A nurse is preparing a client for discharge home who is confused and incontinent after a stroke. Which instructions regarding bladder training will the nurse include in the teaching plan for the client's family?
"Offer the client the commode or urinal every 2 hours."
"Decrease the client's oral fluid intake to 1 L/day."
"Instruct the client to hold urine as long as possible to restore bladder tone."
"Use a Foley catheter at night to prevent accidents."
The Correct Answer is A
The nurse will include the instruction "Offer the client the commode or urinal every 2 hours" in the teaching plan for the client's family. This approach is known as timed voiding and can help the client re-establish a regular pattern of urination. Option "a" promotes frequent voiding, which helps
prevent accidents and promotes bladder health. Option "b" is not a recommended approach and can lead to dehydration, urinary tract infections, and other complications. Option "c" is also not recommended since holding urine for extended periods can lead to bladder distention and increase the risk of urinary tract infections. Option "d" is also not recommended since catheterization should only be considered in specific cases where other options have failed or are not feasible.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
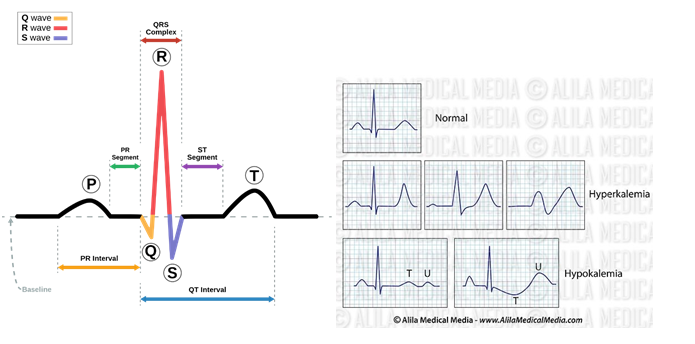
Electrocardiographic (ECG) changes and dysrhythmias related to hypokalemia are the main reasons for initiating cardiac monitoring in patients with diabetic ketoacidosis. In diabetic ketoacidosis, insulin deficiency causes the body to break down fat for energy, leading to the production of ketones and resulting in metabolic acidosis. In addition, glucose and potassium are lost in the urine due to osmotic diuresis. Hypokalemia can cause ECG changes and dysrhythmias, which can be life-threatening.
Hypokalemia is a common complication of DKA and can lead to ECG changes such as ST-segment depression, T-wave inversion, and U waves².
Hypovolemic shock related to osmotic diuresis is an important consideration in the management of diabetic ketoacidosis, but it is not the primary reason for initiating cardiac monitoring.
Cardiovascular collapse resulting from the effects of hyperglycemia is not a common complication of diabetic ketoacidosis, and it is not the primary reason for initiating cardiac monitoring.
Fluid overload resulting from aggressive fluid replacement is a potential complication of diabetic ketoacidosis, but it is not the primary reason for initiating cardiac monitoring.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Based on the given arterial blood gas results, the patient's pH is elevated, indicating alkalosis. The PaCO2 level is decreased, which suggests respiratory compensation. The bicarbonate (HCO3-) level is within the normal range. Therefore, the interpretation of the arterial blood gas results is respiratory alkalosis.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.