When describing the menstrual cycle to a group of young women, the nurse explains that estrogen levels are highest during which phase of the endometrial cycle?
Menstrual
Ischemic
Secretory
Proliferative
The Correct Answer is D
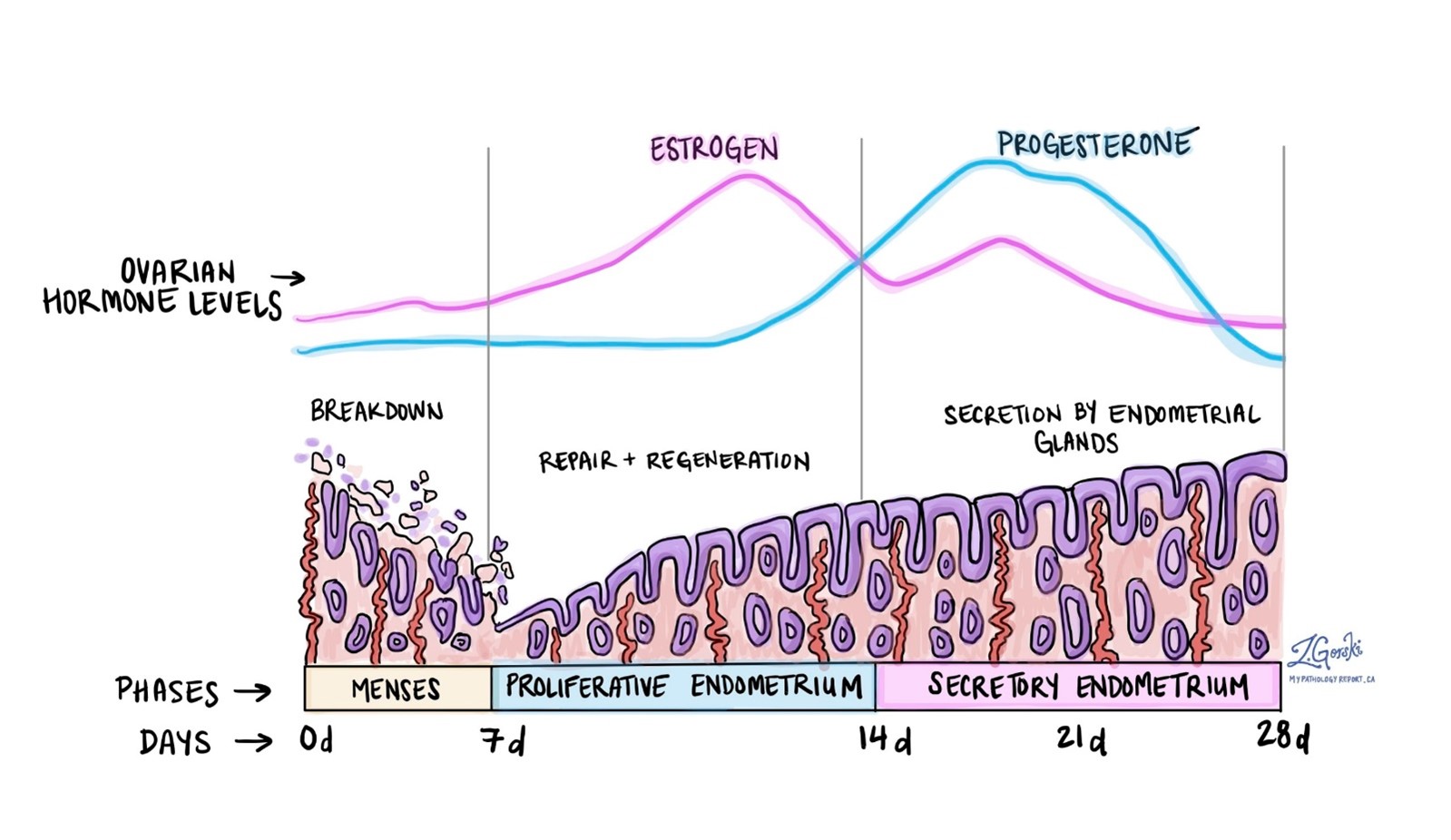
Choice A: Menstrual is not the correct answer because it is the phase when estrogen levels are lowest. The menstrual phase occurs when the endometrium (the lining of the uterus) is shed along with blood and mucus through the vagina.
