The client is brought to the emergency department with a reported overdose of morphine. Which drug does the nurse anticipate will be prescribed?
Butorphanol
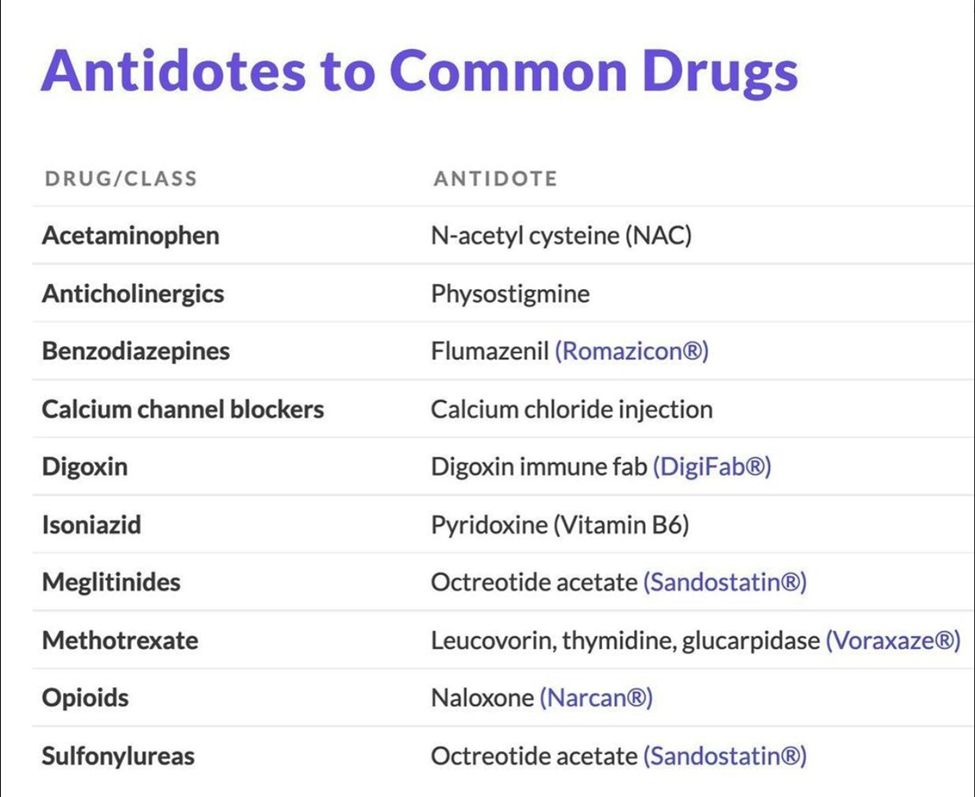
Naloxone
Flumazenil
Pentazocine
The Correct Answer is B
A. Butorphanol
Butorphanol is a mixed opioid agonist-antagonist. It has both agonist and antagonist properties at opioid receptors. While it can be used for pain management, it is not commonly used for opioid overdose reversal.
B. Naloxone
Naloxone is an opioid receptor antagonist and is the drug of choice for reversing opioid overdose, including morphine overdose. It works by competitively binding to opioid receptors, blocking the effects of opioids.
C. Flumazenil
Flumazenil is a selective antagonist for benzodiazepines. It is used to reverse the effects of benzodiazepine overdose but does not have an effect on opioid overdose.
D. Pentazocine
Pentazocine is a mixed opioid agonist-antagonist. Like butorphanol, it has both agonist and antagonist properties at opioid receptors. It is used for pain management but is not commonly used for opioid overdose reversal.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["3"]
Explanation
To calculate the dosage of furosemide (Lasix), a diuretic medication, you need to divide the ordered amount by the tablet strength.
In this case, the ordered amount is 120 mg and the tablet strength is 40 mg.
Therefore, you need to divide 120 by 40, which gives you 3.
This means you would administer 3 tablets of furosemide (Lasix) to the patient.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. Combination therapy has the best outcomes when omeprazole, propranolol, bismuth salicylate are used.
Propranolol is not an antibiotic and is not part of the standard combination therapy for H. pylori. Bismuth subsalicylate may be used in some regimens, but the standard involves a proton pump inhibitor, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin or metronidazole.
B. Combination therapy has the best outcomes when omeprazole, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin are used.
This is the correct choice. The standard combination therapy for H. pylori infection includes a proton pump inhibitor (such as omeprazole), clarithromycin, and amoxicillin or metronidazole.
C. The use of sucralfate along with antibiotics is the best combination therapy for peptic ulcer disease.
Sucralfate is not typically part of the standard antibiotic combination therapy for H. pylori. It is a cytoprotective agent that may be used to treat ulcers but is not a primary component in eradicating H. pylori.
D. Various antibiotics are used to eradicate the bacteria that are responsible for the development of peptic ulcer disease.
While this statement is true, it does not specify the standard combination therapy. The most common antibiotics used in combination therapy for H. pylori include clarithromycin and amoxicillin or metronidazole, along with a proton pump inhibitor.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
