The parents of a child with juvenile idiopathic arthritis call the clinic nurse because the child is experiencing a painful exacerbation of the disease. The parents ask the nurse if the child can perform range-of-motion exercises at this time. The nurse would make which response?
"Range-of-motion exercises must be performed every day."
"Administer additional pain medication before performing range-of-motion exercises."
"Have the child perform simple isometric exercises during this time."
"Avoid all exercise during painful periods."
The Correct Answer is C
A. "Range-of-motion exercises must be performed every day."
Explanation: While range-of-motion exercises are important for maintaining joint flexibility in juvenile idiopathic arthritis, it is not advisable to perform these exercises during painful exacerbations. The frequency and intensity of exercises may need to be adjusted based on the child's current condition.
B. "Administer additional pain medication before performing range-of-motion exercises."
Explanation: While pain management is important in the care of a child with juvenile idiopathic arthritis, relying solely on pain medication before exercises may not be the most effective approach. Isometric exercises that are less likely to cause pain can be a better option during exacerbations.
C. "Have the child perform simple isometric exercises during this time."
Explanation:
During a painful exacerbation of juvenile idiopathic arthritis, it is important to maintain joint flexibility and prevent joint contractures. Simple isometric exercises that do not involve joint movement can help in maintaining muscle strength and joint flexibility without exacerbating pain. Range-of-motion exercises may be too painful during an exacerbation, but isometric exercises can be less painful and still beneficial.
D. "Avoid all exercise during painful periods."
Explanation: Complete avoidance of exercise during painful periods is not recommended. Maintaining joint flexibility and muscle strength is important for managing juvenile idiopathic arthritis. However, the type and intensity of exercises should be adjusted based on the child's pain level during exacerbations.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
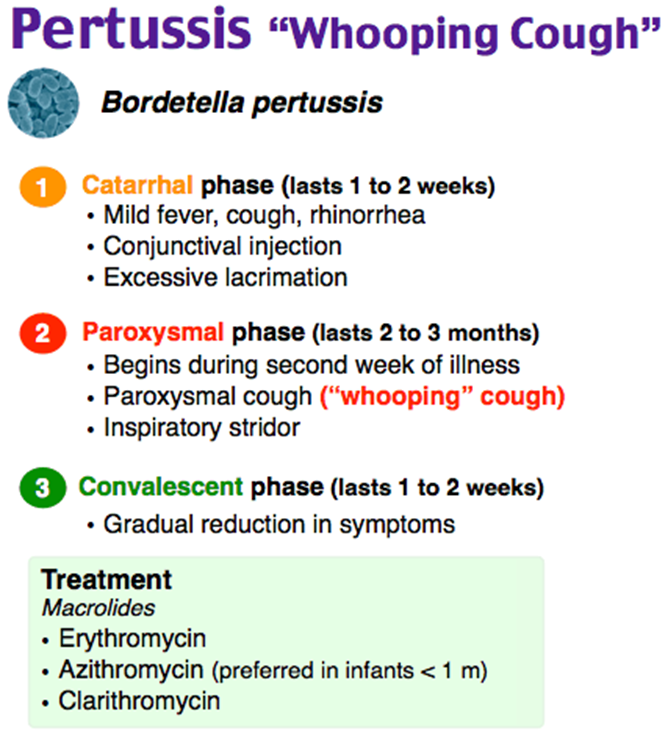
A. Coughing spells may be triggered by dust or smoke:
Incorrect: This is a correct statement. Irritants like dust or smoke can trigger coughing spells in a child recovering from pertussis.
B. We need to maintain droplet precautions and a quiet environment for at least 2 weeks.
Correct Answer: Pertussis is highly contagious during the catarrhal and paroxysmal stages, but once the child has reached the convalescent stage (usually after 2-4 weeks of illness), the risk of spreading the infection decreases significantly. Continuing strict droplet precautions and a quiet environment for two weeks after the convalescent stage is not necessary.
C. "We need to encourage our child to drink fluids":
Incorrect: This is a correct statement. Encouraging fluid intake is important to prevent dehydration, especially during coughing spells.
D. Vomiting may occur when our child has coughing episodes:
Incorrect: This is a correct statement. Vomiting can be a common occurrence during coughing episodes in pertussis due to the forceful nature of the cough. Parents should be aware of this symptom.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
A. "Has the child had any difficulty swallowing food?"
Explanation:
Cleft palate repair can impact various aspects of a child's development, and one potential long-term effect is difficulty with swallowing or feeding. This question is relevant to assessing the child's oral and feeding function, which can be influenced by the cleft palate repair.
B. "Does the child play with an imaginary friend?"
Explanation: Imaginary play and social interactions are not directly related to the long-term effects of cleft palate repair. This question focuses more on social and imaginative development.
C. "Does the child respond when called by name?"
Explanation: Responsiveness to one's name is a general developmental milestone and is not directly related to the long-term effects of cleft palate repair.
D. "Was the child recently treated for pneumonia?"
Explanation: While respiratory issues can be a concern in children with a history of cleft palate, this question is more specific to recent health issues and does not address the long-term effects of cleft palate repair.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
