A nurse begins her shift and is completing her first turn of the night. While turning, she also assesses her patient's skin. When she turns her patient she finds the following wound on her coccyx. How should she document the following wound? (The base of the wound is muscle, with some subcutaneous tissue)
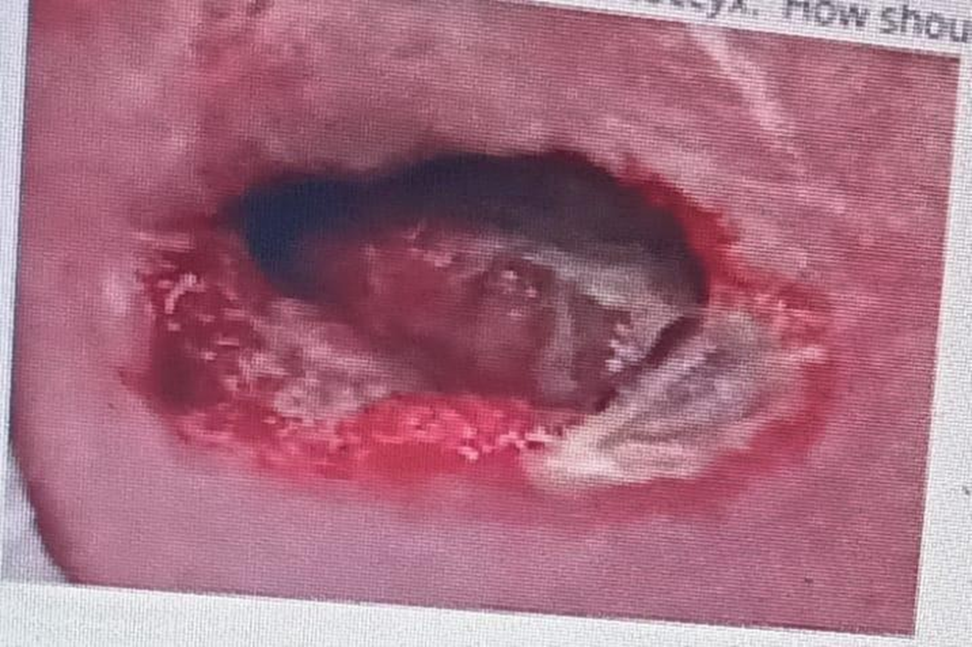
Stage III Pressure Ulcer
Stage IV Pressure Ulcer
Stage II Pressure Ulcer
Unstageable Ulcer
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A rationale: Stage III pressure ulcers involve full-thickness tissue loss with visible fat but do not extend to the underlying muscle.
Choice B rationale: Stage IV pressure ulcers involve full-thickness tissue loss with exposed muscle, bone, or other structures.
Choice C rationale: Stage II pressure ulcers involve partial-thickness skin loss but do not extend into the deeper layers.
Choice D rationale: Unstageable ulcers have a base covered by slough or eschar, making it difficult to assess the depth of tissue involvement. In this case, the wound's base is described as muscle, indicating a stage IV pressure ulcer.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A rationale: The stool test for occult blood is not primarily designed to detect bacteria.
Choice B rationale: Parasites are not typically detected through a stool test for occult blood.
Choice C rationale: Steatorrhea refers to the presence of excess fat in the stool and is not the primary focus of a stool test for occult blood.
Choice D rationale: The purpose of the stool test for occult blood is to check for the presence of blood in the stool, which may not be visible to the naked eye. This can be an indicator of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Stress incontinence is characterized by involuntary urine leakage during activities that increase intra-abdominal pressure, such as coughing or sneezing.
Choice B rationale: Transient incontinence is temporary and often related to factors like medications or medical conditions.
Choice C rationale: Total incontinence refers to continuous and unpredictable leakage of urine.
Choice D rationale: Reflex incontinence is associated with neurologic dysfunction, and the lack of warning or stress preceding involuntary urination aligns with this description.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
