A client who is having gastrointestinal (GI) difficulties is undergoing diagnostic procedures.
The client asks the nurse about the difference between ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.
Which information should the nurse offer?
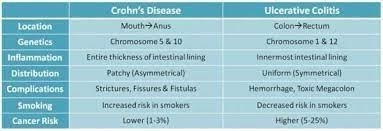
Anal abscess and fistula rarely occur in Crohn's disease.
Rectal bleeding is a predominant symptom in ulcerative colitis.
Constipation is more common in Crohn's disease.
Colitis and Crohn's disease don't involve chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract
The Correct Answer is B
A) Incorrect- Anal abscesses and fistulas are more commonly associated with Crohn's disease than with ulcerative colitis. Crohn's disease can involve the entire thickness of the bowel wall and create tunnels or connections (fistulas) between different parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
B) Correct- Rectal bleeding is a common symptom of ulcerative colitis, as the inflamed tissue can bleed easily.
C) Incorrect- Constipation is not a common characteristic of Crohn's disease. In fact, both ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease can lead to a range of bowel habits, including diarrhea and constipation, depending on the extent and location of inflammation.
D) Incorrect- Both ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease are inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) that involve chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. Ulcerative colitis primarily affects the colon and rectum, causing continuous areas of inflammation and ulceration. Crohn's disease can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the anus. It often involves patches of inflammation with healthy tissue in between, and it can affect different layers of the bowel wall.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
less than body requirements would be the nursing problem with the highest priority for an adolescent with anorexia nervosa. Anorexia nervosa is characterized by a severe restriction of food intake leading to a significantly low body weight, which can have serious physical and psychological consequences. Therefore, addressing the client's malnutrition and promoting adequate nutrition intake is crucial to prevent further complications.
Disturbed Body Image, Interrupted Family Processes, and Noncompliance with treatment regimen are important nursing problems to address, but they are secondary to the client's malnutrition.
Correct Answer is ["A","E","F"]
Explanation
Correct- This statement indicates a misunderstanding about the relationship between acute stress disorder (ASD) and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). While both are related to traumatic events, ASD is considered an initial reaction that typically resolves within three days to four weeks, whereas PTSD involves symptoms persisting for more than a month. The nurse should provide education on the different timelines and criteria for these disorders.
Incorrect- This statement reflects a proactive approach to managing symptoms and stress through holistic methods like meditation. There's no need for follow-up teaching here.
Incorrect- This statement shows the client's recognition of the potential benefits of therapy in managing their thoughts and emotions. It indicates their willingness to engage in effective coping strategies.
Incorrect- This statement reflects an understanding that their response to the traumatic event is not uncommon and that others may have similar reactions. It's a valid perspective on shared experiences during challenging times.
Correct- The statement "This diagnosis means that I am crazy" reflects a common misconception about mental health diagnoses. The term "crazy" is stigmatizing and does not accurately represent the nature of mental health conditions. The nurse should offer reassurance that a diagnosis of ASD does not define a person's overall mental state and emphasize the importance of seeking help without judgment.
Correct- The statement "I will probably need to be on medication for the rest of my life" implies a sense of hopelessness or a narrow perspective about treatment options. While medication might be part of the treatment plan for some individuals, it's important to emphasize that treatment is personalized and can include a combination of therapies, coping strategies, and lifestyle adjustments. The nurse should encourage an open discussion about treatment goals and possibilities.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
