The practical nurse (PN) is monitoring the neurological vital signs of a client with a recently closed head injury. Which vital sign trends indicate increased intracranial pressure (ICP) and should be reported to the charge nurse?
Heart rate above 110 beats/minute, elevated respiratory rate, and hypotension.
Bounding pulse rate, groaning respiratory effort, and elevated blood pressure.
Thready rapid pulse, trembling, perspiration, weakness, and irritability.
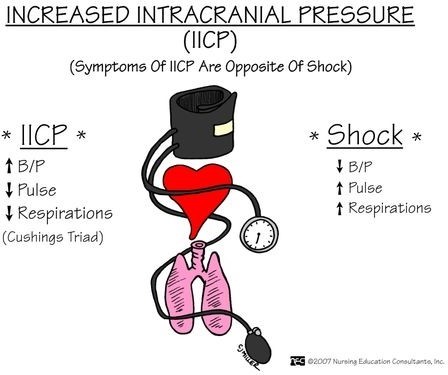
Bradycardia, irregular respiratory patterns, widening pulse pressure.
The Correct Answer is D
The vital sign trends that indicate increased intracranial pressure (ICP) and should be reported to the charge nurse are:
Bradycardia: A slow heart rate can be a sign of increased ICP.
Irregular respiratory patterns: Abnormal breathing patterns, such as irregular or Cheyne-Stokes respirations, can be indicative of increased ICP.
Widening pulse pressure: An increased difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure (widening pulse pressure) can be a sign of increased ICP.
A- Heart rate above 110 beats/minute, elevated respiratory rate, and hypotension: While an elevated heart rate and respiratory rate can be associated with increased ICP, hypotension (low blood pressure) is not typically seen in this condition. Hypotension can be a sign of other factors, such as hypovolemia or shock, which may or may not be related to the head injury.
B- Bounding pulse rate, groaning respiratory effort, and elevated blood pressure: Bounding pulse rate and elevated blood pressure are not specific to increased ICP. They can be influenced by other factors such as pain, anxiety, or medications. Groaning respiratory effort may indicate respiratory distress, but it is not directly related to increased ICP.
C- Thready rapid pulse, trembling, perspiration, weakness, and irritability: These signs and symptoms can be associated with various conditions such as anxiety, stress, or other physiological responses. While they may occur in the context of increased ICP, they are not specific to this condition alone.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["B","E"]
Explanation
The PN should instruct the UAP to observe and report any ear drainage after removing the device, as this may indicate an infection or irritation of the ear canal. The PN should also instruct the UAP to verify that the device is labeled with client's identification, as this can prevent mix-ups or misplacement of the device. The PN should also instruct the UAP to remove ear wax from the device's surface, as this can improve the sound quality and prevent damage to the device.
The other options are not correct because:
a. Keeping the battery door closed during storage is not a correct instruction, as it can drain the battery and shorten its life span. The PN should instruct the UAP to keep the battery door open during storage, as this can conserve the battery power and prevent corrosion.
c. Storing the device on the window sill to prevent loss is not a correct instruction, as it can expose the device to heat, moisture, or sunlight, which can damage its components or affect its function. The PN should instruct the UAP to store the device in a dry, cool, and safe place, such as a case or a drawer.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Hives (also known as urticaria) are raised, red, itchy welts on the skin that can be caused by an allergic reaction to medication, including antibiotics. It is essential for the PN to recognize this potentially severe allergic reaction and take immediate action.
Immediate action steps include:
- Stop the infusion of the intravenous antibiotic immediately.
- Notify the healthcare provider and report the allergic reaction.
- Assess the client's airway, breathing, and circulation to ensure there are no signs of respiratory distress or anaphylaxis.
- Administer prescribed emergency medications if needed (e.g., epinephrine, antihistamines).
- Monitor the client closely for any further signs of an allergic reaction or anaphylaxis.
The other assessment findings mentioned are also important to address, but they do not require immediate action:
A- Dry mouth with thirst: This may indicate dehydration, which should be addressed by encouraging the client to drink fluids, but it does not pose an immediate threat to the client's safety.
B- Warm skin with elastic turgor: This suggests that the client is adequately hydrated, and the skin's elasticity is normal, which is a positive finding.
C- Low-grade fever with diaphoresis: A low-grade fever indicates a mild elevation in temperature, and diaphoresis (sweating) may be the body's response to regulate temperature. The PN should monitor the client's temperature and assess for other signs of infection, but this finding does not require immediate action
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