Choice B: Ischemic is not the correct answer because it is the phase when estrogen levels are decreasing. The ischemic phase occurs when the blood supply to the endometrium is reduced due to vasoconstriction (narrowing of blood vessels). This phase prepares the endometrium for shedding if fertilization does not occur.
Choice C: Secretory is not the correct answer because it is the phase when progesterone levels are highest. The secretory phase occurs when the endometrium becomes thick and spongy due to increased secretion of mucus and glycogen (a form of sugar). This phase provides a suitable environment for implantation if fertilization occurs.
Choice D: Proliferative is the correct answer because it is the phase when estrogen levels are highest. The proliferative phase occurs when the endometrium regenerates and grows due to increased stimulation by estrogen. This phase prepares the endometrium for implantation if fertilization occurs.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["B","C","D","E"]
Explanation
Choice A: Rectal incontinence is not the correct answer because it is not a disorder related to pelvic organ prolapse. Rectal incontinence is a condition that causes loss of control over bowel movements, resulting in leakage of stool or gas. It can be caused by various factors, such as nerve damage, muscle weakness, or diarrhea.
Choice B: Rectocele is the correct answer because it is a disorder related to pelvic organ prolapse. Rectocele is a condition that occurs when the rectum bulges into the vagina due to weakening of the pelvic floor muscles and connective tissue. It can cause symptoms such as constipation, difficulty emptying the bowel, or a feeling of pressure or fullness in the vagina.
Choice C: Urinary incontinence is the correct answer because it is a disorder related to pelvic organ prolapse. Urinary incontinence is a condition that causes loss of control over urination, resulting in leakage of urine or urgency to urinate. It can be caused by various factors, such as stress, urge, overflow, or mixed types of incontinence.
Choice D: Cystocele is the correct answer because it is a disorder related to pelvic organ prolapse. Cystocele is a condition that occurs when the bladder bulges into the vagina due to weakening of the pelvic floor muscles and connective tissue. It can cause symptoms such as frequent urination, difficulty emptying the bladder, or a feeling of pressure or fullness in the vagina.
Choice E: Enterocele is the correct answer because it is a disorder related to pelvic organ prolapse. Enterocele is a condition that occurs when the small intestine bulges into the vagina due to weakening of the pelvic floor muscles and connective tissue. It can cause symptoms such as lower back pain, pelvic pressure, or difficulty having bowel movements.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A: Cancer is not the correct answer because it is not the leading cause of death among women. According to the World Health Organization, cancer accounted for 15% of all deaths among women in 2019.
Choice B: Heart Disease is the correct answer because it is the leading cause of death among women worldwide. According to the World Health Organization, heart disease accounted for 21% of all deaths among women in 2019. Many women are unaware of the risk factors and symptoms of heart disease, and may not seek timely medical attention. Therefore, educational programs that raise awareness and promote the prevention of heart disease are a priority for women's health.
Choice C: Diabetes is not the correct answer because it is not the leading cause of death among women. According to the World Health Organization, diabetes accounted for 4% of all deaths among women in 2019. However, diabetes can increase the risk of developing other complications such as heart disease, kidney disease, and blindness. Therefore, educational programs that teach women how to manage their blood sugar levels and prevent complications are important for women's health.
Choice D: Smoking is not the correct answer because it is not a condition, but a risk factor for many diseases. Smoking can increase the risk of developing lung cancer, heart disease, stroke, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Therefore, educational programs that help women quit smoking and avoid exposure to secondhand smoke are beneficial for women's health.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
