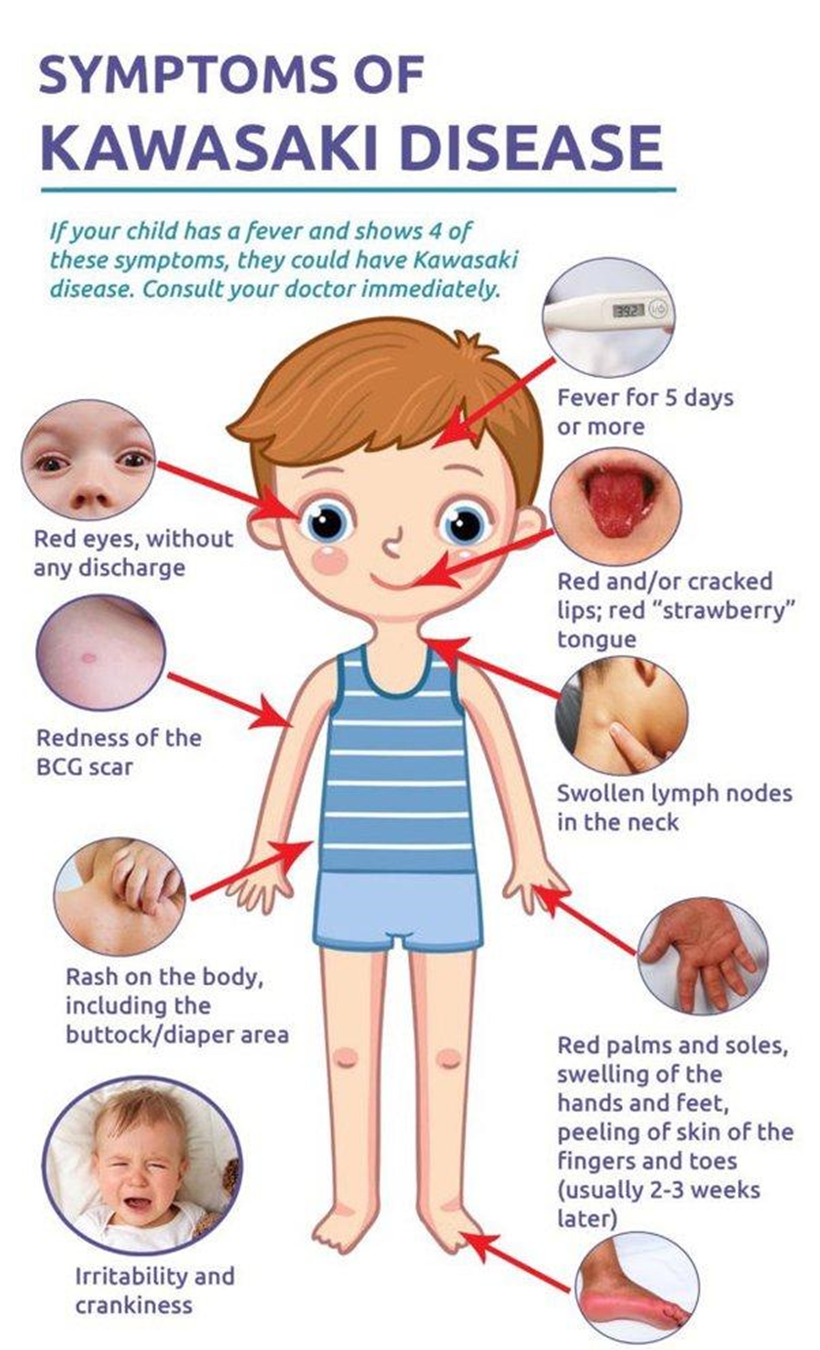
On assessment of a child admitted with a diagnosis of acute-stage Kawasaki disease, the nurse expects to note which clinical manifestation of the acute stage of the disease?
Cracked lips
Desquamation of the skin
Normal appearance
Conjunctival hyperemia
The Correct Answer is D
A. Cracked lips:
Incorrect: While red, cracked lips are part of the mucous membrane changes seen in Kawasaki disease, they are not specific to the acute stage. Mucous membrane changes can occur in both the acute and subacute stages.
B. Desquamation of the skin:
Incorrect: Desquamation, or peeling of the skin, is more characteristic of the subacute or convalescent stages of Kawasaki disease, particularly on the fingers and toes.
C. Normal appearance:
Incorrect: In the acute stage, the child with Kawasaki disease typically exhibits signs of illness, including fever and other clinical manifestations. A "normal appearance" would not be expected in the acute stage.
D. Conjunctival hyperemia.
Explanation: Conjunctival hyperemia, or redness of the eyes, is a common clinical manifestation of the acute stage of Kawasaki disease. Other typical signs and symptoms during this stage include fever, mucous membrane changes (such as red, cracked lips), changes in the extremities, rash, and cervical lymphadenopathy.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["A","B","C","D"]
Explanation
A. The child needs to avoid exposure to other illnesses.
Explanation: Children with AIDS have compromised immune systems and are more susceptible to infections. Therefore, it is important to minimize exposure to other illnesses to reduce the risk of infections.
B. Frequent handwashing is important.
Explanation: Good hand hygiene helps prevent the spread of infections. Encouraging frequent handwashing is crucial in the care of a child with AIDS.
C. Clean up body fluid spills with bleach solution (10:1 ratio of water to bleach).
Explanation: Using a bleach solution to clean up body fluid spills helps to disinfect and reduce the risk of transmission of infections. The recommended ratio is 10 parts water to 1 part bleach.
D. Monitor the child's weight.
Explanation: Monitoring the child's weight is important for assessing nutritional status and overall health. Weight loss may indicate underlying health issues that need attention.
E. The child's immunization schedule will need revision.
Explanation: Children with AIDS may have altered immune function, but the need for immunizations is still crucial. However, live vaccines may need to be avoided. The immunization schedule should be discussed and individualized with the healthcare provider.
F. Fever, malaise, fatigue, weight loss, vomiting, and diarrhea are expected to occur and do not require special intervention.
Explanation: While these symptoms may occur, they should not be dismissed without evaluation. Any changes in the child's health, including symptoms such as fever, malaise, fatigue, weight loss, vomiting, and diarrhea, should be reported to the healthcare provider for appropriate assessment and intervention.
Correct Answer is ["A","D","F"]
Explanation
A.Move furniture away from the child.
Explanation: Creating a safe environment is important during a seizure. Moving furniture away from the child helps prevent injury.
B.Place the child in a prone position.
Explanation: Placing the child in a prone position (face down) is not recommended. The child should be placed on their side to allow for drainage of oral secretions and to prevent aspiration.
C. Restrain the child.
Explanation: Restraint is generally not recommended during a seizure, as it may cause injury to the child or the person providing care. Allow the seizure to run its course, and focus on keeping the environment safe.
D.Time the seizure.
Explanation: Timing the duration of the seizure is important for medical evaluation and management. Note the start and end times of the seizure.
E. Insert a padded tongue blade in the child's mouth.
Explanation: Inserting any object, including a padded tongue blade, into the child's mouth during a seizure is not recommended. This can lead to oral and dental injuries. Maintaining a clear airway and protecting the child from injury are priorities.
F. Stay with the child.
Explanation: Staying with the child provides support and ensures the child's safety during the seizure. It also allows the caregiver to observe and provide information to healthcare professionals.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
