A male client with acute kidney injury (AKI) is scheduled for his first hemodialysis treatment and asks the practical nurse (PN) how the treatments will be evaluated for effectiveness. The PN explains that blood samples will be collected for analysis. Which laboratory value should the PN explain as the best indicator of each hemodialysis?
Elevated potassium.
Decreased calcium.
Lowered hemoglobin.
Decreased creatinine.
The Correct Answer is D
Hemodialysis is a procedure used to remove waste products and excess fluid from the blood when the kidneys are unable to function properly. One of the waste products that accumulate in the blood during kidney dysfunction is creatinine. Creatinine is a byproduct of muscle metabolism, and its levels in the blood are normally regulated and eliminated by the kidneys. In AKI, the kidneys are not able to effectively filter and eliminate creatinine, leading to elevated levels in the blood. Hemodialysis helps to remove excess creatinine from the blood, resulting in decreased creatinine levels.
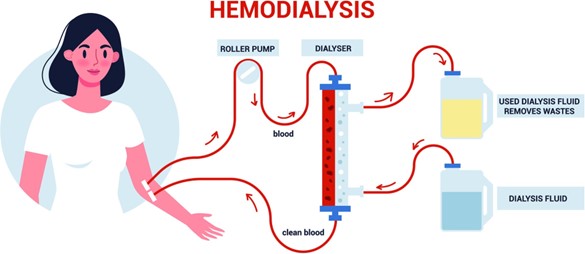
A- Elevated potassium levels (hyperkalemia) are common in AKI and can be life-threatening. Hemodialysis helps to remove excess potassium from the blood, restoring normal levels.
However, the best indicator of the effectiveness of hemodialysis in managing hyperkalemia would be monitoring the potassium levels before and after the session rather than considering it as the "best" indicator.
B- Decreased calcium levels can occur in kidney dysfunction due to impaired activation of vitamin D and decreased absorption of calcium from the intestines. While hemodialysis can help restore calcium levels, it may not be the primary laboratory value used to evaluate the effectiveness of each session.
C- Lowered hemoglobin levels can be seen in AKI due to various factors, including decreased production of red blood cells and blood loss. Hemodialysis can help remove waste products and excess fluid, but it may not directly address the underlying causes of lowered hemoglobin levels.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
This question is related to the responsibilities and scope of practice of a practical nurse (PN) and a medication aide. A medication aide is a certified nursing assistant (CNA) who is responsible for administering daily medication to patients under the supervision of a licensed nurse, such as a PN or a registered nurse (RN). A PN is a licensed nurse who can provide routine care, observe patients’ health, assist doctors and RNs, and communicate instructions to patients regarding medication, home-based care, and preventative lifestyle changes.
Based on this information, the best action that the PN should take in this situation is c. Assign the remainder of medication administration to another PN who is performing treatments. This is because it would ensure that the medication administration is completed by another licensed nurse who has the knowledge, skills, and authority to do so. The PN who is performing treatments may have some spare time or be able to rearrange their schedule to accommodate the additional task. The PN should also communicate with the other PN and the medication aide about the situation and document the change of assignment in the patients’ records.
Option a is not a good choice, because it would be unfair and unethical to deny the medication aide’s request to leave if they are sick. The medication aide’s health and well-being are also important, and forcing them to stay and work could compromise their safety and the quality of care they provide to the patients.
Option b is not a good choice, because it would be outside the scope of practice of the UAPs to give medications to the patients. UAPs are not trained or certified to administer medications, and doing so could pose serious risks to the patients’ health and safety. The PN would also be liable for any errors or adverse outcomes that may result from the UAPs’ actions.
Option d is not a good choice, because it would not solve the problem of the medication administration being incomplete. Documenting why the medications were not given is important, but it is not enough to ensure that the patients receive their prescribed drugs and treatments. The PN still has the responsibility to find a way to complete the medication administration or delegate it to another qualified and available person.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
When admitting a client with complications of left-sided heart failure, the practical nurse (PN) should prioritize assessing the client's bilateral lung sounds. Left-sided heart failure can result in the accumulation of fluid in the lungs, leading to pulmonary congestion and impaired gas exchange. By auscultating the client's lung sounds, the PN can assess for the presence of crackles, wheezes, or diminished breath sounds, which are indicative of pulmonary congestion and fluid accumulation. This assessment helps to identify the severity of the client's condition and guides further interventions and treatment.
While assessing heart sounds (option a) is important in evaluating cardiac function, assessing lung sounds takes priority as pulmonary congestion is a common manifestation of left-sided heart failure. Chest pain (option b) is a significant symptom that should be assessed promptly, but in this scenario, the focus is on assessing for signs of pulmonary congestion and impaired gas exchange. Assessing the client's mood and affect (option d) is important for a comprehensive assessment, but it is not the priority when the client is admitted with complications of left-sided heart failure.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
