Preterm birth
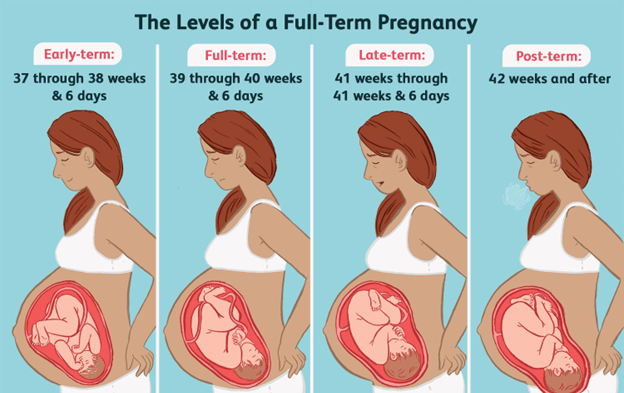
- Definition: Birth before 37 weeks of gestation
- Causes: Maternal infections, chronic diseases (e.g., hypertension, diabetes), multiple gestation (twins or more), placental problems (e.g., abruption, previa), cervical incompetence (weakness), preterm labor
- Signs and symptoms: Low birth weight (<2500 g), small size for gestational age (SGA), immature appearance (e.g., lanugo hair, vernix caseosa coating), large head relative to body size, thin skin with visible blood vessels, poor muscle tone, respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH), retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), patent ductus arteriosus (PDA), anemia, infection, hypothermia, hypoglycemia, hyperbilirubinemia
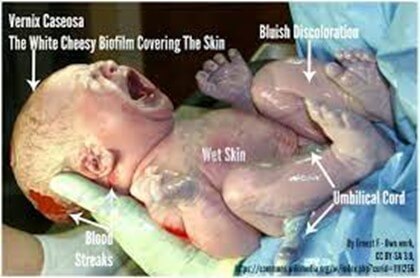
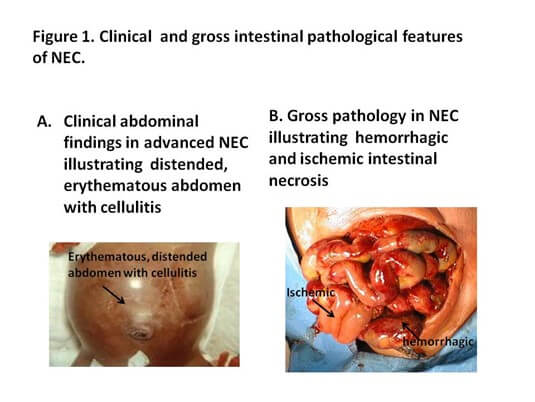
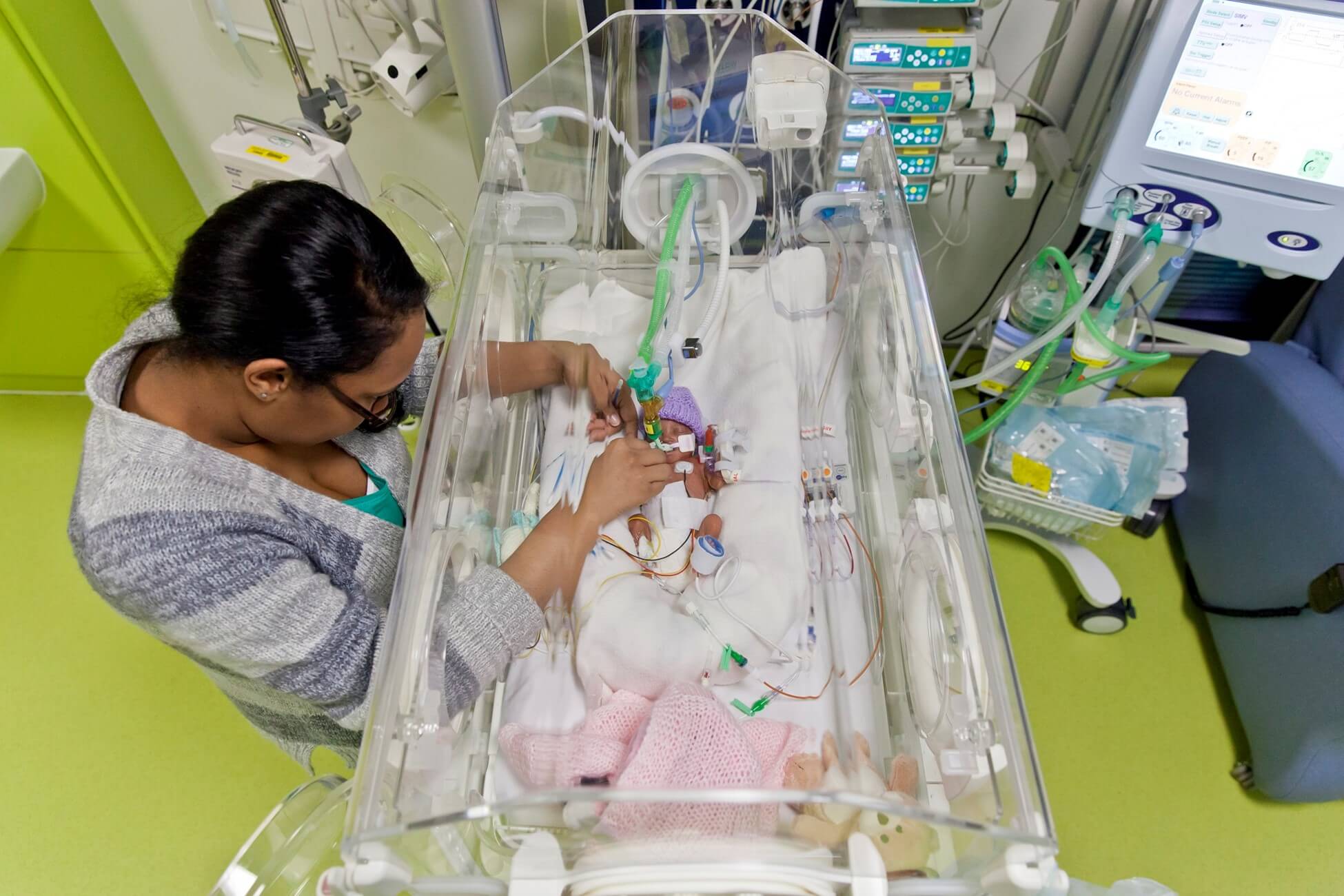
- Assessment: Determine gestational age using Ballard score; measure weight, length, head circumference; monitor vital signs and oxygen saturation; assess respiratory status using Silverman-Anderson index; observe for signs of distress or infection; perform laboratory tests as ordered (e.g., blood gas analysis, blood glucose level, bilirubin level); perform diagnostic tests as ordered (e.g., chest X-ray, cranial ultrasound, echocardiogram)
- Nursing interventions: Transfer the baby to neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) if needed; provide respiratory support as ordered (e.g., oxygen therapy, mechanical ventilation, surfactant administration); maintain thermoregulation by placing the baby in an incubator or under a radiant warmer; monitor fluid and electrolyte balance and administer IV fluids as ordered; provide nutrition support as ordered (e.g., parenteral nutrition, enteral feeding via nasogastric tube or gavage); prevent infection by using aseptic technique and hand hygiene; administer medications as ordered (e.g., antibiotics, steroids, indomethacin); provide developmental care by minimizing stimuli and promoting bonding; educate parents on preterm care and support them emotionally


Nursing Test Bank
Quiz #1: RN Exams Pharmacology Exams
Quiz #2: RN Exams Medical-Surgical Exams
Quiz #3: RN Exams Fundamentals Exams
Quiz #4: RN Exams Maternal-Newborn Exams
Quiz #5: RN Exams Anatomy and Physiology Exams
Quiz #6: RN Exams Obstetrics and Pediatrics Exams
Quiz #7: RN Exams Fluid and Electrolytes Exams
