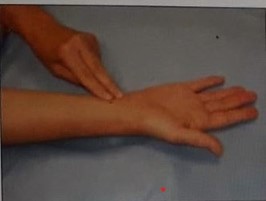
The practical nurse (PN) observes a newly hired unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) who is counting a client's radial pulse as seen in the picture. Which action should the PN take?
Instruct the UAP to report any abnormal findings.
Remind the UAP to check the client's pulse volume.
Demonstrate the correct pulse site to the UAP.
Confirm the accuracy of the pulse rate obtained by the UAP.
The Correct Answer is C
- A radial pulse is the pulse felt at the wrist, where the radial artery runs along the thumb side of the forearm. It is one of the most common sites for measuring a person's heart rate.
- To measure a radial pulse, the examiner should place two or three fingers over the radial artery, just below the wrist crease, and apply gentle pressure until a pulsation is felt. The examiner should not use the thumb, as it has its own pulse and may interfere with the accuracy of the measurement. The examiner should count the number of beats for 15, 30, or 60 seconds, depending on the regularity and rate of the pulse.
- In the picture, the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) is using the thumb to measure the radial pulse, which is incorrect. The practical nurse (PN) should demonstrate the correct pulse site to the UAP and explain why using the thumb is not appropriate. This will help to ensure that the UAP obtains an accurate and reliable pulse rate for the client.
Therefore, option C is the correct answer, while options A, B, and D are incorrect.
Option A is incorrect because instructing the UAP to report any abnormal findings does not address the error in technique.
Option B is incorrect because reminding the UAP to check the pulse volume does not address the error in technique.
Option D is incorrect because confirming the accuracy of the pulse rate obtained by the UAP does not address the error in the technique.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
This client should be reassessed by the RN prior to transfer, as worsening perineal pain may indicate a hematoma, infection, or inadequate pain management. The RN should inspect the perineum, check the vital signs, and evaluate the effectiveness of the medication.
The other options are not correct because:
B. A multigravida whose peri-pad is 1/4 saturated with lochia rubra after one hour does not need to be reassessed by the RN, as this is a normal finding for a client two hours post-birth. Lochia rubra is a red-colored vaginal discharge that contains blood and debris from the placental site, and it usually lasts for 3 to 4 days after delivery. A peri-pad that is 1/4 saturated after one hour is within the expected range of blood loss.
C. A multigravida complaining of strong afterbirth pains when breastfeeding does not need to be reassessed by the RN, as this is a normal finding for a client two hours post-birth. Afterbirth pains are cramps caused by uterine contractions that help shrink the uterus and prevent bleeding. They are more common and intense in multiparous women and during breastfeeding, as oxytocin is released and stimulates contractions.
D. A primigravida who passed a small clot when she sat up on the edge of the bed does not need to be reassessed by the RN, as this is a normal finding for a client two hours post-birth. Small clots may form in the uterus or vagina due to pooling of blood during rest or anesthesia, and they are usually expelled when changing position or ambulating. As long as the clot is smaller than a plum and there is no excessive bleeding or pain, it is not a cause for concern.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Troponin I and CK-MB are cardiac enzymes that are released into the bloodstream when the heart muscle is injured or necrotic. Elevated levels of these enzymes indicate that the client has suffered a myocardial infarction (MI) or heart atack. The damaged heart tissue can impair the electrical conduction system of the heart and cause abnormal heart rhythms or dysrhythmias, which can be life-threatening. The PN should monitor the client's cardiac status closely and report any changes to the charge nurse.
The other options are not correct because:
- The client is not at risk for pulmonary embolism, which is a blockage of a pulmonary artery by a blood clot or other material. Pulmonary embolism does not cause elevated cardiac enzymes, but it can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, and hypoxia.
- The client is not at risk for recurrent long-term angina pain, which is chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle due to narrowed or blocked coronary arteries. Angina pain does not cause elevated cardiac enzymes, but it can be a warning sign of an impending MI.
- The lab results do not indicate risk factors for transient ischemic atack (TIA), which is a temporary interruption of blood flow to a part of the brain due to a clot or plaque. TIA does not cause elevated cardiac enzymes, but it can cause neurological symptoms such as weakness, numbness, or speech difficulties.

Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
