Growth and Development Evaluation
-
Growth and development evaluation is the process of measuring and monitoring the physical and mental progress of infants and children
-
Growth and development evaluation includes assessing the following parameters:
-
Length or height: The distance from the top of the head to the bottom of the feet. Length is measured in infants who cannot stand, while height is measured in children who can stand. Length or height reflects the growth of the long bones and is influenced by genetic, nutritional, hormonal, and environmental factors
-
Weight: The force of gravity on the body mass. Weight reflects the balance between energy intake and expenditure and is influenced by genetic, nutritional, hormonal, metabolic, and environmental factors
-
Head circumference: The distance around the largest part of the head. Head circumference reflects the growth of the brain and skull and is influenced by genetic, nutritional, hormonal, and neurological factors
-
Body mass index (BMI): The ratio of weight to height squared. BMI reflects the relative proportion of fat and lean tissue in the body and is influenced by genetic, nutritional, hormonal, metabolic, and environmental factors
-
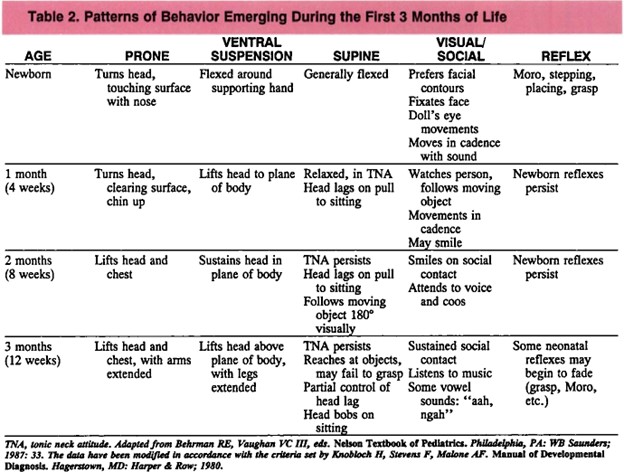
Developmental milestones: The skills or abilities that infants and children acquire at certain ages. Developmental milestones include motor, language, cognitive, social, emotional, and behavioral domains and are influenced by genetic, nutritional, hormonal, neurological, psychological, and environmental factors
-
-
Growth and development evaluation should be done regularly and systematically using standardized tools and methods
-
Growth and development evaluation should be done at the following ages:
-
Birth
-
Within one week after delivery
-
1 month
-
2 months
-
4 months
-
6 months
-
9 months
-
12 months
-
15 months
-
18 months
-
24 months
-
30 months
-
36 months
-
Annually thereafter until adulthood
-
-
Growth and development evaluation should be plotted on appropriate growth charts and compared with the expected norms for age and sex. Growth charts are graphical tools that show how infants and children grow over time in relation to a reference population. Growth charts can help identify normal or abnormal patterns of growth and development. The World Health Organization (WHO) growth charts are recommended for infants and children up to two years of age. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) growth charts are recommended for children from two to twenty years of age
-
Growth and development evaluation should be interpreted in the context of the individual child’s history, physical examination, family background, cultural background, medical conditions, medications, or other factors that may affect growth and development
-
Growth and development evaluation should be used to identify any deviations from the normal or expected patterns of growth and development. Deviations may include:
-
Growth failure: A condition characterized by inadequate or impaired growth due to insufficient nutrition, chronic disease, genetic disorder, endocrine disorder, psychosocial stress, or other causes. Growth failure may manifest as low birth weight, small for gestational age, failure to thrive, short stature, underweight, wasting, stunting, or microcephaly
-
Growth excess: A condition characterized by excessive or accelerated growth due to overnutrition, genetic disorder, endocrine disorder, tumor, or other causes. Growth excess may manifest as large for gestational age, macrosomia, tall stature, overweight, obesity, or macrocephaly
-
Developmental delay: A condition characterized by a significant lag or deviation in one or more domains of development compared with the expected norms for age. Developmental delay may be caused by genetic disorder, chromosomal abnormality, metabolic disorder, congenital anomaly, prenatal exposure to drugs or toxins, perinatal complications, prematurity, low birth weight, malnutrition, infection, brain injury, hypoxia, hypoglycemia, hypothyroidism, hearing loss, vision loss, autism spectrum disorder (ASD), cerebral palsy (CP), intellectual disability (ID), learning disability (LD), attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), emotional disorder (ED), behavioral disorder (BD), or environmental deprivation
-
-
Growth and development evaluation should be used to guide further assessment, diagnosis, intervention, referral, follow-up, counseling, education, or support for infants and children with growth or developmental problems
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Questions on Growth and Development Evaluation
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Correct Answer is ["A","B","C","E"]
Explanation
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Search Here
Related Topics
More on Nursing
- Newborn Complications
- Physiological And Physical Changes In Pregnancy
- Prenatal Diagnostic Tests And Procedures
- Pre-eclampsia, Eclampsia
- Pre-term Labor
- Contraception
- Prolonged and Obstructed Labor and Ruptured Uterus
- Phases of Maternal Role Attainment
- Postpartum Depression
- Postpartum Disorders: DVT, Pulmonary Embolism
Free Nursing Study Materials
Access to all study guides and practice questions for nursing for free.
- Free Nursing Study Trials
- Free Nursing Video tutorials
- Free Nursing Practice Tests
- Free Exam and Study Modes
- Free Nursing Revision Quizlets
