A nurse collects the health history of a 65-year-old client. Which of the following risk factors in the client's history puts the client at the highest risk for embolic stroke?
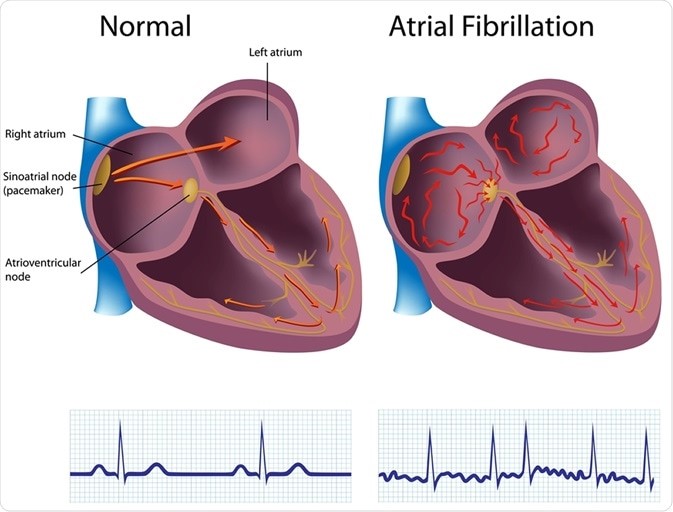
Atrial fibrillation.
Hypertension.
Diabetes.
Alcohol abuse.
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A reason: This is the correct answer because atrial fibrillation is the risk factor that puts the client at
the highest risk for embolic stroke. Atrial fibrillation is an irregular and rapid heart rate that causes poor blood flow and blood pooling in the heart chambers. This can lead to the formation of blood clots that can travel to the brain and block an artery, causing an embolic stroke.
Choice B reason: This is incorrect because hypertension is not the risk factor that puts the client at
the highest risk for embolic stroke. Hypertension is high blood pressure that puts stress on the blood vessels and increases the risk of bleeding or rupture. This can lead to a hemorrhagic stroke, but not an embolic stroke.
Choice C reason: This is incorrect because diabetes is not the risk factor that puts the client at
the highest risk for embolic stroke. Diabetes is a condition that causes high blood sugar levels and damages the blood vessels and nerves. This can lead to poor circulation and increased risk of infection and ulcers, but not an embolic stroke.
Choice D reason: This is incorrect because alcohol abuse is not the risk factor that puts the client at
the highest risk for embolic stroke. Alcohol abuse is excessive consumption of alcohol that affects liver function and blood clotting factors. This can lead to liver disease and bleeding disorders, but not an embolic stroke.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is incorrect because using sign language when communicating with the client is not an appropriate action for the nurse to take. Sign language is a form of communication that uses hand gestures, facial expressions, and body movements. It is not a universal language and requires training and practice. The nurse should not assume that the client knows or prefers sign language unless they have indicated so.
Choice B reason: This is incorrect because speaking loudly and into the client's good ear is not an appropriate action for the nurse to take. Speaking loudly can distort the sound quality and cause discomfort or irritation to the client. Speaking into the client's good ear can also create a sense of imbalance and isolation. The nurse should speak at a normal volume and tone, and face the client directly.
Choice C reason: This is the correct answer because speaking directly to the client in a normal, clear voice is an appropriate action for the nurse to take. Speaking directly to the client can help them see the nurse's mouth movements and facial expressions, which can enhance understanding and communication. Speaking in a normal, clear voice can help convey the message clearly and respectfully.
Choice D reason: This is incorrect because sitting by the client's side and speaking very slowly is not an appropriate action for the nurse to take. Sitting by the client's side can make it difficult for them to see the nurse's face and hear their voice. Speaking very slowly can also make the message unclear and patronizing. The nurse should sit in front of the client and speak at a normal pace.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A Reason: This is incorrect because rotating nursing staff may not provide emotional support for the client who is rehabilitating from major burns. The client may benefit from having consistent and familiar staff who can establish rapport and trust with him. The nurse should assign staff who are experienced and comfortable with burn care and who can communicate effectively and empathetically with the client.
Choice B Reason: This is incorrect because keeping family members aware of his condition may not provide emotional support for the client who is rehabilitating from major burns. The client may have privacy or confidentiality concerns or may not want his family members to see him in his current state. The nurse should respect the client's wishes and preferences regarding family involvement and obtain his consent before sharing any information.
Choice C Reason: This is correct because talking with the client during wound care can provide emotional support for the client who is rehabilitating from major burns. Wound care can be painful and stressful for the client, so the nurse should use therapeutic communication skills to distract, reassure, and encourage him. The nurse should also explain the procedures and rationale for wound care and allow the client to express his feelings and concerns.
Choice D Reason: This is incorrect because assigning assistive personnel to keep his room neat and clean may not provide emotional support for the client who is rehabilitating from major burns. The client may appreciate a clean environment, but he may also need more direct and personal contact with the nurse. The nurse should spend time with the client and provide holistic care that addresses his physical, psychological, social, and spiritual needs.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
