A nurse is preparing to administer 10 units of regular insulin and 20 units of NPH insulin to a client who has diabetes. Identify the steps the nurse should take when preparing the two insulins. (Move the steps into the box on the right, placing them in the selected order of performance. Use all the steps.)
Inject 10 units of air into the regular insulin vial.
Inject 20 units of air into the NPH insulin vial.
Withdraw 10 units of air from the regular insulin vial.
Withdraw 20 units of air from the NPH insulin vial.
The Correct Answer is B, A, C, D
B. Inject 20 units of air into the NPH insulin vial. Injecting air into the NPH vial first helps equalize the pressure. A. Inject 10 units of air into the regular insulin vial. This prepares the regular insulin vial for withdrawal without creating a vacuum. C. Withdraw 10 units of regular insulin. After injecting air into the regular insulin vial, withdraw the regular insulin first to avoid contaminating it with the NPH insulin. D. Withdraw 20 units of NPH insulin. Finally, withdraw the NPH insulin after the regular insulin.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Diminished reflexes:
Explanation: Diminished reflexes are not typically associated with hypoglycemia. Instead, hypoglycemia may cause hyperactive reflexes or tremors.
B. Rapid respirations:
Explanation: Rapid respirations are not a common manifestation of hypoglycemia. In hypoglycemia, the body might respond with shallow, rapid breathing or hyperventilation.
C. Acetone breath:
Explanation: Acetone breath, often described as fruity or sweet, is associated with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), which is a complication of hyperglycemia rather than hypoglycemia.
D. Headache:
Explanation: Headache is a common manifestation of hypoglycemia. It can occur as a result of decreased glucose levels affecting the brain.

Correct Answer is C
Explanation
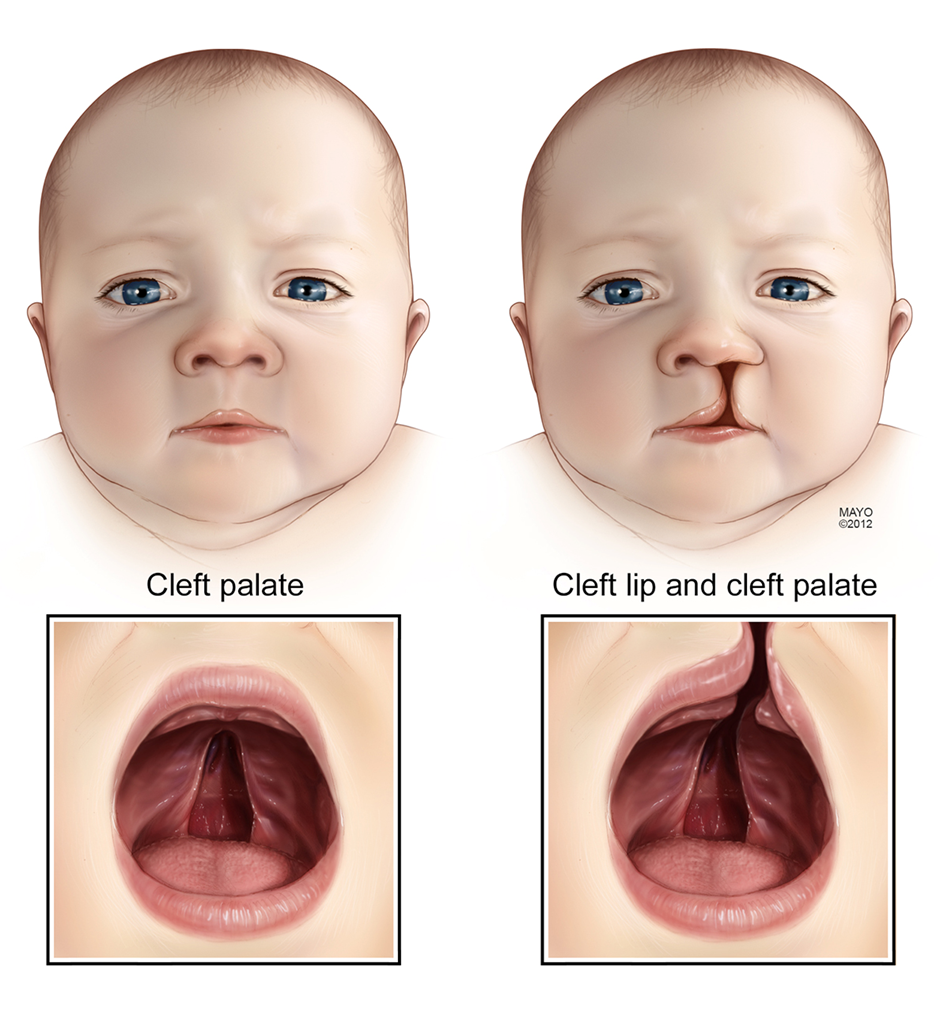
A. Apply Neosporin to avoid infection:
This choice suggests applying Neosporin to the surgical site. However, the immediate postoperative care for cleft lip surgery often involves keeping the incision site covered with sterile dressings. Topical antibiotics may be prescribed by the healthcare provider if deemed necessary, but it's not a routine application without specific instructions.
B. Apply elbow immobilizers when not being held:
This choice implies using elbow immobilizers for the child. However, elbow immobilizers are not a standard intervention for cleft lip surgery. The focus is usually on keeping the surgical site clean and preventing complications like infection.
C. Suction secretions away from the suture line:
This is the recommended choice. Suctioning helps maintain a clear airway and prevents secretions from affecting the surgical site. It's a crucial step in the immediate postoperative period.
D. Feed increased amounts of formula to prevent weight loss:
While feeding is an essential aspect of care, especially for nutritional support, the immediate concern in the first few days after cleft lip surgery is often related to maintaining a patent airway and preventing infection. Feeding interventions might be guided by the healthcare provider's recommendations, but it's not the primary focus in the initial postoperative period.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
