A nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client who reports taking pseudoephedrine for sinus congestion as needed. The nurse should identify that pseudoephedrine is contraindicated for which of the following client conditions?
Migraines
Eczema
Hypertension
Diverticulitis
The Correct Answer is C
Pseudoephedrine is a sympathomimetic medication that acts as a decongestant by constricting blood vessels in the nasal passages, which helps to relieve sinus congestion. However, it can also cause vasoconstriction in other parts of the body, leading to an increase in blood pressure. Therefore, it is contraindicated for individuals with hypertension (high blood pressure).
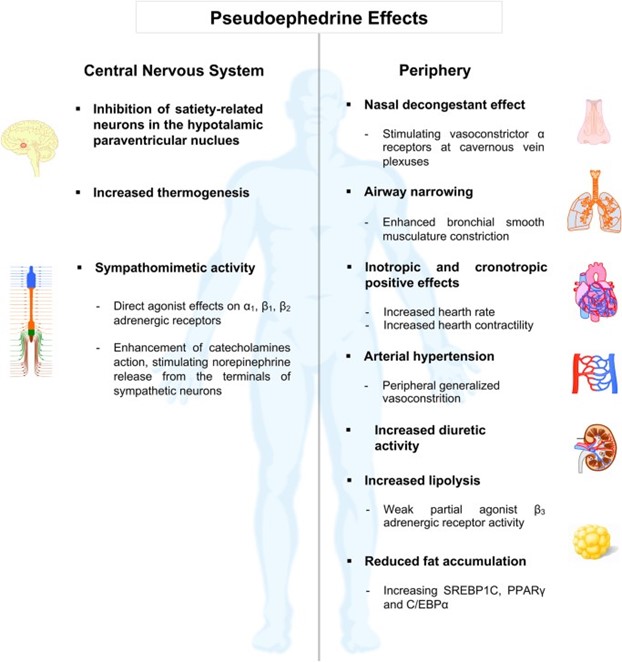
The other conditions mentioned, migraines, eczema, and diverticulitis, are not contraindications for the use of pseudoephedrine. However, it is important for individuals with these conditions to consult their healthcare provider before taking pseudoephedrine, as it may interact with other medications or exacerbate certain symptoms.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
This response demonstrates that the patient understands the dosing frequency (twice a day) and the importance of taking it with a full glass of water, which aligns with the instructions provided by the nurse.
The other choices are incorrect because:
A. "Taking this medication can cause me to develop a non-productive cough.": This response is about a potential side effect of the medication, rather than showing an understanding of the dosing instructions.
B. "I will take my medication Daily with a full glass of water.": This response indicates a misunderstanding of the dosing frequency, as the prescription specifically states "BID" (twice a day) rather than "daily."
D. "The medication will have to be given by my Home Health Nurse twice a day.": This response suggests a reliance on the home health nurse to administer the medication, which contradicts the instructions for the patient to take it themselves. It shows a misunderstanding of the patient's responsibility in self-administering the medication.
Correct Answer is ["A","C","D"]
Explanation
"The infant's nasal congestion appeared to improve following the administration of hypertonic nasal drops. The infant tolerated the insertion of saline nose drops well, with no signs of distress or adverse reactions. The nasal passages appeared clearer after the instillation, and the infant's breathing appeared less congested. There was no significant increase in respiratory rate or other signs of respiratory distress observed. The intervention seemed to have a positive effect on the infant's nasal congestion."
This statement indicates that the mucolytic medication (hypertonic nasal drops) was administered and had a positive effect on the infant's nasal congestion. It also mentions that the infant tolerated the procedure well without any adverse reactions, such as shortness of breath or fever. The absence of distress or adverse symptoms and the observed improvement in nasal congestion indicate the effectiveness of the medication in the nurse's narrative note. The additional information about the saline nose drops and respiratory rate may not directly address the effectiveness of the mucolytic medication and can be documented separately if necessary.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
