A nurse is contributing to the plan of care for a client prescribed continuous enteral feedings. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take?
Check the gastric residual every 8 hr.
Change the feeding bag every 24 hr.
Flush the tube with sterile sodium chloride solution every 2 hr.
Position the head of the client's bed at 15.
Correct Answer : B
Correct answer: B
A. Check the gastric residual every 8 hr:
Explanation: It is generally recommended to check gastric residuals more frequently than every 8 hours, often every 4-6 hours, especially in the initial stages of continuous enteral feedings, to monitor tolerance and prevent complications such as aspiration.
B. Change the feeding bag every 24 hr:
Explanation: Changing the feeding bag and tubing at regular intervals helps prevent bacterial contamination and maintain aseptic technique. The frequency of bag changes is typically scheduled every 24 hours or according to facility protocols.
C. Flush the tube with sterile sodium chloride solution every 2 hr:
Explanation: While it is important to flush the feeding tube regularly to maintain patency, using sterile water is typically recommended unless there is a specific clinical indication for sterile sodium chloride. The frequency of flushing (usually every 4-6 hours for continuous feeding) should be determined based on the institution's protocol and the client's specific needs.
D. Position the head of the client's bed at 15 degrees:
Explanation: To reduce the risk of aspiration, the head of the bed should be elevated to at least 30-45 degrees during enteral feedings, not just 15 degrees. Elevating the head of the bed helps prevent reflux and aspiration.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
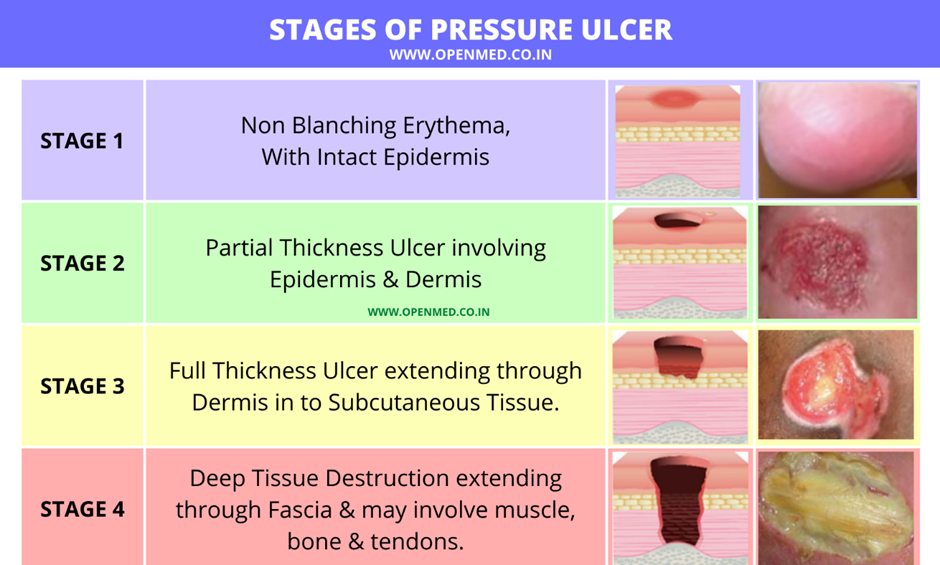
A. Intact skin with localized erythema:
Explanation: This description is more consistent with a stage 1 pressure injury, where there is non-blanchable erythema.
B. Full thickness skin loss with visible bone:
Explanation: This description is more consistent with a stage 4 pressure injury, which involves extensive tissue loss, including exposure of bone.
C. Full thickness skin loss with visible adipose tissue:
Explanation: This finding is characteristic of a stage 3 pressure injury, where the loss of tissue extends down to the subcutaneous layer.
D. Partial-thickness skin loss with red tissue in the wound bed:
Explanation: This description is consistent with a stage 2 pressure injury, where there is partial-thickness skin loss involving the epidermis and possibly the dermis, forming a shallow open ulcer with a red-pink wound bed.
Correct Answer is B, A, C, D
Explanation
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
