A nurse is planning care for a client who has a central venous access device for intermittent infusions.
Which of the following actions should the nurse include in the plan of care?
Use an aseptic technique when changing the dressing.
Cleanse the site with povidone-iodine.
Flush the catheter using a 10-mL syringe.
Change the dressing every 24 hours.
The Correct Answer is A
The aseptic technique is important to prevent infection when changing the dressing of a central venous access device.
Choice B is not correct because povidone-iodine is not always the recommended cleansing agent for central venous access devices.
Choice C is not correct because a 10-mL syringe may generate too much pressure and damage the catheter.
Choice D is not correct because the dressing does not always need to be changed every 24 hours; the frequency of dressing changes depends on the type of dressing and the condition of the site.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
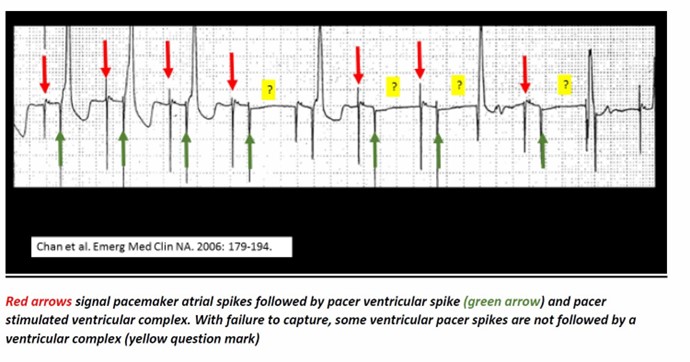
A pacemaker sends electrical signals to the heart to regulate the heartbeat.
On an electrocardiogram (ECG), these signals appear as small spikes followed by a QRS complex, which represents the contraction of the ventricles.
Choice A, A regular sinus rhythm, is not the correct answer because a regular sinus rhythm is a normal heart rhythm that originates from the sinoatrial (SA) node and does not involve a pacemaker.
Choice B, A chaotic, irregular rhythm, is not the correct answer because a pacemaker is designed to regulate the heartbeat and prevent chaotic or irregular rhythms.
Choice C, the Absence of any electrical activity, is not the correct answer because a pacemaker sends electrical signals to the heart to regulate its activity.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The nurse’s priority assessment in the PACU (Post-Anesthesia Care Unit) should be the client’s respiratory status.
This is because the client is recovering from anesthesia and may have an altered respiratory function.
Choice B, assessing the surgical site, is not an answer because it is not the priority assessment for a client in the PACU.
Choice C, assessing the level of consciousness, is not an answer because it is not the priority assessment for a client in the PACU.
Choice D, assessing the pain level, is not an answer because it is not the priority assessment for a client in the PACU.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