Quiz #8: RN Exams Community Health Exams
Quiz #9: RN Exams Promoting Health across the lifespan Exams
Quiz #10: RN Exams Multidimensional care Exams
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Quiz #1: Naxlex RN Comprehensive online practice 2019 B with NGN
Quiz #2: Naxlex RN Comprehensive Predictor 2023
Quiz #3: Naxlex RN Comprehensive Predictor 2023 Exit Exam A
Quiz #4: Naxlex HESI Exit LPN Exam
Quiz #5: Naxlex PN Comprehensive Predictor PN 2020
Quiz #6: Naxlex VATI PN Comprehensive Predictor 2020
Quiz #8: Naxlex PN Comprehensive Predictor 2023 - Exam 1
Quiz #10: Naxlex HESI PN Exit exam
Quiz #11: Naxlex HESI PN EXIT Exam 2
Questions on Preterm birth
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
<p>All of these findings can indicate a possible bowel perforation in a preterm infant with necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC).NEC is a serious condition that causes inflammation and necrosis of the intestinal tissue, and can lead to a hole (perforation) in the bowel wall.Bacteria can leak through this hole and cause infection and sepsis.NEC usually develops within two to six weeks after birth, and mostly affects premature babies.</p>
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
<p>It does not measure the widest part of the head, which may be above or below the chin.</p>
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
<p>Glasses do not improve vision in ROP. Glasses can correct refractive errors such as nearsightedness or farsightedness, but they cannot fix the damage to the retina caused by ROP.</p>
Changing the infant’s position frequently can disrupt the infant’s sleep and cause stress. Preterm infants should be positioned in a way that supports their posture and alignment, such as flexion, midline orientation, and containment. Positioning aids such as blankets, rolls, or nests can be u
Normal vital signs and neurological status do not reflect the effectiveness of phototherapy on bilirubin levels.
Normal ranges for serum bilirubin levels vary by age and risk factors, but generally they should be less than 15 mg/dL (257 μmol/L) for term newborns and less than 18 mg/dL (308 μmol
Search Here
Related Topics
More on Nursing
Free Nursing Study Materials
Access to all study guides and practice questions for nursing for free.
- Free Nursing Study Trials
- Free Nursing Video tutorials
- Free Nursing Practice Tests
- Free Exam and Study Modes
- Free Nursing Revision Quizlets
