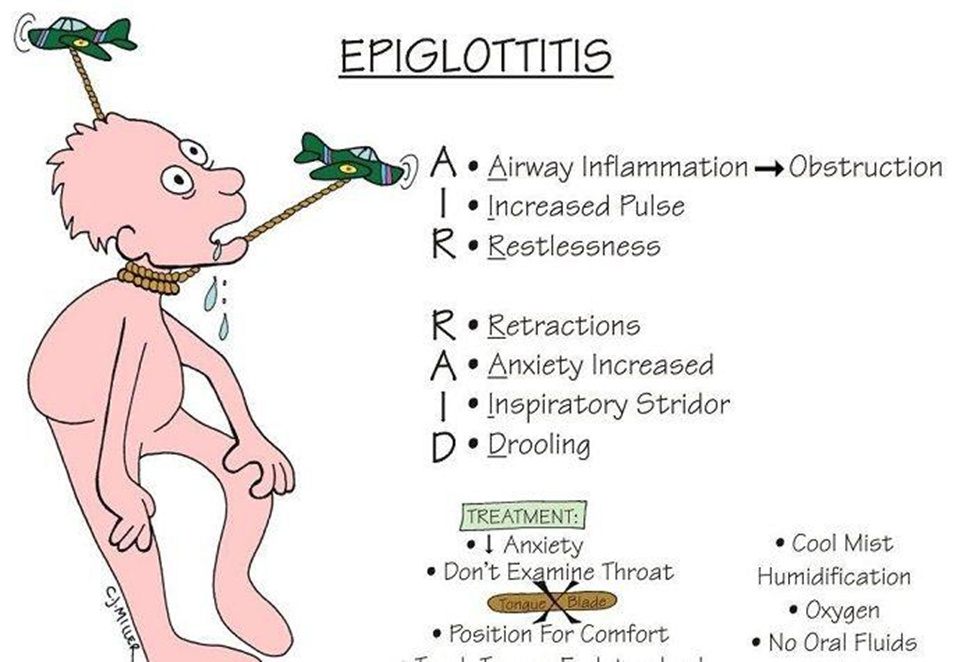
The nurse in the emergency department is caring for a child who appears extremely ill with a high fever, unable to control their oral secretions. with voice hoarseness and inspiratory stridor and inspiratory sternal retractions while breathing. The nurse suspects epiglottitis. Which would the nurse do next?
Contact the assigned emergency room physician to evaluate the need for an advanced airway
Administer intravenous corticosteroids
Obtain a throat culture
inspect the throat to obtain further data to support the diagnosis
The Correct Answer is A
A. Contact the assigned emergency room physician to evaluate the need for an advanced airway
Explanation:
Epiglottitis is a medical emergency that can rapidly progress to airway obstruction. The classic signs and symptoms include a high fever, difficulty swallowing, voice hoarseness, inspiratory stridor, and sternal retractions. Immediate intervention may be necessary to secure the airway. Therefore, contacting the emergency room physician to evaluate the need for an advanced airway (such as intubation) is a priority.
B. Administer intravenous corticosteroids
Explanation: While corticosteroids may be used in the management of epiglottitis to reduce airway inflammation, securing the airway is the priority in the acute phase. Corticosteroids would typically be administered after securing the airway.
C. Obtain a throat culture
Explanation: Obtaining a throat culture is not the immediate priority in the case of suspected epiglottitis. Prompt intervention to secure the airway takes precedence over diagnostic tests.
D. Inspect the throat to obtain further data to support the diagnosis
Explanation: Direct visualization of the throat (inspection) may exacerbate the airway obstruction and is not recommended in the acute management of suspected epiglottitis. The priority is to secure the airway while minimizing agitation and discomfort for the child. Diagnostic procedures, such as obtaining a throat culture, can be considered after the airway is stabilized.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Valley fever
Explanation: Valley fever is a respiratory infection caused by inhaling spores of the Coccidioides fungus. It is not related to tinea pedis.
B. Shingles
Explanation: Shingles is a painful rash caused by the varicella-zoster virus. It is not related to tinea pedis.
C. Fever blister
Explanation: A fever blister is another term for a cold sore, typically caused by the herpes simplex virus. It is not related to tinea pedis, which is a fungal infection of the feet.
D. "Athlete's foot"
Explanation:
Tinea pedis is commonly known as athlete's foot. It is a fungal infection that affects the skin of the feet, particularly the spaces between the toes. The condition is often associated with warm and moist environments, such as those found in athletic shoes, hence the term "athlete's foot."
Correct Answer is ["A","C","E"]
Explanation
A. "The manifestations are lessened by taking the prednisone every other day instead of daily."
Correct Answer: Cushingoid characteristics can be associated with long-term corticosteroid use. Taking prednisone every other day, rather than daily, can help minimize these manifestations while still providing the needed therapeutic effect.
B. "You need to be sure to talk to the doctor about the Cushingoid characteristics."
Incorrect: While it is important for the parents to communicate with the doctor, this statement is less therapeutic than option 3, which opens up a more collaborative and supportive conversation.
C. "Which manifestations of this condition do you find most troublesome?"
Correct Answer: This open-ended question allows the parents to express their concerns and frustrations. It facilitates communication between the parents and healthcare provider to address specific issues they find most troublesome.
D. "I am sure it will be all right; they hardly look unusual."
Incorrect: Downplaying the parents' concerns may not be the most therapeutic approach. Acknowledging their concerns and providing information about the reversible nature of cushingoid characteristics would be more helpful.
E. "The cushingoid appearance will gradually disappear once the corticosteroids are tapered and discontinued."
Correct Answer: Cushingoid characteristics are reversible, and they tend to improve as the dose of corticosteroids is tapered and eventually discontinued.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
