Exhibits
The nurse reviews the physician's orders for clonazepam and gives the medication as ordered. What nursing interventions are appropriate for the client starting clonazepam? Select all that apply.
Screen for orthostatic hypotension
Provide oral care at least twice a day
Monitor calcium levels
Assess mental status regularly
Assist the client to the bathroom
Have an opioid agonist at the bedside
Correct Answer : A,B,D,E
Nursing Interventions for Client Starting Clonazepam:
The following nursing interventions are appropriate for the client starting clonazepam 0.25 mg PO every 12 hours:
a. Screen for orthostatic hypotension:
Rationale:
- Clonazepam, like other benzodiazepines, can cause central nervous system (CNS) depression, which can lead to hypotension, particularly orthostatic hypotension. This occurs when blood pressure drops suddenly upon standing due to impaired autonomic nervous system regulation.
- Screening for orthostatic hypotension involves measuring the client's blood pressure and heart rate while lying down and then again after standing for 3 minutes. A significant drop in blood pressure (systolic decrease of 20 mmHg or diastolic decrease of 10 mmHg) or increase in heart rate (over 20 beats per minute) indicates orthostatic hypotension.
- Monitoring for orthostatic hypotension is crucial to prevent falls and other complications, especially in older adults or those with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions.
b. Provide oral care at least twice a day:
Rationale:
- Clonazepam can cause dry mouth as a side effect, which can increase the risk of cavities, gum disease, and oral infections.
- Regular oral care helps to remove plaque and bacteria, promoting oral hygiene and preventing complications. Providing oral care at least twice a day, especially before bedtime and upon waking, is essential.
d. Assess mental status regularly:
Rationale:
- Clonazepam, while indicated for anxiety and insomnia, can paradoxically cause agitation, confusion, and even hallucinations in some individuals, particularly older adults or those with pre-existing psychiatric conditions.
- Regular assessment of mental status helps to identify any adverse behavioral or cognitive changes early on. This includes monitoring for anxiety, depression, suicidal ideation, confusion, disorientation, hallucinations, and changes in sleep patterns.
e. Assist the client to the bathroom:
Rationale:
- Clonazepam can cause drowsiness and dizziness, which can increase the risk of falls, especially in older adults or those with impaired mobility.
- Assisting the client to the bathroom and providing support during toileting activities helps to prevent falls and injuries.
Choices not included:
c. Monitor calcium levels:
- There is no specific indication for monitoring calcium levels with clonazepam use.
f. Have an opioid agonist at the bedside:
- Clonazepam is not indicated for pain management and does not interact significantly with opioid analgesics. Therefore, having an opioid agonist readily available is not a necessary intervention for clonazepam initiation.
Additional Considerations:
- Educate the client about the potential side effects of clonazepam, including drowsiness, dizziness, dry mouth, and cognitive changes.
- Advise the client to avoid alcohol and other CNS depressants while taking clonazepam, as this can increase the risk of sedation and respiratory depression.
- Instruct the client to take clonazepam exactly as prescribed and not to stop taking it abruptly, as this can lead to withdrawal symptoms.
- Monitor the client's sleep patterns and adjust the medication schedule if necessary.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The presenting symptoms of the infant, including persistent vomiting, poor skin turgor, significant weight loss, and a palpable abdominal mass, indicate a potential serious condition that requires immediate attention. These findings may suggest dehydration, malnutrition, and the presence of an abdominal mass that could be causing gastrointestinal obstruction or other underlying pathology.
Initiating a prescribed IV for parenteral fluid is the priority intervention to address the potential dehydration and fluid imbalance in the infant. This will help restore and maintain adequate hydration while further diagnostic evaluations and interventions are initiated.
Feeding the infant, giving 5% dextrose in water orally, or inserting a nasogastric tube for feeding should not be implemented as the first intervention in this case. It is important to stabilize the infant's fluid status before initiating oral feedings or other interventions to address the underlying cause of the symptoms.

Correct Answer is B
Explanation
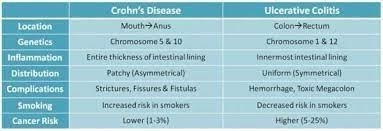
A) Incorrect- Anal abscesses and fistulas are more commonly associated with Crohn's disease than with ulcerative colitis. Crohn's disease can involve the entire thickness of the bowel wall and create tunnels or connections (fistulas) between different parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
B) Correct- Rectal bleeding is a common symptom of ulcerative colitis, as the inflamed tissue can bleed easily.
C) Incorrect- Constipation is not a common characteristic of Crohn's disease. In fact, both ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease can lead to a range of bowel habits, including diarrhea and constipation, depending on the extent and location of inflammation.
D) Incorrect- Both ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease are inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) that involve chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. Ulcerative colitis primarily affects the colon and rectum, causing continuous areas of inflammation and ulceration. Crohn's disease can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the anus. It often involves patches of inflammation with healthy tissue in between, and it can affect different layers of the bowel wall.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
