Both B and T cells are originally derived from cells of the:
gut-associated lymphoid tissue.
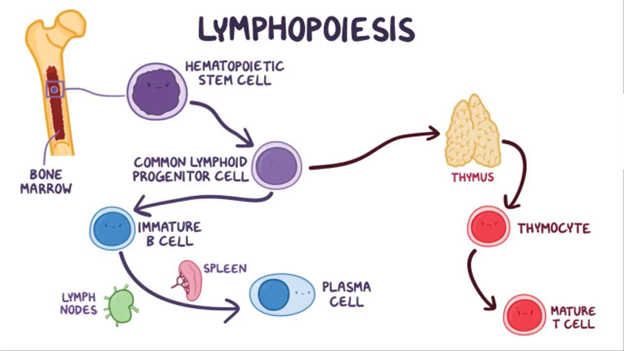
bone marrow.
Thymus.
lymph nodes.
The Correct Answer is B
A. Gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT): GALT is a component of the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) and refers to the immune cells found in the gastrointestinal tract. These cells play a significant role in local immune responses in the gut.
B. Bone marrow: The bone marrow is the primary site of blood cell production in the body. It contains stem cells that can differentiate into various blood cells, including B cells. B cells mature in the bone marrow.
C. Thymus: The thymus is an organ located near the heart and is crucial for the development of T cells. T cells mature in the thymus, where they learn to recognize self from non-self antigens.
D. Lymph nodes: Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures that produce and store cells that help fight infection. While they are essential parts of the immune system, B and T cells are not originally derived from lymph nodes.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Reddened tongue and gums: This side effect is not typically associated with ampicillin. However, certain medications or medical conditions can cause changes in oral tissues, leading to redness in the tongue and gums.
B. Digit numbness and tingling: Ampicillin does not commonly cause numbness and tingling in the fingers and toes. These symptoms can be associated with neurological issues or circulatory problems.
C. Bruising and petechiae: These symptoms can indicate bleeding disorders or low platelet count and are not usually caused by ampicillin. It's essential to investigate further if a patient experiences unexplained bruising or petechiae.
D. Skin rash and loose stools: Skin rash is a known side effect of penicillin-type antibiotics, including ampicillin. Loose stools or diarrhea can also occur due to disruption of the gut flora caused by the antibiotic. Patients should be aware of these possibilities and report any severe or persistent symptoms to their healthcare provider.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. 8:00 AM: This time is too early to draw a trough level for a medication administered at 10:00 AM. The trough level should be drawn just before the next dose is given to get the lowest concentration in the bloodstream.
B. 11:00 AM: This time is after the scheduled dose of vancomycin at 10:00 AM. Waiting until 11:00 AM would not provide an accurate trough level because the patient has already received the medication.
C. 9:00 AM: This is the correct time to obtain the patient's blood sample. It is one hour before the scheduled dose of vancomycin at 10:00 AM. Drawing the trough level at this time ensures it reflects the lowest concentration of the drug in the bloodstream.
D. 12:00 noon: This time is after the scheduled dose of vancomycin at 10:00 AM. Waiting until noon would not provide an accurate trough level because the patient has already received the medication.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
