Hyperbilirubinemia
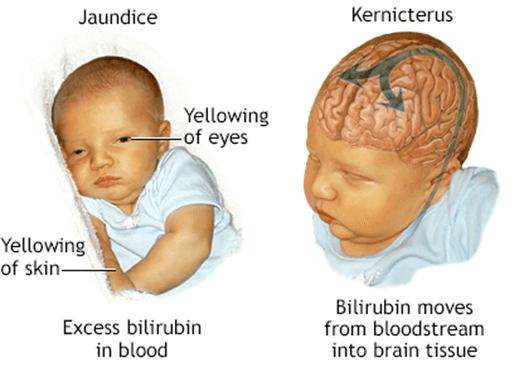
- Definition: Elevated serum bilirubin level that causes jaundice (yellowish skin color)
- Causes: Physiologic jaundice due to breakdown of fetal red blood cells and immaturity of liver enzymes that occurs after 24 hours of age; pathologic jaundice due to blood incompatibility between mother and baby or infection that occurs within 24 hours of age or lasts longer than 7 days; kernicterus due to untreated hyperbilirubinemia that causes brain damage
- Signs and symptoms: Yellowish skin color that progresses from head to toe; yellowish sclerae (whites of eyes); lethargy; poor feeding; dark urine; pale stools; high-pitched cry; seizures
- Assessment: Perform transcutaneous bilirubin measurement using a device that measures skin reflectance at multiple wavelengths; confirm with laboratory serum bilirubin test if abnormal; monitor vital signs and neurological status; observe for signs of jaundice; note the time that jaundice set in to determine whether physiologic or pathologic
- Nursing interventions
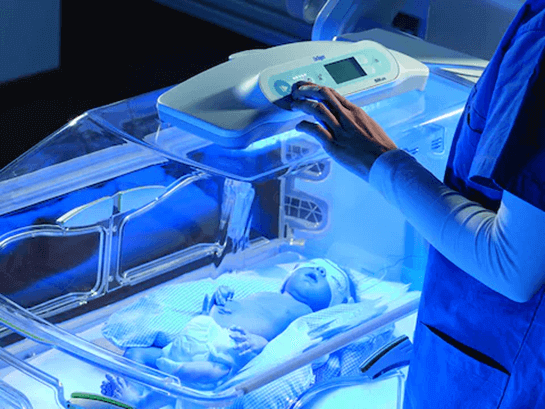
- Provide phototherapy as ordered if newborn’s bilirubin level is above 15 mg/dL before 48 hours of age or above 18 mg/dL before 72 hours of age or above 20 mg/dL at any point; place eye mask on baby, keep newborn undressed, cover genitalia; avoid applying lotions; remove newborn from phototherapy every 4 hours, remove eye mask; reposition newborn every 2 hours; bronze discoloration or rash is not a serious complication; monitor for dehydration by checking sunken fontanels and number of diapers produced per day; feed newborn frequently to promote bilirubin excretion through stool; administer IV fluids or blood transfusion if needed; educate parents on signs of hyperbilirubinemia and how to care for the baby
Nursing Test Bank
Quiz #1: RN Exams Pharmacology Exams
Quiz #2: RN Exams Medical-Surgical Exams
Quiz #3: RN Exams Fundamentals Exams
Quiz #4: RN Exams Maternal-Newborn Exams
Quiz #5: RN Exams Anatomy and Physiology Exams
Quiz #6: RN Exams Obstetrics and Pediatrics Exams
Quiz #7: RN Exams Fluid and Electrolytes Exams
Quiz #8: RN Exams Community Health Exams
Quiz #9: RN Exams Promoting Health across the lifespan Exams
Quiz #10: RN Exams Multidimensional care Exams
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Quiz #1: Naxlex RN Comprehensive online practice 2019 B with NGN
Quiz #2: Naxlex RN Comprehensive Predictor 2023
Quiz #3: Naxlex RN Comprehensive Predictor 2023 Exit Exam A
Quiz #4: Naxlex HESI Exit LPN Exam
Quiz #5: Naxlex PN Comprehensive Predictor PN 2020
Quiz #6: Naxlex VATI PN Comprehensive Predictor 2020
Quiz #8: Naxlex PN Comprehensive Predictor 2023 - Exam 1
Quiz #10: Naxlex HESI PN Exit exam
Quiz #11: Naxlex HESI PN EXIT Exam 2
Questions on Hyperbilirubinemia
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Placing the newborn on a radiant warmer during phototherapy can increase the risk of dehydration, hyperthermia, and skin burns.
The newborn should be monitored for temperature and fluid balance during phototherapy and kept in a crib or bassinet with a blanket.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Observing the newborn’s urine and stool color is not a reliable way to detect jaundice.
The color of urine and stool may vary depending on the hydration status, feeding type and other factors of the newborn. Moreover, urine and stool color may not change until the bilirubin level is very high.
It includes choices A and B, which are incorrect.
Elevated direct bilirubin level: Pathologic jaundice is caused by an excessive breakdown of red blood cells due to blood incompatibility or liver disease.
This leads to an increased production of bilirubin, which is a yellow pigment that results from the breakdown of heme.
Bilirubin can be eit
Search Here
Related Topics
More on Nursing
Free Nursing Study Materials
Access to all study guides and practice questions for nursing for free.
- Free Nursing Study Trials
- Free Nursing Video tutorials
- Free Nursing Practice Tests
- Free Exam and Study Modes
- Free Nursing Revision Quizlets
