A client with paranoia is admitted to the mental health unit and immediately goes to the corner of the room and sits quietly without communicating. In approaching the client, what intervention should the practical nurse (PN) implement first?
Explain the daily schedule of unit activities.
Review client rights of hospitalization.
Offer the client an as-needed (PRN) medication.
Describe the functions of the practical nurse (PN).
The Correct Answer is D
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
This is the correct answer because it is the most important and relevant action that the PN should do for a postoperative patient with a PCA machine. A PCA machine is a computerized device that allows the patient to self-administer a preset dose of pain medication, usually an opioid, by pressing a buton. The PCA machine is attached to an intravenous (IV) line that delivers the medication directly into the bloodstream. The PCA machine can provide effective and individualized pain relief for postoperative patients, as well as increase their sense of control and satisfaction¹².
The PN should assess the pain management response of the postoperative patient with a PCA machine by monitoring their pain level, vital signs, oxygen saturation, sedation level, and side effects. The PN should use a valid and reliable pain scale, such as the numeric rating scale (NRS) or the visual analog scale (VAS), to measure the patient's pain intensity and relief. The PN should also check the settings and functioning of the PCA machine, such as the dose, lockout interval, and limit. The PN should document and report the patient's pain management response and any problems or complications with the PCA machine to the health care provider.
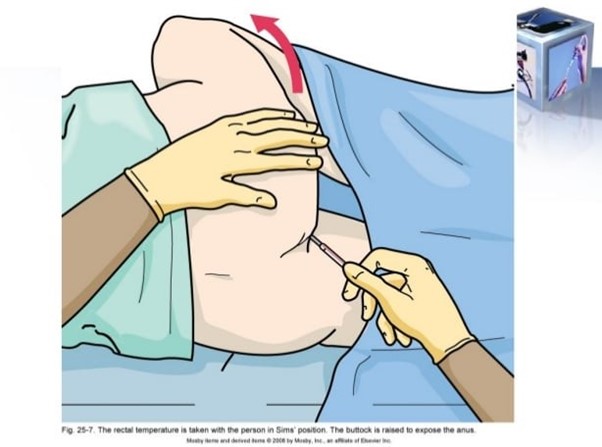
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Taking a rectal temperature requires a higher level of skill and carries a higher risk of injury compared to other methods, especially when dealing with a 2-year-old child with leukemia. Given the client's condition, it is important to minimize any potential harm or discomfort. Taking a tympanic temperature is a safer alternative that provides an accurate reading without the risk of injury.
B. Reminding the UAP to lubricate the thermometer before insertion is not appropriate because the PN should not encourage or support the UAP in performing a rectal temperature on a high-risk client. The focus should be on using a safer and less invasive method.
C. Instructing the UAP to report the results to the PN immediately is not necessary in this situation because the PN has already determined that taking a rectal temperature is not appropriate.
Instead, the PN should guide the UAP toward using the tympanic method.
D. Observing the UAP to ensure the thermometer is inserted correctly is not appropriate in this case because the PN has already determined that taking a rectal temperature is not the recommended course of action. It is more appropriate to redirect the UAP to use an alternative method.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
