produces antibodies (immunoglobulins). They are involved in the adaptive immune response, specifically in the production of antibodies that target specific pathogens.
D. Polymorphonuclear Leukocyte: This term typically refers to a group of white blood cells that have a multi-lobed nucleus. Neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils are examples of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. They are involved in innate immune responses, including the phagocytosis of pathogens.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. Gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT): GALT is a component of the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) and refers to the immune cells found in the gastrointestinal tract. These cells play a significant role in local immune responses in the gut.
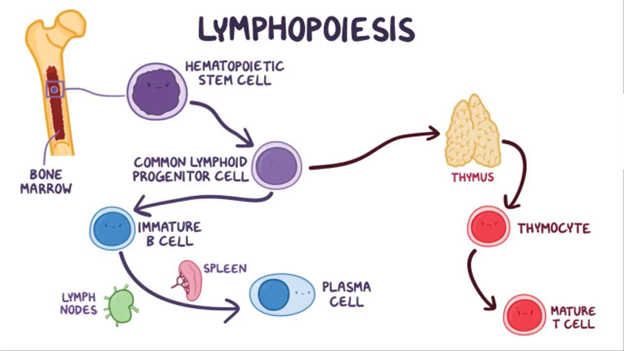
B. Bone marrow: The bone marrow is the primary site of blood cell production in the body. It contains stem cells that can differentiate into various blood cells, including B cells. B cells mature in the bone marrow.
C. Thymus: The thymus is an organ located near the heart and is crucial for the development of T cells. T cells mature in the thymus, where they learn to recognize self from non-self antigens.
D. Lymph nodes: Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures that produce and store cells that help fight infection. While they are essential parts of the immune system, B and T cells are not originally derived from lymph nodes.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
