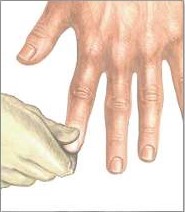
The practical nurse (PN) applies and then releases pressure to a client's fingernail as seen in the photo. Normal nail color returns in 2 seconds. Which action should the PN take?
Report abnormal findings to the charge nurse.
Observe for blanching of the nailbed.
Repeat the process with a different nailbed.
Document the capillary refill time.
The Correct Answer is D
- Capillary refill time is a test that measures how quickly the blood returns to the tissues after pressure is applied and released on a nailbed or a fingertip. It is an indicator of peripheral circulation and tissue perfusion.
- To perform the capillary refill test, the examiner should press firmly on the nailbed or fingertip for a few seconds, then release the pressure and observe how long it takes for the normal color to return. The normal capillary refill time is less than 2 seconds .
- In the photo, the practical nurse (PN) applies and then releases pressure to a client's fingernail. Normal nail color returns in 2 seconds, which indicates a normal capillary refill time and adequate peripheral circulation. This is a normal and expected finding that does not require any further action, except for documentation.
- Therefore, option D is the correct answer, as it reflects the appropriate and standard nursing practice of documenting any assessment findings in the client's chart. Option D also implies that the PN does not need to report, observe, or repeat anything else related to the capillary refill test, as it was done correctly and yielded normal results.
- Options A, B, and C are incorrect answers, as they do not reflect the appropriate or necessary actions for the PN to take after performing a normal capillary refill test.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is {"dropdown-group-1":"A","dropdown-group-2":"B"}
Explanation
Based on the laboratory data, the client has:
Option 1: Pre-diabetes
Option 2: Impaired glucose tolerance
The client's fasting blood glucose level of 122 mg/dL (6.8 mmol/L) falls within the range of 100 to 125 mg/dL (5.56 to 6.9 mmol/L), indicating impaired glucose tolerance. This suggests that the client's blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes mellitus.
Impaired glucose tolerance is considered a precursor to diabetes and indicates an increased risk of developing diabetes in the future. It is important for the practical nurse to educate the client about lifestyle modifications to manage blood sugar levels and prevent the progression to diabetes.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
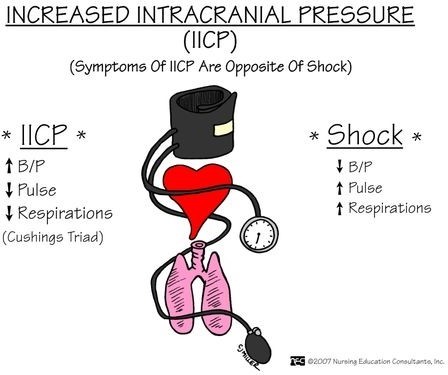
The vital sign trends that indicate increased intracranial pressure (ICP) and should be reported to the charge nurse are:
Bradycardia: A slow heart rate can be a sign of increased ICP.
Irregular respiratory patterns: Abnormal breathing patterns, such as irregular or Cheyne-Stokes respirations, can be indicative of increased ICP.
Widening pulse pressure: An increased difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure (widening pulse pressure) can be a sign of increased ICP.
A- Heart rate above 110 beats/minute, elevated respiratory rate, and hypotension: While an elevated heart rate and respiratory rate can be associated with increased ICP, hypotension (low blood pressure) is not typically seen in this condition. Hypotension can be a sign of other factors, such as hypovolemia or shock, which may or may not be related to the head injury.
B- Bounding pulse rate, groaning respiratory effort, and elevated blood pressure: Bounding pulse rate and elevated blood pressure are not specific to increased ICP. They can be influenced by other factors such as pain, anxiety, or medications. Groaning respiratory effort may indicate respiratory distress, but it is not directly related to increased ICP.
C- Thready rapid pulse, trembling, perspiration, weakness, and irritability: These signs and symptoms can be associated with various conditions such as anxiety, stress, or other physiological responses. While they may occur in the context of increased ICP, they are not specific to this condition alone.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
