A nurse is assessing a toddler who has acute nephrotic syndrome. Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider?
Yellow nasal discharge.
Poor appetite.
Facial edema.
Irritability.
None
None
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A rationale: Yellow nasal discharge in a toddler with acute nephrotic syndrome signifies a potential upper respiratory tract infection, which is critically important. Children with nephrotic syndrome are highly susceptible to infections due to significant urinary loss of immunoglobulins, leading to an immunocompromised state. Furthermore, corticosteroid treatments, often prescribed for nephrotic syndrome, suppress the immune system. An infection can precipitate a relapse of the syndrome, lead to severe complications like peritonitis or sepsis, and requires prompt evaluation and potentially antibiotic therapy to prevent life-threatening outcomes.
Choice B rationale: Poor appetite is a non-specific symptom in toddlers with nephrotic syndrome and does not typically indicate an immediate, life-threatening complication. It can be attributed to generalized malaise, abdominal discomfort due to ascites, or even side effects of medications such as corticosteroids. While important to monitor for nutritional status and overall well-being, it does not carry the same urgency as signs of infection, which can rapidly lead to severe health deterioration in an immunocompromised child.
Choice C rationale: Facial edema is a cardinal clinical manifestation of acute nephrotic syndrome, resulting from profound hypoalbuminemia. Reduced plasma oncotic pressure causes fluid to shift from the intravascular space into the interstitial space, leading to generalized edema, often prominently in the face. This finding is expected and indicates the disease process itself, rather than an acute, unexpected complication requiring immediate reporting, unless there is a sudden, significant worsening or associated respiratory compromise.
Choice D rationale: Irritability in a toddler can be a manifestation of general discomfort, illness, or even a side effect of corticosteroid therapy, which can cause mood disturbances and behavioral changes. While it warrants assessment to identify the underlying cause, irritability is a non-specific symptom and does not directly indicate an urgent, life-threatening complication of nephrotic syndrome requiring immediate medical intervention, unlike the signs of an acute infection in an immunocompromised child.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
The correct answer is d. Modify the environment.
Rationale for each choice:
Choice a. Improve the client's communication skills.
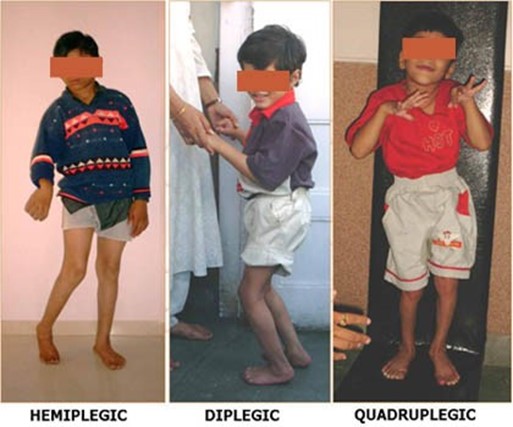
- Statement:While communication is important,it is not the priority for a child with hemiplegic cerebral palsy.
- Rationale:Hemiplegic cerebral palsy primarily affects motor skills,not communication abilities.While some children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy may have speech difficulties,it is not the most pressing concern in this case.Addressing environmental barriers to promote mobility and independence takes precedence.
Choice b. Provide respite services for the parents.
- Statement:Respite services can provide valuable support for parents,but they are not the priority in this case.
- Rationale:The focus of the care plan should be on the child's immediate needs and safety.Modifying the environment to enhance the child's functional abilities is crucial for their development and well-being.
Choice c. Foster self-care activities.
- Statement:Encouraging self-care is essential,but it requires a supportive environment.
- Rationale:Before promoting self-care activities,the nurse must ensure the child has the necessary accommodations and modifications in place to facilitate independence.
Choice d. Modify the environment.
- Statement:This is the priority goal for a child with hemiplegic cerebral palsy.
- Rationale:Modifying the home environment can significantly improve the child's mobility,safety,and ability to participate in daily activities.Examples of modifications include:
- Installing grab bars in the bathroom
- Widening doorways
- Removing tripping hazards
- Providing adaptive equipment such as special chairs or utensils
- Ensuring adequatelighting
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
a.Talcum powder is not recommended for use with infants because it can be inhaled, potentially causing respiratory problems. Instead, a barrier cream or ointment (such as zinc oxide or petroleum jelly) should be used to protect the skin from moisture and irritants.
b.While cloth diapers can be less irritating than some disposable diapers, they may not be as effective at keeping the skin dry. The priority is to keep the area dry and clean, regardless of the type of diaper used. Super-absorbent disposable diapers are often recommended because they can help keep the skin dry.
c.Exposing the skin to hot air can cause burns and further irritation. Instead, allowing the skin to air dry naturally (without the use of hot air) during diaper changes can be beneficial.
d.A moisturizer creates a barrier between the skin and irritants like urine and stool.Wiping with a moisturizer can minimize friction during cleaning, which can be uncomfortable for the baby and further irritate the skin.Some moisturizers can help soothe and hydrate the inflamed skin, promoting healing.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
